A national unity government brings together multiple political parties to form a coalition, aiming to foster stability and address pressing national issues. This cooperative approach can enhance policymaking by combining diverse perspectives and uniting efforts for the country's benefit. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a national unity government can impact your nation's future.
Table of Comparison
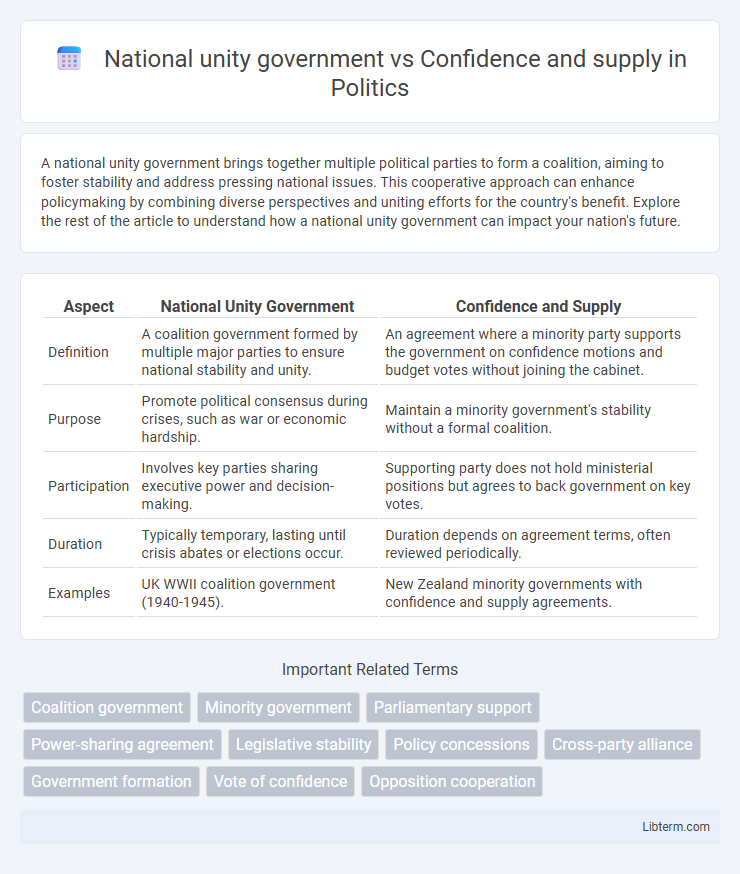
| Aspect | National Unity Government | Confidence and Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A coalition government formed by multiple major parties to ensure national stability and unity. | An agreement where a minority party supports the government on confidence motions and budget votes without joining the cabinet. |
| Purpose | Promote political consensus during crises, such as war or economic hardship. | Maintain a minority government's stability without a formal coalition. |
| Participation | Involves key parties sharing executive power and decision-making. | Supporting party does not hold ministerial positions but agrees to back government on key votes. |
| Duration | Typically temporary, lasting until crisis abates or elections occur. | Duration depends on agreement terms, often reviewed periodically. |
| Examples | UK WWII coalition government (1940-1945). | New Zealand minority governments with confidence and supply agreements. |
Introduction to National Unity Government and Confidence and Supply
National unity governments bring together multiple political parties, often during crises or national emergencies, to form a broad coalition that ensures stability and collective decision-making. Confidence and supply agreements involve smaller parties or independents pledging support to a minority government on key votes such as budgets and confidence motions, without joining the cabinet. These mechanisms maintain governance effectiveness while reflecting different levels of collaboration and political integration.
Defining National Unity Government
A National Unity Government is an inclusive administration formed by major political parties, often during times of crisis, to ensure broad representation and collective decision-making. This type of government incorporates diverse political factions into a single executive framework, aiming to promote stability and national cohesion. Unlike a Confidence and Supply arrangement, which involves limited support from outside parties to maintain a minority government, a National Unity Government entails formal power-sharing among coalition members.
What is a Confidence and Supply Agreement?
A Confidence and Supply Agreement is a formal arrangement where a minority government gains support from one or more parties to pass key legislation, particularly budgets and confidence motions, without forming a full coalition cabinet. This agreement ensures government stability by securing votes necessary for critical decisions while allowing supporting parties to maintain independence without ministerial roles. Unlike a National Unity Government, which combines major parties into a unified coalition, a Confidence and Supply Agreement permits selective cooperation on specific legislative priorities.
Key Differences: Unity Government vs Confidence and Supply
A National Unity Government typically involves a formal coalition of multiple political parties sharing executive power, aiming to represent a broad spectrum of the electorate during crises or significant national issues. Confidence and Supply agreements are arrangements where a minority government secures support from other parties or independents solely on motions of confidence and budgetary legislation, without sharing ministerial positions. The key difference lies in the level of political integration: unity governments involve comprehensive collaboration and power-sharing, whereas confidence and supply maintain distinct party independence with limited legislative cooperation.
Advantages of a National Unity Government
A National Unity Government brings together major political parties to create a stable and inclusive administration, enhancing political stability and fostering collective decision-making during crises. This type of government broadens representation, reducing partisan conflict and improving public trust in governance. It facilitates comprehensive policy-making by incorporating diverse perspectives, which is often limited in Confidence and Supply agreements that depend on conditional support without formal coalition.
Drawbacks of National Unity Governments
National unity governments often face challenges such as reduced policy coherence and slowed decision-making due to the involvement of multiple parties with divergent agendas. This can lead to diluted mandates and inefficiencies in implementing reforms, undermining the government's overall effectiveness. In contrast, confidence and supply arrangements maintain clearer party lines, allowing for more focused governance despite requiring negotiated support from opposition parties.
Pros and Cons of Confidence and Supply Arrangements
Confidence and supply arrangements provide minority governments with crucial parliamentary support to pass budgets and key legislation without forming a full coalition, maintaining greater policy flexibility. They often foster cooperation between parties while reducing political instability, but may result in less comprehensive policy agreements and potential government fragility if support is withdrawn. Compared to national unity governments, these arrangements are less inclusive and can lead to frequent negotiations, impacting long-term governance consistency.
Historical Examples of National Unity Governments
Historical examples of national unity governments include the United Kingdom during World War II under Winston Churchill, where coalition parties set aside differences to address the war effort collectively. Another notable instance is South Africa's Government of National Unity post-apartheid in 1994, involving the African National Congress, National Party, and Inkatha Freedom Party to facilitate democratic transition. These examples contrast with confidence and supply arrangements, which involve minority governments securing legislative support without full coalition integration.
Case Studies: Confidence and Supply in Action
Case studies of confidence and supply agreements, such as New Zealand's Labour Party and the Green Party coalition since 2017, demonstrate how minority governments secure legislative support without forming a full coalition. These arrangements enable governments to pass budgets and key legislation by negotiating specific policy concessions with smaller parties, maintaining flexibility and stability simultaneously. Unlike national unity governments, which unify major parties during crises, confidence and supply agreements foster cooperation while preserving distinct party identities.
Choosing Between Unity Government and Confidence and Supply: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a national unity government and confidence and supply agreements hinges on political stability and policy coherence. National unity governments foster broad coalition-building across party lines to address major crises, ensuring inclusive decision-making. In contrast, confidence and supply arrangements provide selective support from smaller parties or independents, maintaining government stability while preserving distinct party autonomy.
National unity government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com