Strategic voting involves selecting a candidate not solely based on preference but to prevent an undesirable outcome, often influencing election results significantly. This tactic can reshape political landscapes by consolidating votes around viable contenders rather than splitting them among similar options. Explore the rest of the article to understand how strategic voting impacts your choices and the broader electoral process.
Table of Comparison
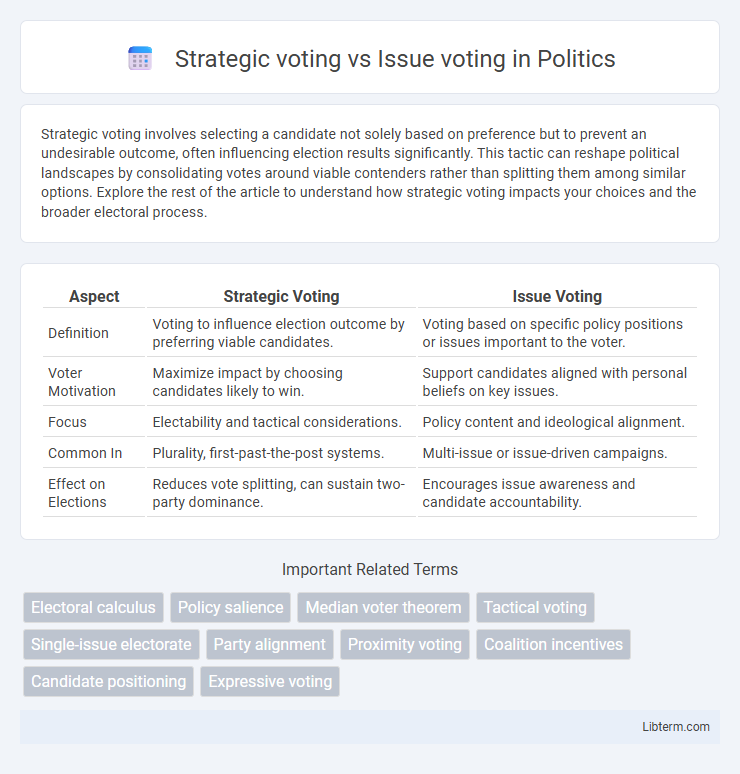
| Aspect | Strategic Voting | Issue Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voting to influence election outcome by preferring viable candidates. | Voting based on specific policy positions or issues important to the voter. |
| Voter Motivation | Maximize impact by choosing candidates likely to win. | Support candidates aligned with personal beliefs on key issues. |
| Focus | Electability and tactical considerations. | Policy content and ideological alignment. |
| Common In | Plurality, first-past-the-post systems. | Multi-issue or issue-driven campaigns. |
| Effect on Elections | Reduces vote splitting, can sustain two-party dominance. | Encourages issue awareness and candidate accountability. |
Defining Strategic Voting
Strategic voting occurs when voters choose a candidate not because of their personal preference but to prevent an undesirable outcome, often supporting a less preferred but more viable contender. This contrasts with issue voting, where decisions are based solely on candidate positions on specific policy matters. Understanding strategic voting highlights how electoral dynamics influence voter behavior beyond pure policy alignment.
Understanding Issue Voting
Issue voting centers on voters making decisions based on specific policy positions or political issues that directly affect their lives, prioritizing alignment with candidates' stances over party loyalty. This approach enhances democratic representation by encouraging voters to support candidates whose issue priorities match their own, fostering policy-driven electoral outcomes. Understanding issue voting emphasizes evaluating candidates on their problem-solving proposals and track records rather than strategic calculations about electability or coalition dynamics.
Key Differences Between Strategic and Issue Voting
Strategic voting involves selecting a candidate based on their likelihood to win or to prevent an undesirable outcome, while issue voting centers on choosing candidates whose policies closely align with the voter's personal beliefs and priorities. Key differences include the motivation behind the vote--strategic voting prioritizes electoral pragmatism, whereas issue voting emphasizes policy agreement and ideological consistency. Additionally, strategic voters may support a less preferred candidate to influence the election result, whereas issue voters focus strictly on policy alignment irrespective of the candidate's winning chances.
Motivations Behind Strategic Voting
Motivations behind strategic voting primarily include the desire to maximize the impact of one's vote by supporting a candidate with a viable chance of winning rather than a preferred but less popular choice. Voters often weigh the potential outcomes to prevent an undesirable candidate from winning, reflecting a pragmatic approach to electoral decision-making. This contrasts with issue voting, where decisions are based solely on alignment with specific policy positions or ideological stances without regard to a candidate's electability.
Motivations Behind Issue Voting
Issue voting is primarily motivated by voters' alignment with specific policy positions or social concerns, reflecting a desire to influence government actions on matters such as healthcare, education, or environmental protection. This form of voting emphasizes the perceived importance and personal relevance of particular issues rather than party loyalty or electoral outcomes. Voters engaging in issue voting often prioritize candidates whose stances closely match their own values and policy preferences.
Impact on Election Outcomes
Strategic voting significantly alters election outcomes by encouraging voters to support candidates with the best chance of winning rather than their preferred choice, often leading to the marginalization of third-party candidates. Issue voting directly influences elections through voters selecting candidates based on specific policy positions, which can shift the focus of campaigns toward those issues. The interplay between strategic and issue voting shapes electoral dynamics, affecting party strategies and the representativeness of elected officials.
Influences of Electoral Systems
Electoral systems significantly shape strategic voting and issue voting behaviors by determining how votes translate into seats. Proportional representation systems encourage issue voting as voters support parties aligned with their policy preferences, while majoritarian systems often incentivize strategic voting to avoid "wasting" votes on less viable candidates. Mixed electoral systems create a complex dynamic, balancing both strategic considerations and genuine policy-driven choices among voters.
Voter Decision-Making Processes
Strategic voting involves voters selecting a candidate not necessarily their top choice but the one most likely to prevent an undesirable outcome, emphasizing election dynamics and perceived candidate viability. Issue voting centers on voters prioritizing specific policy positions or ideological alignment, focusing on substantive political issues that directly impact their preferences. These decision-making processes highlight the tension between pragmatic considerations and value-driven choices in electoral behavior.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Approach
Strategic voting allows voters to influence election outcomes by supporting candidates most likely to win, enhancing the effectiveness of their vote but potentially compromising true preferences and reducing political diversity. Issue voting prioritizes alignment with specific policies, promoting accountability and ideological consistency but may lead to wasted votes if chosen candidates have little chance of winning. Balancing the advantages and disadvantages of both approaches depends on voters' goals, whether maximizing impact or expressing genuine policy support.
Trends in Voter Behavior
Trends in voter behavior reveal a growing preference for strategic voting, where individuals select candidates based on perceived electability and coalition-building potential instead of solely on policy alignment. Issue voting remains significant but is increasingly filtered through strategic considerations, especially in closely contested elections. Data indicates voters often prioritize pragmatic outcomes over ideological purity, reflecting a more calculated approach to influencing election results.
Strategic voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com