Grassroots support plays a crucial role in driving community-driven initiatives and fostering authentic engagement from local populations. It builds a strong foundation for sustainable change by empowering individuals to participate actively in decision-making processes. Discover how grassroots support can transform your efforts and the impact it can achieve in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
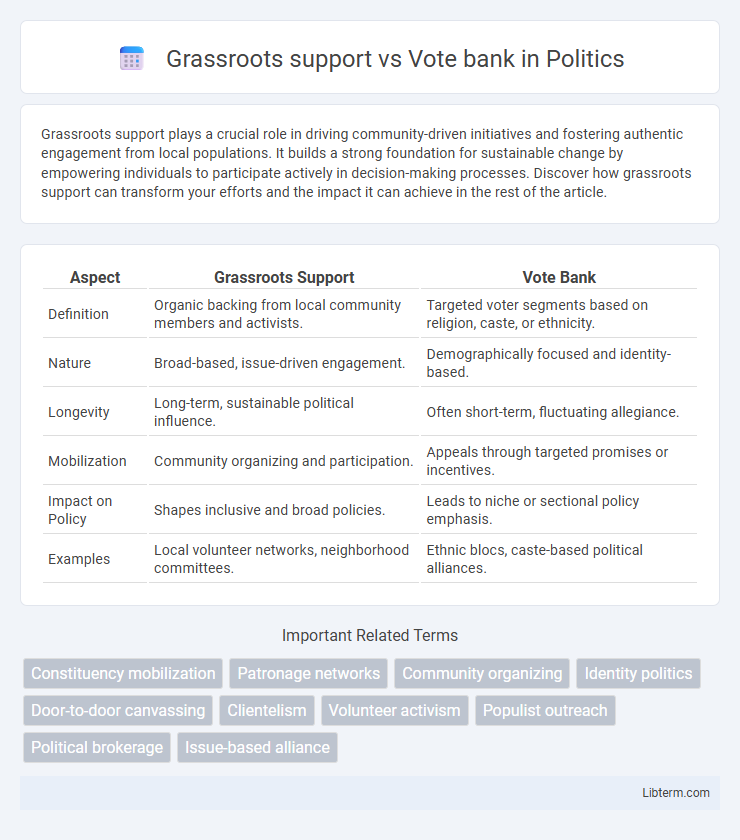
| Aspect | Grassroots Support | Vote Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organic backing from local community members and activists. | Targeted voter segments based on religion, caste, or ethnicity. |
| Nature | Broad-based, issue-driven engagement. | Demographically focused and identity-based. |
| Longevity | Long-term, sustainable political influence. | Often short-term, fluctuating allegiance. |
| Mobilization | Community organizing and participation. | Appeals through targeted promises or incentives. |
| Impact on Policy | Shapes inclusive and broad policies. | Leads to niche or sectional policy emphasis. |
| Examples | Local volunteer networks, neighborhood committees. | Ethnic blocs, caste-based political alliances. |
Understanding Grassroots Support
Grassroots support consists of genuine, community-driven backing that emerges from local populations actively participating in political processes. It contrasts with vote banks, which often rely on securing fixed blocks of votes based on caste, religion, or ethnicity without necessarily encouraging political engagement or awareness. Understanding grassroots support involves recognizing its foundation in mobilizing citizens around shared interests and issues, fostering long-term loyalty and sustainable political influence.
Defining Vote Bank Politics
Vote bank politics refers to the strategy where political parties secure support from specific social, ethnic, or religious groups by promising policies catering to their interests, often prioritizing these groups over broader population needs. Grassroots support involves genuine community engagement and mobilization, emphasizing shared goals and collective empowerment rather than transactional vote-seeking. Defining vote bank politics highlights manipulative tactics that exploit identity divisions to maintain electoral dominance, contrasting with the inclusive nature of grassroots political participation.
Historical Context: Grassroots and Vote Banks in Politics
Grassroots support in politics historically emerges from local communities mobilizing around shared interests and authentic leadership, contrasting with vote banks that are often formed along caste, religion, or ethnic lines to secure consistent electoral loyalty. The evolution of vote banks in post-colonial democracies reflects efforts by political parties to consolidate power by catering to specific demographic groups, sometimes at the expense of broader, issue-based movements characteristic of grassroots politics. Understanding this distinction is crucial for analyzing electoral strategies and the dynamics of political representation in diverse societies.
Key Differences Between Grassroots Support and Vote Banks
Grassroots support involves widespread, organic engagement from diverse community members motivated by shared values, while vote banks consist of fixed voter groups influenced by caste, religion, or ethnicity that political parties target for guaranteed votes. Grassroots movements emphasize active participation and leadership development, aiming for long-term social or political change, whereas vote banks often rely on transactional relationships centered on identity politics and immediate electoral benefits. The key difference lies in the nature of voter mobilization, with grassroots support fostering inclusive, participatory democracy and vote banks promoting segmented, loyalty-based voting patterns.
Advantages of Grassroots Mobilization
Grassroots mobilization fosters genuine community engagement by empowering local voices and building sustainable political movements rooted in shared interests. It enhances voter turnout through direct, personalized outreach, strengthening democratic participation beyond transactional vote banks. This approach cultivates long-term trust and accountability between representatives and constituents, promoting inclusive policy development and social cohesion.
Challenges of Vote Bank Strategies
Vote bank strategies often face challenges such as voter volatility, where allegiance shifts diminish predictable support patterns, and the fragmentation of target demographics, reducing cohesive influence. These strategies risk fostering superficial loyalty based on identity rather than genuine political engagement, limiting long-term trust and policy impact. Consequences include increased polarization and the neglect of broader community interests vital for sustainable governance.
Impact on Democratic Participation
Grassroots support fosters genuine democratic participation by engaging citizens in policymaking and community actions, enhancing political awareness and accountability. Vote banks, often based on identity or patronage, can undermine democratic processes by promoting loyalty over informed decision-making, potentially leading to clientelism. The contrast influences electoral dynamics significantly, where grassroots mobilization tends to encourage active civic involvement, while vote bank reliance risks perpetuating polarization and voter disenfranchisement.
Case Studies: Grassroots vs Vote Bank Success Stories
The success of grassroots support is evident in movements like the Arab Spring, where local community mobilization led to significant political change without reliance on traditional vote bank politics. In contrast, India's vote bank strategy, exemplified by parties targeting specific caste groups, secured electoral victories but often at the cost of broader social cohesion and long-term development. Case studies show that grassroots campaigns foster sustainable political engagement, while vote bank reliance can limit inclusive governance.
Future Trends in Political Campaigning
Grassroots support emphasizes genuine community engagement and organic voter mobilization, contrasting with vote bank strategies that rely on fixed demographic loyalties. Future trends in political campaigning are shifting towards leveraging data analytics and social media to cultivate personalized, issue-based connections with voters, reflecting a move away from traditional vote bank politics. Emerging technologies like AI-driven sentiment analysis enhance the ability to identify and activate grassroots constituencies, promoting more dynamic and responsive electoral strategies.
Choosing the Right Approach: Lessons for Political Leaders
Political leaders must evaluate grassroots support and vote banks by prioritizing genuine community engagement and long-term trust-building over short-term electoral gains. Grassroots support stems from active involvement and addressing real constituent needs, creating sustainable political loyalty. Vote banks, while offering immediate votes, risk fostering dependency and overlooking broader social progress, making grassroots mobilization the more strategic and ethically sound approach.
Grassroots support Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com