National security law encompasses regulations designed to protect a nation from threats such as terrorism, espionage, and cyberattacks, ensuring the safety and stability of a country's institutions and citizens. These laws often involve surveillance, intelligence gathering, and strict enforcement measures to prevent and respond to security breaches. Explore the full article to understand how national security law impacts your safety and privacy rights.
Table of Comparison
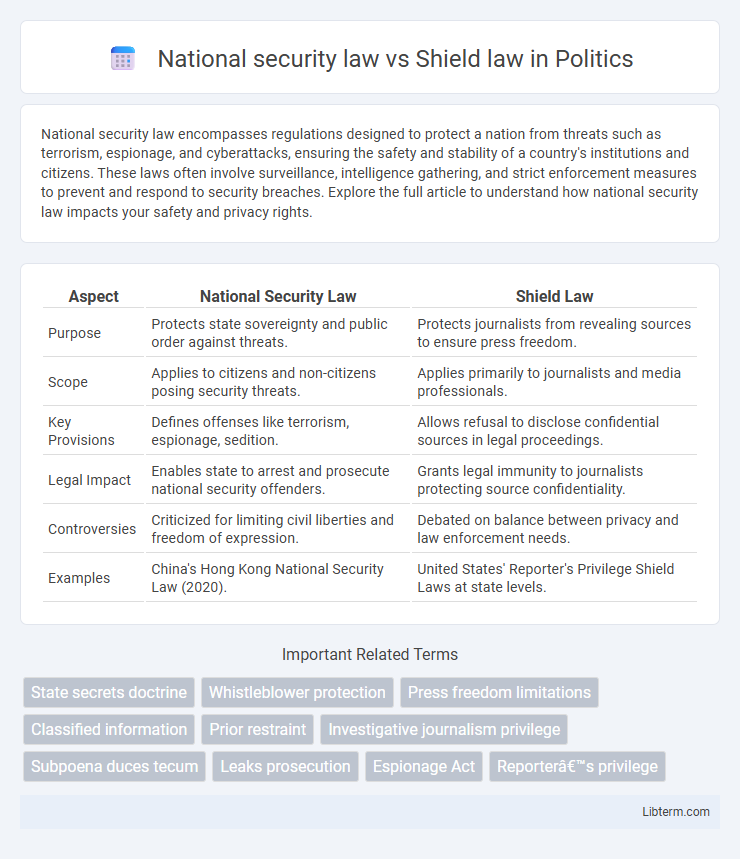
| Aspect | National Security Law | Shield Law |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects state sovereignty and public order against threats. | Protects journalists from revealing sources to ensure press freedom. |
| Scope | Applies to citizens and non-citizens posing security threats. | Applies primarily to journalists and media professionals. |
| Key Provisions | Defines offenses like terrorism, espionage, sedition. | Allows refusal to disclose confidential sources in legal proceedings. |
| Legal Impact | Enables state to arrest and prosecute national security offenders. | Grants legal immunity to journalists protecting source confidentiality. |
| Controversies | Criticized for limiting civil liberties and freedom of expression. | Debated on balance between privacy and law enforcement needs. |
| Examples | China's Hong Kong National Security Law (2020). | United States' Reporter's Privilege Shield Laws at state levels. |
Understanding National Security Law: An Overview
National security law encompasses regulations designed to protect a nation's sovereignty, prevent espionage, terrorism, and cyber threats, thereby safeguarding public safety and state secrets. Shield laws, in contrast, offer legal protections to journalists, allowing them to withhold confidential sources without facing contempt of court, which supports press freedom and investigative reporting. Understanding national security law involves recognizing its role in balancing governmental security interests with civil liberties, often prompting debates over privacy, surveillance, and the limits of state power.
What Is Shield Law? Definition and Purpose
Shield law protects journalists from being compelled to reveal confidential sources or unpublished information in court, ensuring freedom of the press and safeguarding investigative reporting. Its primary purpose is to maintain the confidentiality necessary for reporters to gather news without fear of legal repercussions or government intrusion. Unlike national security laws, which prioritize state protection over information disclosure, shield laws prioritize transparency and the right to inform the public.
Key Differences Between National Security Law and Shield Law
National security law primarily governs the protection of a nation's security interests, focusing on preventing espionage, terrorism, and threats to government stability, whereas shield laws protect journalists from being compelled to reveal confidential sources or unpublished information in court. National security law often involves governmental authority and restrictions on information dissemination to safeguard classified data, contrasting with shield laws that emphasize press freedom and the balance between transparency and confidentiality in journalism. Enforcement mechanisms differ, with national security laws imposing criminal penalties for violations, while shield laws provide legal privileges to reporters, fostering investigative reporting without fear of legal reprisal.
Historical Development of National Security Laws
National security laws have historically evolved in response to geopolitical threats, beginning with early 20th-century espionage acts and expanding significantly during the Cold War to address espionage, terrorism, and cyber threats. These laws prioritize protecting state secrets, national defense, and public order, often granting broad government surveillance and enforcement powers. In contrast, shield laws, which emerged later in the 20th century, focus on protecting journalists from revealing confidential sources, balancing press freedom with national security concerns.
Evolution and Importance of Shield Laws in Journalism
Shield laws have evolved as vital legal protections enabling journalists to safeguard confidential sources and unpublished information, fostering investigative reporting free from government interference. Emerging in response to increasing pressures on press freedom, these laws balance national security concerns with the public's right to know, preventing the misuse of national security laws to suppress critical journalism. Their importance lies in maintaining transparency, accountability, and the flow of information essential to democratic societies.
Legal Conflicts: National Security vs Press Freedom
National security laws often impose restrictions on information dissemination to protect state secrets and prevent threats, which can directly conflict with shield laws designed to protect journalistic sources and uphold press freedom. Legal conflicts arise when governments invoke national security to bypass shield laws, compelling journalists to reveal confidential sources or censor sensitive information. Balancing national security concerns with press freedom remains a critical challenge in safeguarding democratic transparency and accountability.
Case Studies: National Security Law Impact on Media
Case studies examining National Security Law reveal significant challenges for media freedom, notably demonstrated in Hong Kong where journalists face increased censorship and arrests for reporting on sensitive political issues. In contrast, Shield Laws in several U.S. states provide legal protections for journalists to withhold sources and prevent government overreach, supporting investigative reporting and press independence. The stark divergence between these frameworks highlights how National Security Law often suppresses press freedom, while Shield Laws aim to safeguard journalistic integrity and public interest.
Shield Law Protections: Who Qualifies and How
Shield laws protect journalists by allowing them to refuse to disclose confidential sources or unpublished information in legal proceedings, ensuring the freedom of the press. Protections typically extend to professional journalists, including reporters, editors, and sometimes freelancers or bloggers who gather news for public dissemination. Eligibility criteria vary by jurisdiction but often require proof of intent to disseminate information to the public and adherence to ethical journalistic standards.
Balancing National Security and Journalistic Privilege
National security law aims to protect a nation's safety by regulating sensitive information and restricting disclosures that could threaten public safety or government operations. Shield law provides journalists with legal protection to refuse revealing confidential sources or unpublished information, safeguarding press freedom and investigative reporting. Balancing these laws involves ensuring national security without undermining journalistic privilege, requiring clear legal frameworks that prevent misuse of national security claims to suppress legitimate journalism.
Future Trends: The Evolving Relationship Between Security and Press Rights
National security laws increasingly intersect with shield laws as governments intensify efforts to protect classified information while journalists demand robust protections for source confidentiality. Emerging legislative trends reveal a growing need to balance state security interests with press freedoms in digital and globalized communication environments. Advancements in technology and legal frameworks will drive evolving policies that aim to reconcile government transparency obligations with national security imperatives.
National security law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com