A local ordinance is a law enacted by municipal or county governments to regulate activities within their jurisdiction. These regulations address various community needs such as zoning, public safety, and noise control, directly impacting Your daily life and property rights. Explore the full article to understand how local ordinances might affect You and what steps to take for compliance.
Table of Comparison
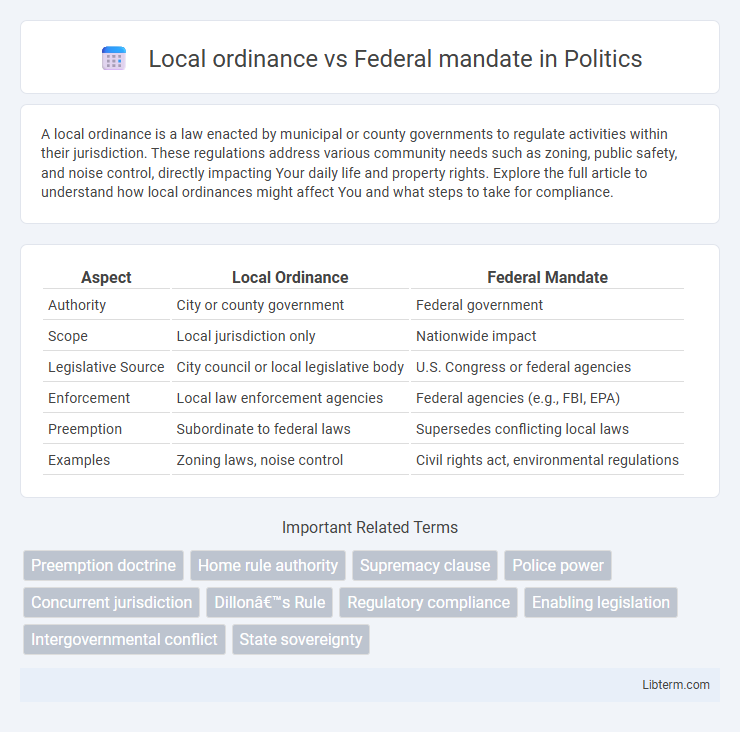
| Aspect | Local Ordinance | Federal Mandate |
|---|---|---|
| Authority | City or county government | Federal government |
| Scope | Local jurisdiction only | Nationwide impact |
| Legislative Source | City council or local legislative body | U.S. Congress or federal agencies |
| Enforcement | Local law enforcement agencies | Federal agencies (e.g., FBI, EPA) |
| Preemption | Subordinate to federal laws | Supersedes conflicting local laws |
| Examples | Zoning laws, noise control | Civil rights act, environmental regulations |
Understanding Local Ordinances and Federal Mandates
Local ordinances are laws enacted by city or county governments to address community-specific issues, while federal mandates are directives issued by the federal government that require compliance across all states. Understanding the hierarchy between them is essential, as federal mandates generally override conflicting local ordinances due to the Supremacy Clause of the U.S. Constitution. Knowledge of this legal framework helps clarify jurisdictional authority and the enforcement scope of local and federal regulations.
Key Differences Between Local and Federal Regulations
Local ordinances are laws enacted by municipal or county governments tailored to address community-specific issues, such as zoning, noise control, and public safety, reflecting localized priorities and conditions. Federal mandates, on the other hand, are nationwide directives established by the federal government to ensure uniform compliance on critical matters like environmental standards, civil rights, and interstate commerce regulations. The key difference lies in jurisdiction scope: local ordinances apply within a defined area with flexibility, while federal mandates have overarching authority, often superseding conflicting local laws to maintain consistency across states.
Legal Authority: Who Holds the Power?
Local ordinances derive their legal authority from state constitutions and statutes, granting municipal governments the power to regulate within their jurisdictions. Federal mandates stem from the U.S. Constitution's Supremacy Clause, which establishes that federal laws take precedence over conflicting state or local laws. When local ordinances conflict with federal mandates, courts often uphold federal authority, reinforcing the hierarchical legal structure in the United States.
Conflict Resolution: When Local Ordinances Clash with Federal Mandates
Local ordinances may conflict with federal mandates when local governments enact regulations that contradict federal laws or policies, creating legal ambiguity and enforcement challenges. The Supremacy Clause of the U.S. Constitution establishes that federal mandates generally preempt conflicting local ordinances, requiring local authorities to comply with overarching federal standards. Courts often resolve these disputes by invalidating local regulations that interfere with federal objectives, ensuring uniformity and consistency in law enforcement across jurisdictions.
Supremacy Clause: Federal Law Over Local Laws
The Supremacy Clause establishes that federal law takes precedence over conflicting local ordinances, ensuring a uniform legal framework across the United States. When local regulations contradict federal mandates, courts generally uphold the federal statutes as the supreme law of the land. This constitutional principle prevents local governments from enacting laws that undermine or conflict with federally enacted policies and regulations.
Impact on Businesses and Residents
Local ordinances often allow for tailored regulations that address specific community needs, offering businesses and residents more adaptable compliance options compared to federal mandates. Federal mandates impose uniform standards that businesses must follow nationwide, ensuring consistency but sometimes limiting flexibility in local economic conditions. The impact on residents includes variations in service provision and regulatory burdens, with local ordinances reflecting community priorities and federal mandates delivering broader protections and infrastructure benefits.
Case Studies: Real-world Examples of Ordinance vs Mandate
The 2015 Sanctuary Cities debate highlighted how local ordinances in cities like San Francisco resist federal immigration mandates, illustrating legal tensions between municipal autonomy and national policy enforcement. In environmental regulation, California's strict vehicle emissions standards, enforced through state and local ordinances, often exceed federal Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) mandates, demonstrating a proactive stance on climate change. The COVID-19 pandemic showcased conflicts as some cities imposed mask mandates and business restrictions contrary to federal guidelines, emphasizing the complex interplay between local public health initiatives and federal directives.
Compliance Challenges for Local Governments
Local governments face significant compliance challenges when federal mandates conflict with local ordinances, creating legal ambiguity and resource allocation issues. Managing divergent requirements often forces municipalities to allocate limited budgets toward legal counsel and enforcement, hindering effective service delivery. Navigating these complexities requires local governments to balance adherence to federal directives while honoring community-specific regulations, leading to frequent legal disputes and administrative burdens.
The Role of Courts in Resolving Jurisdictional Disputes
Courts play a critical role in resolving jurisdictional disputes between local ordinances and federal mandates by interpreting constitutional principles such as federal supremacy and states' rights. Judicial review determines whether a federal mandate overrides conflicting local laws, often referencing the Supremacy Clause of the U.S. Constitution. Landmark cases like McCulloch v. Maryland and Arizona v. United States establish precedents that guide courts in balancing local autonomy against federal authority.
Future Trends in Local and Federal Regulatory Interactions
Future trends in local and federal regulatory interactions indicate increasing tension and complexity as municipalities assert stronger local ordinances to address community-specific issues like climate change and public health, often challenging broader federal mandates. Emerging patterns show a push toward cooperative federalism, where shared regulatory frameworks enable more adaptive and regionally nuanced policy enforcement, especially in sectors such as environmental regulation and housing. Advances in data analytics and digital governance tools are enhancing transparency and coordination between local governments and federal agencies, fostering more dynamic and responsive regulatory environments.
Local ordinance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com