Effective policy implementation ensures that strategic plans transform into tangible results by aligning resources, processes, and stakeholders. Challenges such as inadequate communication, resistance to change, or lack of accountability can hinder the success of your initiatives. Explore the full article to discover practical steps for overcoming obstacles and achieving impactful policy execution.
Table of Comparison
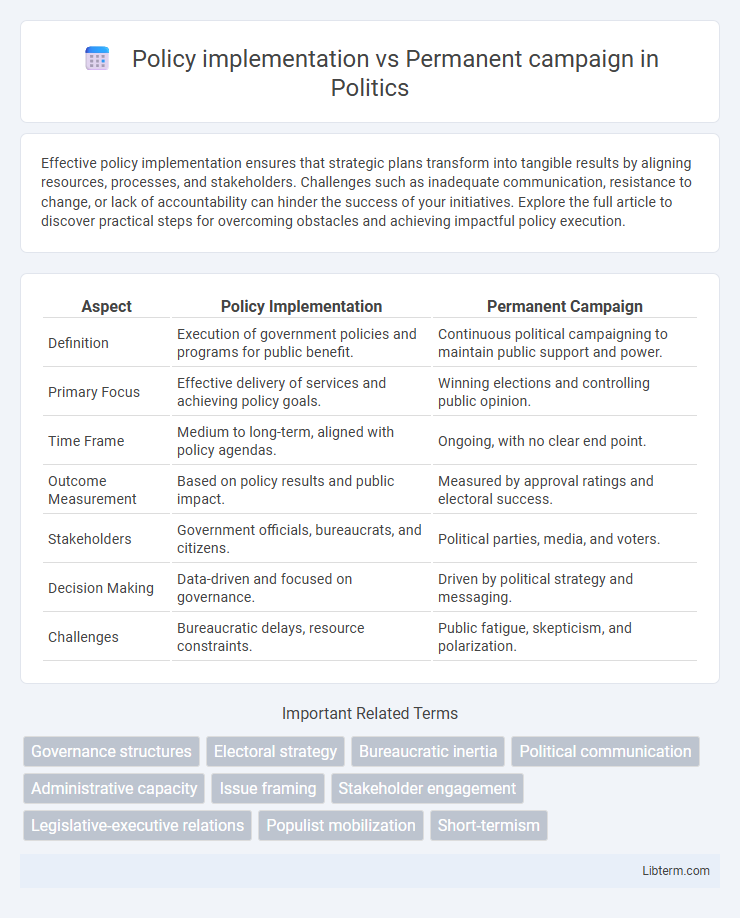
| Aspect | Policy Implementation | Permanent Campaign |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Execution of government policies and programs for public benefit. | Continuous political campaigning to maintain public support and power. |
| Primary Focus | Effective delivery of services and achieving policy goals. | Winning elections and controlling public opinion. |
| Time Frame | Medium to long-term, aligned with policy agendas. | Ongoing, with no clear end point. |
| Outcome Measurement | Based on policy results and public impact. | Measured by approval ratings and electoral success. |
| Stakeholders | Government officials, bureaucrats, and citizens. | Political parties, media, and voters. |
| Decision Making | Data-driven and focused on governance. | Driven by political strategy and messaging. |
| Challenges | Bureaucratic delays, resource constraints. | Public fatigue, skepticism, and polarization. |
Understanding Policy Implementation
Policy implementation entails executing government decisions through structured procedures and resources to achieve specific public goals. Effective implementation requires coordination among agencies, clear communication, and adaptability to overcome bureaucratic obstacles and stakeholder resistance. Understanding policy implementation emphasizes the translation of legislative intent into concrete actions that impact society, distinct from the ongoing political strategies of a permanent campaign.
Defining the Permanent Campaign
The permanent campaign refers to the continuous political strategy where elected officials prioritize ongoing electoral success over traditional policy implementation. This approach blurs the lines between governing and campaigning by maintaining constant voter engagement, fundraising, and media presence. Unlike discrete policy stages, the permanent campaign integrates political messaging into every aspect of governance to sustain public support.
Key Differences Between Policy Implementation and Permanent Campaign
Policy implementation involves enacting and managing government programs based on legislative mandates and regulatory frameworks, aiming for long-term societal impact and administrative efficiency. The permanent campaign centers on continuous political messaging, public opinion management, and voter engagement to maintain electoral support and party dominance. Key differences include the focus on bureaucratic execution and policy outcomes in implementation versus strategic communication and image shaping in permanent campaigns.
Historical Evolution of Policy Implementation
The historical evolution of policy implementation reveals a shift from rigid, top-down administrative processes to more adaptive, collaborative approaches reflecting the complexities of modern governance. Early 20th-century models emphasized hierarchical control and clear accountability, whereas contemporary theories highlight network governance and continuous feedback loops shaped by political cycles, including permanent campaigns. Understanding this progression aids in analyzing how political agendas influence policy execution and the balance between sustained administrative goals and electoral strategies.
Origins and Growth of the Permanent Campaign
The concept of the permanent campaign emerged in the late 20th century as political leaders increasingly prioritized continuous electoral strategy over traditional governance cycles. Originating from changes in media dynamics and voter behavior, it reflects a shift where policy implementation is often subordinated to ongoing political positioning. This growth was catalyzed by the rise of 24-hour news cycles, data-driven voter targeting, and the need for constant public engagement.
Stakeholders Influencing Policy Decisions
Stakeholders influencing policy decisions play a critical role in both policy implementation and permanent campaigns by shaping agendas through advocacy, lobbying, and public opinion efforts. During policy implementation, institutional stakeholders such as government agencies and interest groups ensure regulations align with defined objectives, while in permanent campaigns, political actors and media continuously engage stakeholders to maintain support and adapt messaging. This dynamic interaction underscores the importance of stakeholder networks in sustaining policy momentum and electoral viability over time.
Political Communication in Permanent Campaigns
Political communication in permanent campaigns emphasizes continuous message control and voter engagement beyond traditional election cycles, contrasting with policy implementation that centers on executing governance objectives. Strategies include relentless media presence, targeted advertising, and issue framing to maintain public support and influence opinion. This approach often blurs the boundary between governing and campaigning, prioritizing image management over substantial policy outcomes.
Challenges of Balancing Governance with Campaigning
Navigating the challenges of balancing policy implementation with permanent campaigning requires managing limited time and resources while addressing both governance priorities and electoral messaging. Political leaders face the difficulty of maintaining public trust and effective legislative progress amid constant campaign pressures and media scrutiny. This tension often leads to compromises in long-term policy outcomes as officials juggle immediate voter appeal against substantive governance goals.
Impacts on Public Trust and Democratic Processes
Policy implementation directly affects public trust by demonstrating government accountability and effectiveness, while permanent campaigns often prioritize image management over substantive governance. This shift can erode citizens' confidence in democratic institutions by fostering skepticism about policymakers' true priorities and increasing political polarization. Sustained emphasis on campaigning risks undermining long-term policy outcomes and weakening the democratic process through decreased transparency and reduced public engagement.
Strategies for Effective Policy Implementation Amid Political Pressures
Effective policy implementation demands clear goal-setting, resource allocation, and stakeholder collaboration to translate decisions into tangible outcomes. Strategies include building bipartisan support, maintaining transparent communication, and leveraging evidence-based practices to counteract the interruptions caused by permanent campaign dynamics. Prioritizing adaptive management and continuous feedback allows policymakers to navigate political pressures while sustaining focus on long-term policy objectives.
Policy implementation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com