The general public refers to the broad population without specific distinctions based on profession, age, or social status. Understanding the concerns and interests of the general public is essential for effective communication and policy-making. Explore the rest of the article to discover how public opinion shapes decision-making processes and societal trends.
Table of Comparison
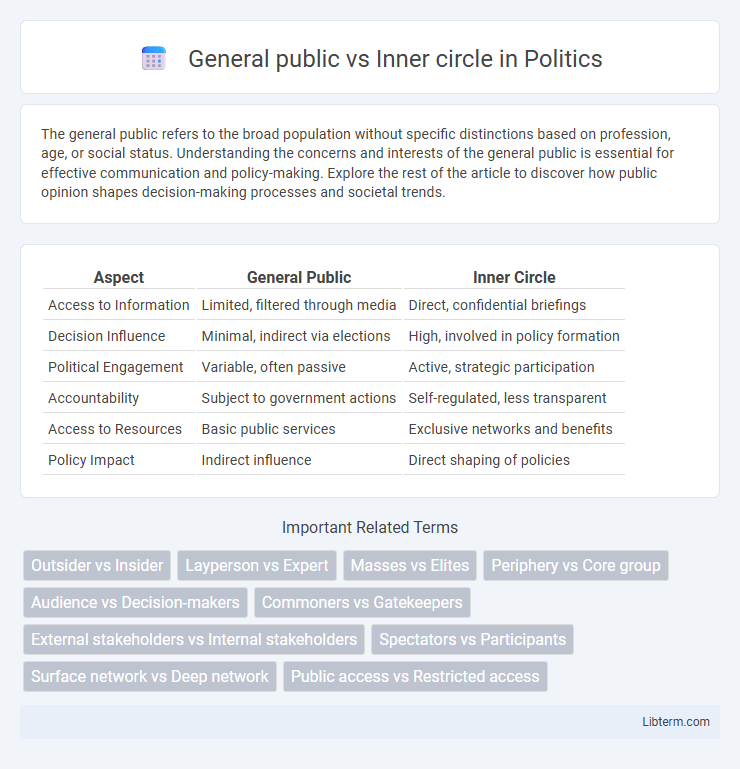
| Aspect | General Public | Inner Circle |
|---|---|---|
| Access to Information | Limited, filtered through media | Direct, confidential briefings |
| Decision Influence | Minimal, indirect via elections | High, involved in policy formation |
| Political Engagement | Variable, often passive | Active, strategic participation |
| Accountability | Subject to government actions | Self-regulated, less transparent |
| Access to Resources | Basic public services | Exclusive networks and benefits |
| Policy Impact | Indirect influence | Direct shaping of policies |
Defining the General Public and the Inner Circle
The general public refers to a broad, diverse group encompassing individuals outside exclusive social or professional networks, typically characterized by limited access to insider information or privileged connections. The inner circle consists of a select, trusted group of individuals with close relationships, often sharing confidential knowledge, strategic decision-making roles, or influential positions within an organization or community. Defining these groups hinges on levels of access, trust, and influence, with the inner circle playing a critical role in shaping core dynamics unavailable to the general public.
Key Differences Between Public Perception and Inner Knowledge
General public perception often relies on surface-level information shaped by media and social narratives, whereas the inner circle possesses nuanced, firsthand knowledge rooted in direct experience and confidential contexts. Public opinions tend to be influenced by broad stereotypes and incomplete data, while the inner circle's understanding encompasses detailed insights, strategic intentions, and behind-the-scenes dynamics. This disparity creates a gap where external assumptions may conflict with internal realities, affecting decision-making and communication effectiveness.
Access to Information: Who Knows What?
The inner circle typically has privileged access to strategic information, sensitive data, and confidential communications, enabling faster decision-making and more informed actions. In contrast, the general public often receives filtered or delayed information through official channels, media, or public statements, limiting transparency and real-time awareness. This disparity in access to information shapes power dynamics and influences public perception and trust.
Influence and Power Dynamics
General public influence operates through widespread social trends and collective behavior, shaping political and economic landscapes at large. Inner circle power dynamics concentrate decision-making authority among a select group, leveraging exclusive access and strategic networks to direct outcomes. The tension between mass mobilization and elite control defines the evolving interplay of influence and authority in society.
Trust and Transparency Issues
The general public often demands greater transparency and clear communication, as trust tends to be fragile due to limited access to information and perceived exclusivity. Inner circles benefit from direct, frequent interactions and shared knowledge, fostering higher levels of trust through openness and mutual understanding. Disparities in transparency between these groups can lead to skepticism and decreased confidence among the broader audience.
Impact on Decision-Making Processes
The influence of the general public on decision-making processes often centers on broad consensus, reflecting diverse opinions and societal values that guide policy and organizational strategies. In contrast, the inner circle wields concentrated power, leveraging exclusive information and strategic priorities to shape critical decisions swiftly and with less transparency. The dynamic between these groups affects accountability, speed of decisions, and the inclusivity of stakeholder perspectives in governance and leadership contexts.
Communication Strategies for Each Group
Effective communication strategies differ significantly between the general public and the inner circle, requiring tailored messaging approaches for each group. For the general public, clarity, simplicity, and broad appeal are essential, utilizing mass communication channels such as social media, press releases, and public statements to ensure wide reach and comprehension. In contrast, the inner circle demands more personalized, confidential, and detailed communication through direct meetings, secure emails, and private briefings to foster trust and facilitate nuanced discussions.
Case Studies: Inner Circle vs Public Reaction
Case studies reveal distinct differences between inner circle and general public reactions, with inner circles often exhibiting greater empathy and nuanced understanding due to direct involvement. Public responses tend to be shaped by media portrayal and social narratives, leading to polarized or simplified views. Analyzing specific incidents highlights how personal connections within inner circles influence emotional intensity and support strategies compared to generalized public sentiment.
Challenges in Bridging the Gap
The challenges in bridging the gap between the general public and the inner circle stem from differing access to information, exclusive decision-making processes, and varying levels of trust. Limited transparency and communication barriers exacerbate misunderstandings and fuel skepticism among the broader population. Overcoming these obstacles requires deliberate efforts to foster inclusivity, enhance information flow, and build mutual credibility.
Long-term Consequences of Exclusivity
Exclusivity within an inner circle often leads to long-term consequences such as social fragmentation and reduced trust among the general public. This separation fosters a sense of alienation and inequality, which can undermine social cohesion and fuel resentment. Over time, such divisions may hinder collective progress and stability by creating barriers to inclusive decision-making and resource distribution.
General public Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com