Advocacy groups play a crucial role in influencing public policy and raising awareness about specific social, political, or environmental issues. These organizations mobilize supporters, engage in lobbying efforts, and provide valuable resources to empower your voice in driving change. Explore the rest of the article to learn how advocacy groups can amplify your impact and create meaningful progress.
Table of Comparison
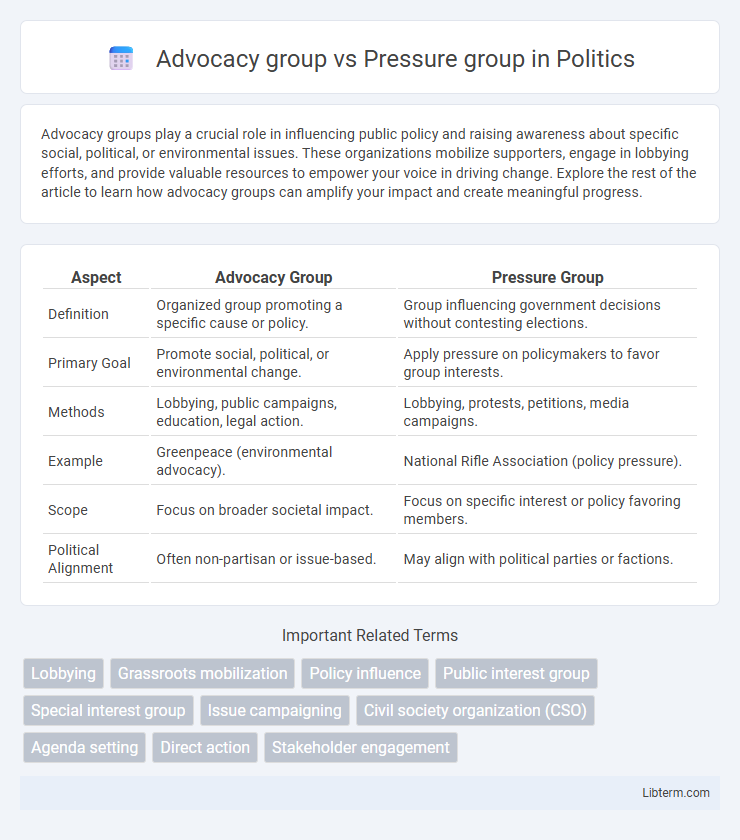
| Aspect | Advocacy Group | Pressure Group |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organized group promoting a specific cause or policy. | Group influencing government decisions without contesting elections. |
| Primary Goal | Promote social, political, or environmental change. | Apply pressure on policymakers to favor group interests. |
| Methods | Lobbying, public campaigns, education, legal action. | Lobbying, protests, petitions, media campaigns. |
| Example | Greenpeace (environmental advocacy). | National Rifle Association (policy pressure). |
| Scope | Focus on broader societal impact. | Focus on specific interest or policy favoring members. |
| Political Alignment | Often non-partisan or issue-based. | May align with political parties or factions. |
Introduction to Advocacy and Pressure Groups
Advocacy groups focus on promoting specific causes or social issues by raising public awareness and influencing policy through education and persuasion. Pressure groups aim to influence government decisions and legislation by lobbying, mobilizing public support, and applying direct pressure on policymakers to achieve specific political or economic objectives. Both types of groups play crucial roles in democratic processes by representing diverse interests and encouraging citizen participation in governance.
Defining Advocacy Groups
Advocacy groups are organizations that actively promote specific causes or policies by seeking to influence public opinion and policymakers through education, lobbying, and grassroots mobilization. Unlike pressure groups, which primarily focus on applying direct pressure on decision-makers to achieve specific outcomes, advocacy groups emphasize raising awareness and fostering long-term social or political change. Key examples include environmental organizations, human rights groups, and public health advocates that use research and public campaigns to shape legislation and societal attitudes.
Defining Pressure Groups
Pressure groups are organized collectives aiming to influence public policy and decision-making without seeking to hold political office. These groups focus on specific issues or causes, leveraging lobbying, protests, and campaigns to apply pressure on policymakers. Unlike advocacy groups, pressure groups often employ direct tactics to sway legislation or government actions in favor of their interests.
Key Differences Between Advocacy and Pressure Groups
Advocacy groups primarily focus on promoting specific causes or social issues to influence public opinion and policy through education and awareness campaigns. Pressure groups typically concentrate on exerting direct influence on policymakers and government officials to achieve targeted legislative or regulatory outcomes, often using lobbying or protest tactics. The key difference lies in advocacy groups seeking broad societal change, while pressure groups emphasize immediate political or economic benefits for their members.
Objectives and Goals of Each Group
Advocacy groups primarily focus on promoting specific social, political, or environmental causes by raising public awareness and influencing legislative change through education and grassroots mobilization. Pressure groups aim to directly influence policymakers and government decisions by lobbying, campaign contributions, and strategic negotiation to protect or advance the interests of a particular industry, demographic, or issue. While advocacy groups seek broad societal transformation, pressure groups concentrate on achieving targeted policy outcomes aligning with their members' objectives.
Methods and Strategies Employed
Advocacy groups primarily use methods such as public education campaigns, lobbying policymakers, and mobilizing grassroots support to influence legislation and public opinion. Pressure groups often employ direct tactics like protests, strikes, and targeted lobbying to exert immediate pressure on decision-makers. Both groups aim to shape policy but differ in their approach, with advocacy groups focusing more on long-term awareness and pressure groups on short-term, forceful influence.
Influence on Policy and Public Opinion
Advocacy groups focus on influencing public opinion and shaping policy through education, awareness campaigns, and lobbying efforts that align with specific causes or social issues. Pressure groups exert influence primarily by applying direct pressure on policymakers and institutions through tactics like protests, petitions, and targeted lobbying to achieve immediate political or economic objectives. Both groups impact policymaking, but advocacy groups tend to foster long-term attitude changes while pressure groups seek rapid policy adjustments.
Examples of Advocacy and Pressure Groups
Advocacy groups like the Sierra Club and Amnesty International focus on promoting specific causes such as environmental protection and human rights through public education and lobbying. Pressure groups, including the National Rifle Association (NRA) and the Chamber of Commerce, exert direct influence on policymakers to achieve favorable legislative or regulatory outcomes. Both types of groups play key roles in shaping public policy, but advocacy groups typically emphasize awareness and long-term change while pressure groups prioritize immediate political influence.
Challenges Faced by Both Groups
Advocacy groups and pressure groups both face challenges in mobilizing public support and influencing policy amidst limited resources and political opposition. Navigating regulatory constraints, combating misinformation, and maintaining credible communication pose significant obstacles to their effectiveness. Both groups must also address internal divisions and public skepticism to sustain long-term impact on social and political change.
Conclusion: Comparing Impact and Effectiveness
Advocacy groups typically achieve long-term societal change by promoting specific causes through public awareness and policy reform, whereas pressure groups focus on influencing specific political decisions, often through direct lobbying. The impact of advocacy groups is measured by their success in shifting public opinion and enacting legislation, while pressure groups gauge effectiveness by their ability to sway policymakers and secure immediate policy outcomes. Both types of groups play crucial roles in democratic processes, but advocacy groups often generate broader cultural shifts, whereas pressure groups excel in targeted political influence.
Advocacy group Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com