The rule of man refers to a system where power is exercised based on individuals' authority rather than established laws, often leading to arbitrary decisions and potential abuses. This form of governance contrasts with the rule of law, which prioritizes consistent legal frameworks to ensure fairness and accountability. Discover how understanding the rule of man can impact your perspective on justice and authority by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
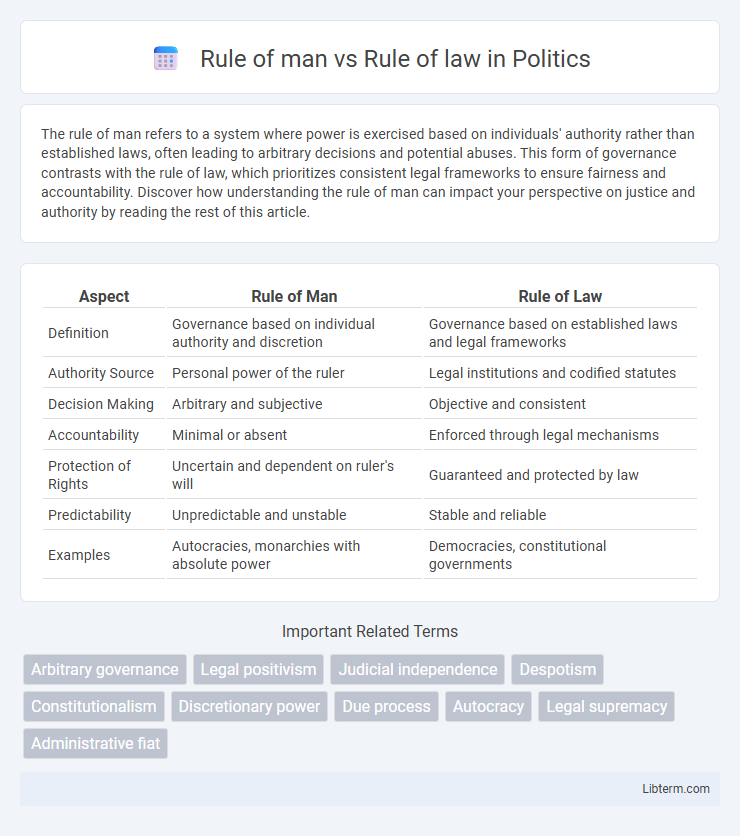
| Aspect | Rule of Man | Rule of Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance based on individual authority and discretion | Governance based on established laws and legal frameworks |
| Authority Source | Personal power of the ruler | Legal institutions and codified statutes |
| Decision Making | Arbitrary and subjective | Objective and consistent |
| Accountability | Minimal or absent | Enforced through legal mechanisms |
| Protection of Rights | Uncertain and dependent on ruler's will | Guaranteed and protected by law |
| Predictability | Unpredictable and unstable | Stable and reliable |
| Examples | Autocracies, monarchies with absolute power | Democracies, constitutional governments |
Introduction to Rule of Man vs Rule of Law
Rule of Man refers to a governance system where decisions are made based on individual discretion, often influenced by personal interests, power, or authority. Rule of Law emphasizes that all individuals and institutions are subject to and accountable under laws that are fairly applied and enforced, ensuring consistency and justice. This contrast highlights the importance of predictable legal frameworks in preventing arbitrary rule and protecting fundamental rights.
Defining Rule of Man
The Rule of Man refers to governance where authority is vested in individual rulers who exercise power based on personal discretion rather than established laws. This system often leads to arbitrary decisions, as it lacks formal constraints and legal accountability. Historical examples include autocratic regimes and absolute monarchies where laws are subordinate to the whims of the ruler.
Understanding Rule of Law
The Rule of Law ensures that all individuals and institutions are subject to and accountable under established legal frameworks, promoting fairness, stability, and predictability in governance. It safeguards against arbitrary decision-making by emphasizing transparent, impartial laws rather than personal authority or discretion. This principle underpins democratic societies by protecting rights, enforcing contracts, and maintaining checks and balances within government structures.
Historical Context and Evolution
The Rule of Man, dominant in ancient monarchies and autocratic regimes, vested absolute power in rulers whose decisions were often arbitrary and unchecked by formal laws. Over time, the Rule of Law emerged, particularly during the Enlightenment and through documents like the Magna Carta (1215) and the U.S. Constitution (1787), establishing the principle that all individuals and government officials are subject to and must abide by consistent, codified laws. This evolution marked a critical shift toward limiting arbitrary power, promoting justice, and securing individual rights within structured legal frameworks.
Key Differences Between Rule of Man and Rule of Law
Rule of man centers on the arbitrary power of individuals to govern based on personal discretion, while rule of law emphasizes governance according to established, transparent legal frameworks applicable equally to all. Under rule of man, laws are flexible and subject to change by the whims of rulers, contrasting with the rule of law's consistent enforcement of codified laws designed to limit power and protect individual rights. The key difference lies in accountability and predictability, with rule of law promoting fairness and stability through institutional checks, unlike the unpredictable and personalized authority found in rule of man systems.
Impacts on Governance and Society
Rule of law ensures governance is transparent, accountable, and consistent, promoting social stability and protecting individual rights through clearly defined legal frameworks. In contrast, rule of man leads to arbitrary decisions, undermining institutional trust and fostering social inequality due to the concentration of power in individuals rather than laws. Strong legal institutions under the rule of law drive economic growth, reduce corruption, and enhance citizen participation in governance processes.
Case Studies: Rule of Man in Practice
The Rule of Man in practice is exemplified by historical case studies such as Zimbabwe under Robert Mugabe, where arbitrary decisions and personal authority shaped governance, sidelining formal legal frameworks. In Venezuela, Hugo Chavez's leadership showcased how executive dominance and weakened institutions eroded the Rule of Law, resulting in political instability and economic decline. These cases highlight the risks of centralized power without institutional checks, contrasting sharply with systems governed by established legal principles.
Case Studies: Rule of Law in Action
Case studies of the Rule of Law in action highlight institutions where laws govern societal behavior, not individual whims, exemplifying systems with judicial independence like South Africa's Constitutional Court enforcing rights post-apartheid. In contrast, nations exemplifying the Rule of Man, such as Belarus under Alexander Lukashenko, reveal how arbitrary power without legal constraints leads to systemic human rights abuses. These instances underscore the Rule of Law's role in promoting accountability, protecting civil liberties, and ensuring fair governance through codified legal frameworks.
Challenges in Implementing Rule of Law
Challenges in implementing the rule of law often stem from entrenched authoritarianism where the rule of man prevails, leading to arbitrary governance and lack of legal accountability. Weak judicial systems, corruption, and political interference undermine the independence of courts, obstructing fair enforcement of laws. Limited access to legal resources and civic education further inhibit public participation and trust in lawful governance frameworks.
Conclusion: Choosing the Path Forward
Choosing the path forward requires embracing the Rule of Law, which ensures fairness, accountability, and protection of individual rights. Rule of man fosters unpredictability and potential abuse of power, undermining social stability and trust in governance. Upholding the Rule of Law creates a foundation for sustainable development, equality, and democratic principles in society.
Rule of man Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com