An inner cabinet is a specialized compartment within a larger cabinet used for organizing smaller items or valuables. It offers enhanced security and efficient storage solutions for your household or office needs. Explore the rest of the article to discover the benefits and design options of inner cabinets.
Table of Comparison
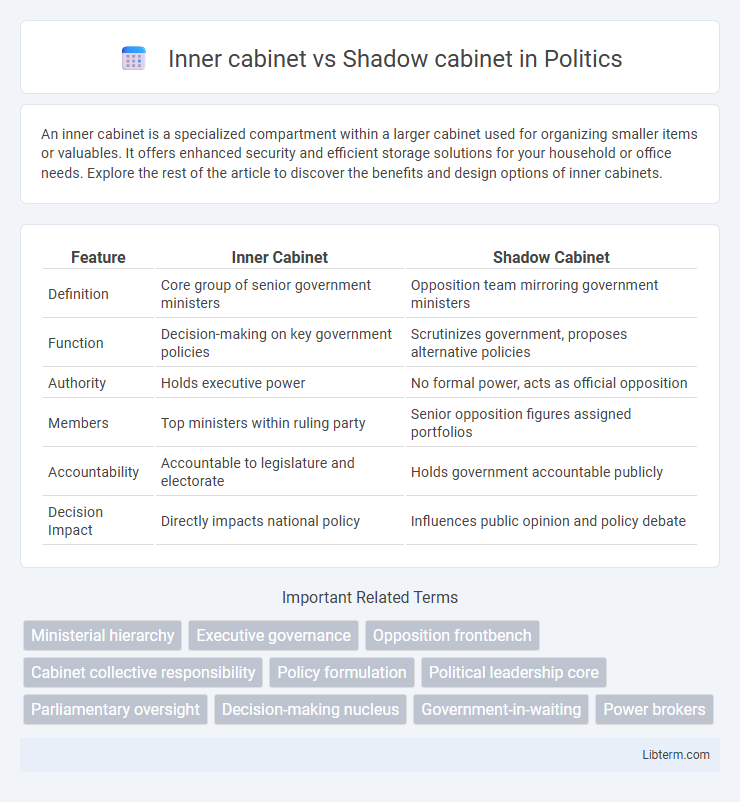
| Feature | Inner Cabinet | Shadow Cabinet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Core group of senior government ministers | Opposition team mirroring government ministers |
| Function | Decision-making on key government policies | Scrutinizes government, proposes alternative policies |
| Authority | Holds executive power | No formal power, acts as official opposition |
| Members | Top ministers within ruling party | Senior opposition figures assigned portfolios |
| Accountability | Accountable to legislature and electorate | Holds government accountable publicly |
| Decision Impact | Directly impacts national policy | Influences public opinion and policy debate |
Understanding the Inner Cabinet
The Inner Cabinet consists of a small group of senior government ministers who meet regularly to make key policy decisions and coordinate the government's agenda. This core team contrasts with the larger Shadow Cabinet, which is formed by the main opposition party to scrutinize and challenge the government's policies. Understanding the Inner Cabinet is crucial for analyzing how executive power is centralized and how strategic governance priorities are set within a parliamentary system.
Defining the Shadow Cabinet
The shadow cabinet is a group of senior opposition party members tasked with scrutinizing and challenging the policies of the ruling government by mirroring the official cabinet positions. Unlike the inner cabinet, which consists of the most trusted and influential ministers within the ruling party, the shadow cabinet functions as a government-in-waiting, offering alternative policies and holding ministers accountable. This system ensures a structured and organized opposition that enhances democratic debate and government transparency.
Historical Origins of Both Cabinets
The Inner Cabinet traces its origins to the early 19th century British government, where a small group of senior ministers met privately to make key decisions before presenting them to the full Cabinet. The Shadow Cabinet emerged in the 20th century within parliamentary systems, particularly in the UK, as the official opposition's team of senior spokespeople mirroring the actual Cabinet to scrutinize and challenge government policies. Both structures evolved from the need for efficient governance and effective political opposition, reflecting the dynamics of constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy.
Key Roles and Functions
The Inner Cabinet consists of the most influential government ministers who directly advise the Prime Minister on critical policy decisions and strategic direction, often controlling major portfolios such as finance, defense, and foreign affairs. The Shadow Cabinet, composed of opposition party members, mirrors the official Cabinet by scrutinizing government policies, proposing alternatives, and holding ministers accountable through detailed critiques. Both structures are essential for parliamentary democracy, with the Inner Cabinet driving policymaking and the Shadow Cabinet ensuring transparency and opposition readiness.
Composition and Membership
The Inner Cabinet consists of the most senior government ministers who handle the core policy areas and make key decisions, typically including the Prime Minister, Chancellor of the Exchequer, and Foreign Secretary. The Shadow Cabinet mirrors this structure within the opposition party, composed of senior members responsible for scrutinizing and challenging each corresponding government minister's portfolio. Membership of the Inner Cabinet is more exclusive and stable, while the Shadow Cabinet may undergo more frequent changes based on the opposition party's strategy and leadership.
Influence on Government Policy
The Inner Cabinet holds significant influence on government policy through direct decision-making and close collaboration with the Prime Minister, shaping key legislative priorities and strategic agendas. The Shadow Cabinet influences government policy by scrutinizing the current administration's actions, proposing alternative policies, and preparing to assume office with a ready policy framework. Both structures impact policy development, with the Inner Cabinet driving implementation and the Shadow Cabinet providing critical oversight and policy alternatives.
Accountability and Decision-Making
The Inner Cabinet consists of key ministers who hold primary decision-making responsibilities and are directly accountable to the Prime Minister, ensuring swift and unified policy direction. The Shadow Cabinet, formed by opposition parties, scrutinizes government actions and holds the Inner Cabinet accountable by presenting alternative policies and challenging decisions. This dynamic facilitates transparent governance and promotes responsible leadership within a parliamentary system.
Interactions with the Public and Media
The Inner Cabinet, composed of senior government ministers, often communicates official policy and key decisions directly to the public through formal channels and press briefings, maintaining tight message control. The Shadow Cabinet, representing the opposition, interacts with the media to scrutinize government actions and present alternative policies, leveraging press interviews and public statements to influence public opinion. Both cabinets use media as a strategic tool to shape narratives, but the Shadow Cabinet focuses more on critique and advocacy to hold the government accountable.
Differences in Power and Authority
The Inner Cabinet consists of senior government ministers with direct access to the Prime Minister, wielding greater decision-making power and authority in shaping key policies. In contrast, the Shadow Cabinet is composed of opposition party members who scrutinize and challenge the government's decisions but lack formal executive power. The Inner Cabinet's influence lies in governance and implementation, while the Shadow Cabinet holds authority primarily in political oversight and critique.
Comparative Significance in Modern Governance
The Inner Cabinet comprises key ministers who make critical policy decisions, often shaping the government's strategic direction with direct access to the head of government, while the Shadow Cabinet functions as the official opposition's team, scrutinizing government actions and proposing alternative policies. The Inner Cabinet holds significant power in driving legislative agendas and executive actions, reflecting the government's core priorities in modern governance. In contrast, the Shadow Cabinet plays a vital democratic role by ensuring accountability, fostering policy debate, and preparing opposition members for potential future governance.
Inner cabinet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com