Effective government systems promote stability, ensure public welfare, and uphold the rule of law through transparent policies and accountable leadership. Understanding how different forms of government operate can help you engage better with civic processes and contribute to societal progress. Explore the rest of the article to discover how government structures impact your daily life and global affairs.
Table of Comparison
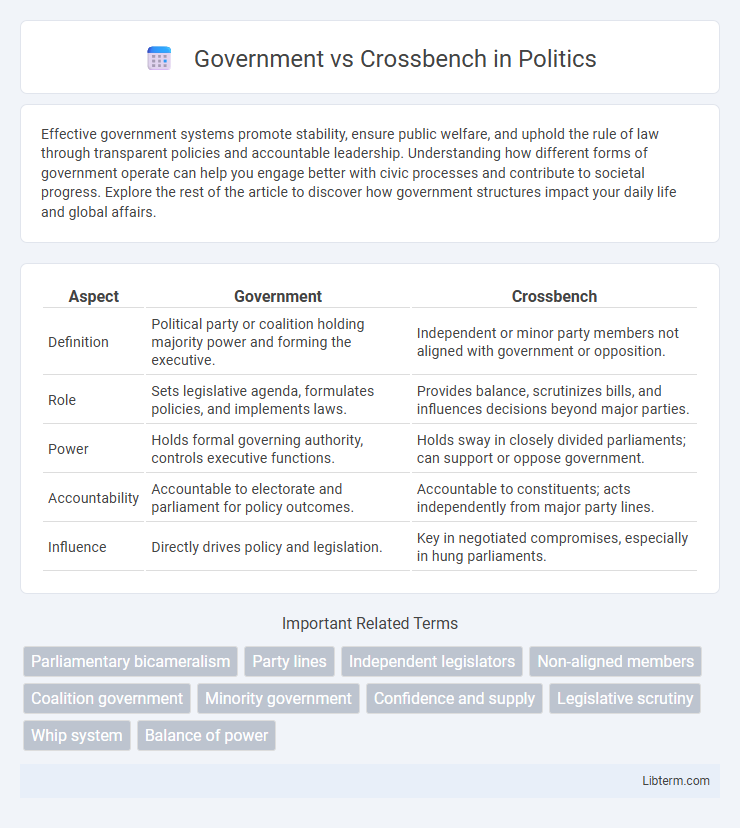
| Aspect | Government | Crossbench |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political party or coalition holding majority power and forming the executive. | Independent or minor party members not aligned with government or opposition. |
| Role | Sets legislative agenda, formulates policies, and implements laws. | Provides balance, scrutinizes bills, and influences decisions beyond major parties. |
| Power | Holds formal governing authority, controls executive functions. | Holds sway in closely divided parliaments; can support or oppose government. |
| Accountability | Accountable to electorate and parliament for policy outcomes. | Accountable to constituents; acts independently from major party lines. |
| Influence | Directly drives policy and legislation. | Key in negotiated compromises, especially in hung parliaments. |
Introduction to Government and Crossbench
The Government refers to the political party or coalition holding the majority in parliament, responsible for forming policies and executing laws. The Crossbench consists of independent and minor party members who are not aligned with either the Government or Opposition, playing a crucial role in balancing power. Understanding their distinct roles and interactions is essential for grasping parliamentary dynamics.
Defining the Government in Parliament
Defining the Government in Parliament involves identifying the political party or coalition holding the majority of seats, responsible for forming and leading the executive branch. The Government drives legislative agendas, proposes bills, and manages public policy through Cabinet ministers appointed from the majority party. The Crossbench, consisting of independents and minor parties, holds a pivotal balance of power by supporting or opposing Government initiatives, influencing parliamentary outcomes.
Who Are the Crossbenchers?
Crossbenchers in parliamentary systems are independent or minor party members who do not align strictly with the government or opposition. They play a crucial role in legislative decision-making, often holding the balance of power in closely divided chambers. Their positions reflect diverse interests, enhancing democratic representation beyond major party agendas.
Historical Context: Evolution of the Crossbench
The crossbench in parliamentary systems evolved as a distinct group representing independents and minor parties outside the government and official opposition, emerging prominently in the 20th century to reflect a broader spectrum of political views. Historically, their role expanded as governments became more fragmented, increasing the influence of crossbench members in balancing power and shaping legislation. This evolution underscores the shift from a binary government-opposition dynamic to a more pluralistic and negotiated policymaking process.
Roles and Responsibilities: Government vs Crossbench
The Government is responsible for formulating and implementing policies, managing public administration, and enacting legislation to fulfill its political agenda. Crossbench members hold a critical role in scrutinizing government decisions, providing independent oversight, and representing diverse or minority interests not aligned with major parties. Their responsibilities include ensuring legislative accountability, fostering balanced debates, and influencing policy outcomes through negotiation and cooperation.
Influence on Legislation and Policy
The government holds primary authority in shaping legislation and policy through majority control and agenda-setting powers. Crossbench members, though smaller in number, play a crucial role by influencing amendments and blocking legislation when the government lacks a clear majority, ensuring broader representation and debate. Their ability to negotiate and demand concessions often results in more balanced and inclusive policy outcomes.
Key Differences in Parliamentary Power
Government members hold majority seats, enabling them to set legislative agendas and pass bills efficiently, while crossbenchers typically hold fewer seats and act as independents or minor party representatives influencing debates through negotiated support. The government controls executive functions and policy implementation, whereas crossbenchers wield power by holding balance of power in hung parliaments, making their support crucial for forming government or passing legislation. Crossbench influence grows in scenarios with slim government majorities, emphasizing their role in scrutinizing government decisions and advocating diverse constituent interests.
Collaboration and Conflict: Notable Cases
The dynamic between Government and Crossbench members often shapes legislative outcomes through both collaboration and conflict, with notable cases such as the Australian Senate's handling of climate change policies highlighting this balance. Instances like the rejection of the government's proposed bill in 2019 demonstrated the crossbench's pivotal role in negotiating amendments and influencing policy direction. Effective collaboration has occasionally led to bipartisan support on critical issues, while conflicts underscore the crossbench's power in holding the government accountable and ensuring diverse representation in decision-making.
The Impact on Democratic Processes
The dynamic between government and crossbench members significantly influences democratic processes by ensuring diverse representation and preventing unilateral decision-making. Crossbenchers often act as pivotal voices in legislative scrutiny, fostering transparency and accountability within parliamentary debates. This balance strengthens democratic legitimacy by encouraging negotiation and compromise, essential for responsive governance.
Future Trends in Government-Crossbench Relations
Future trends in government-crossbench relations indicate growing collaboration as minority parliaments become more common, necessitating negotiated policymaking and power-sharing arrangements. Crossbenchers increasingly leverage their position to influence legislative agendas, reflecting a shift toward consensus-driven governance in parliamentary systems. Enhanced transparency and digital engagement tools are expected to facilitate more dynamic interactions between governments and crossbench members, reshaping political negotiation processes.
Government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com