Blondel's typology categorizes leadership styles based on decision-making processes and leader-member interactions to enhance organizational effectiveness. Understanding this framework can help you identify which leadership approach best suits your team dynamics and goals. Explore the article to uncover how Blondel's typology can transform your leadership strategy.
Table of Comparison
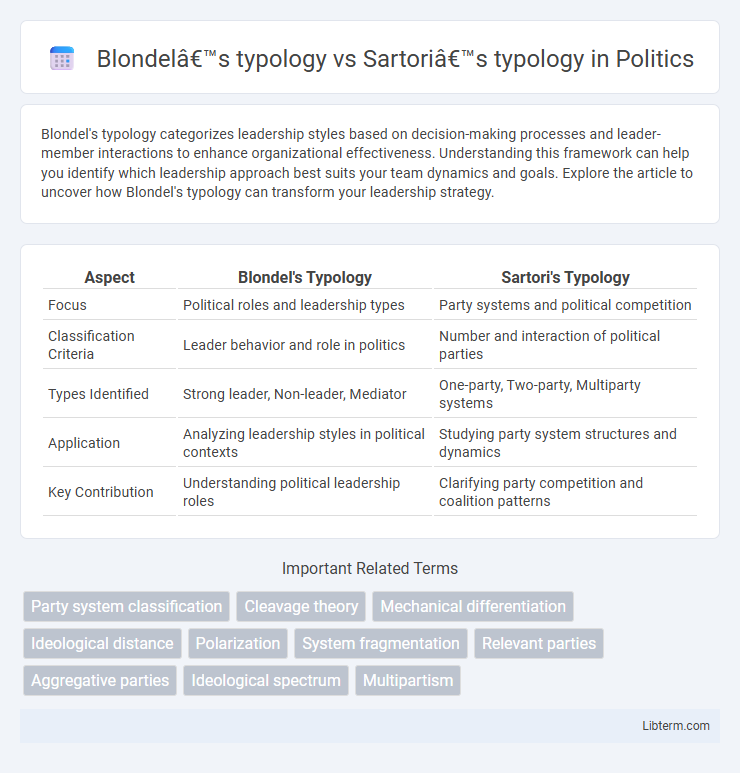
| Aspect | Blondel's Typology | Sartori's Typology |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Political roles and leadership types | Party systems and political competition |
| Classification Criteria | Leader behavior and role in politics | Number and interaction of political parties |
| Types Identified | Strong leader, Non-leader, Mediator | One-party, Two-party, Multiparty systems |
| Application | Analyzing leadership styles in political contexts | Studying party system structures and dynamics |
| Key Contribution | Understanding political leadership roles | Clarifying party competition and coalition patterns |
Introduction to Typologies in Political Science
Blondel's typology emphasizes the structural and functional classification of political systems based on authority patterns, while Sartori's typology centers on party systems by analyzing the number and size of parties and their interactions. Both approaches serve as foundational frameworks in the introduction to typologies in political science, providing systematic methods for categorizing political entities and behaviors. Their comparative analysis enhances understanding of political dynamics by linking institutional structures with party competition and political behavior.
Overview of Blondel’s Typology
Blondel's typology classifies democratic systems based on their executive structures, distinguishing primarily between parliamentary, presidential, and semi-presidential models. It emphasizes the distribution of executive power and the relationship between the executive and legislative branches, highlighting how these variations influence political stability and government accountability. This framework contrasts with Sartori's typology, which focuses more on party systems and electoral dynamics rather than institutional design.
Key Features of Sartori’s Typology
Sartori's typology emphasizes a rigorous classification system based on the number of relevant characteristics and the differentiation of categories through clear, mutually exclusive criteria. It incorporates concepts such as "ladder of abstraction" and "family resemblance" to manage complexity and enhance analytical precision compared to Blondel's broader, less formalized typological approach. Sartori's method prioritizes conceptual validity and empirical adequacy by ensuring that typologies serve as effective tools for comparison and theory building in political science.
Conceptual Foundations: Blondel vs Sartori
Blondel's typology emphasizes structural and functional distinctions within political systems, focusing on institutional configurations and governance processes, whereas Sartori develops a more systematic and analytical framework centered on empirical classification and comparative analysis of party systems. Blondel's approach is grounded in the qualitative understanding of political roles and systemic functions, contrasting with Sartori's emphasis on rigorous typological criteria designed to improve conceptual clarity and measurement. Sartori's typology is recognized for its precision in differentiating party systems by the number, interrelation, and competition patterns of parties, enhancing the empirical applicability of political analysis.
Methodological Approaches Compared
Blondel's typology emphasizes empirical observation and inductive reasoning to categorize political systems based on leadership styles and institutional frameworks. Sartori's typology employs a more deductive, conceptual approach, focusing on refining classifications through rigorous definition and logical coherence, especially within party systems. Methodologically, Blondel prioritizes qualitative, context-driven analysis, while Sartori advances systematic, formalized criteria to enhance comparative political theory.
Scope and Application Differences
Blondel's typology emphasizes the scope of political systems by categorizing them based on the extent of political engagement, distinguishing between limited, intermediate, and extensive scopes of political participation. Sartori's typology, in contrast, focuses on the application of party systems by classifying them according to the number and type of parties, such as one-party, two-party, and multi-party systems, highlighting their organizational complexity and electoral dynamics. The key difference lies in Blondel's broader analytical lens on political activity scope, whereas Sartori offers a more granular framework tailored specifically to party system structures and their functional implications.
Strengths of Blondel’s Typology
Blondel's typology offers a unique analytical framework by emphasizing the dynamic relationship between political parties and their social bases, allowing for a nuanced understanding of party alignment and voter behavior. Its strength lies in capturing the interplay between political competition and societal structures, providing insights into patterns of party support that reflect underlying social cleavages. This approach enhances the explanatory power in comparative politics by linking party systems directly to social realities, making it valuable for analyzing party competition in diverse political contexts.
Advantages of Sartori’s Typology
Sartori's typology offers greater analytical precision by providing clear, distinct categories that reduce ambiguity in political party classification. It facilitates cross-national comparisons through its robust conceptual framework, enhancing the study of party systems and voter behavior. This typology also supports empirical testing and operationalization, making it preferable for systematic political analysis compared to Blondel's broader, less structured approach.
Limitations and Criticisms of Both Typologies
Blondel's typology faces criticism for its overly simplistic classification of political regimes, often neglecting nuanced variations within systems and historical contexts. Sartori's typology, while more detailed, is criticized for its Eurocentric bias and limited applicability to non-Western political environments. Both frameworks struggle with static categorizations that inadequately capture political dynamics and evolving institutional complexities.
Conclusion: Relevance in Contemporary Political Analysis
Blondel's typology emphasizes the psychological motivations and behavioral patterns behind political participation, offering nuanced insights into individual voter behavior, while Sartori's typology categorizes party systems based on structural and institutional factors, enabling comprehensive comparisons between political regimes. Their combined relevance in contemporary political analysis lies in integrating micro-level voter dynamics with macro-level party system structures to better understand electoral outcomes and party competition. This dual approach enhances the accuracy of political forecasting and enriches the study of democratic consolidation across diverse political contexts.
Blondel’s typology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com