A strategic vote involves casting your ballot not just for your preferred candidate but to influence the overall election outcome by supporting a viable contender. This approach aims to prevent an undesirable candidate from winning, making your vote more impactful in tightly contested races. Discover how strategic voting can shape your election influence and when it might be the right choice for you in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
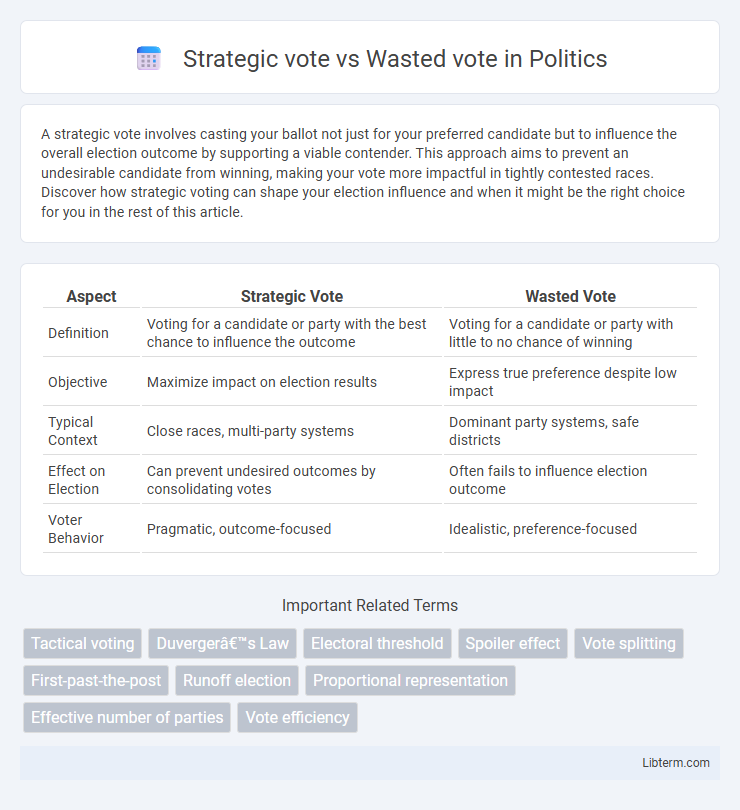
| Aspect | Strategic Vote | Wasted Vote |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voting for a candidate or party with the best chance to influence the outcome | Voting for a candidate or party with little to no chance of winning |
| Objective | Maximize impact on election results | Express true preference despite low impact |
| Typical Context | Close races, multi-party systems | Dominant party systems, safe districts |
| Effect on Election | Can prevent undesired outcomes by consolidating votes | Often fails to influence election outcome |
| Voter Behavior | Pragmatic, outcome-focused | Idealistic, preference-focused |
Understanding Strategic Voting: Definition and Scope
Strategic voting occurs when voters select a candidate not as their first preference but to prevent an undesirable outcome, often termed a wasted vote when support goes to a candidate unlikely to win. This behavior reflects an electoral calculus where individuals prioritize influence on the election result over expressing genuine preferences, impacting overall democratic representation. Understanding the scope of strategic voting involves analyzing electoral systems, voter psychology, and the perceived viability of candidates within a given political context.
What Constitutes a Wasted Vote?
A wasted vote occurs when a ballot cast does not contribute to electing a preferred candidate, either because it supports a losing candidate or exceeds the number needed for victory beyond what influences the outcome. In plurality voting systems, votes for losing candidates count as wasted since they fail to impact the election result, while surplus votes for a winning candidate also become ineffective in changing the winner. Understanding wasted votes helps explain voter behavior in strategic voting, where individuals might choose a less preferred but more viable candidate to avoid squandering their vote.
Key Differences Between Strategic and Wasted Votes
Strategic votes are cast deliberately to influence the election outcome by supporting a candidate with a realistic chance of winning, maximizing the voter's impact within a given electoral system. Wasted votes occur when ballots are cast for candidates unlikely to win or surplus votes beyond what the winning candidate needed, effectively having little to no influence on the result. The key difference lies in the voter's intention and the practical effectiveness of the vote, where strategic voting aims to avoid wasted votes by aligning preferences with electability.
Why Voters Choose to Vote Strategically
Voters choose to vote strategically to maximize the impact of their ballot in elections with plurality or first-past-the-post systems, where votes for less popular candidates often do not influence the outcome. Strategic voting helps avoid wasting votes on candidates unlikely to win by supporting a more viable candidate whose platform aligns closely with the voter's preferences. This behavior often emerges in closely contested races or when voters seek to prevent an unfavorable candidate from winning.
Impact of Voting Systems on Strategic vs Wasted Votes
Voting systems significantly influence the prevalence of strategic and wasted votes, with plurality systems often encouraging strategic voting to avoid "wasting" a vote on less viable candidates. Proportional representation systems reduce wasted votes by allocating seats more closely to the percentage of votes received, decreasing incentives for voters to cast strategic votes. Mixed voting systems attempt to balance representation and voter choice, mitigating wasted votes while maintaining some strategic considerations.
Real-World Examples of Strategic Voting Outcomes
In the 2000 U.S. presidential election, strategic voting played a crucial role as voters in swing states chose candidates most likely to defeat their least preferred option, impacting the overall electoral outcome. The 2017 French presidential election demonstrated strategic voting when supporters of eliminated candidates consolidated their votes behind Emmanuel Macron to prevent the far-right candidate Marine Le Pen from winning. In the 2019 Canadian federal election, strategic voting influenced several ridings where Liberals and Conservatives garnered votes primarily aimed at unseating the incumbent New Democratic Party, illustrating how voters navigate the risk of wasted votes in plurality systems.
Psychological Factors Influencing Voting Choices
Psychological factors influencing voting choices often lead individuals to engage in strategic voting, where they select a candidate with a realistic chance of winning rather than their preferred option to avoid a wasted vote. Voters weigh the perceived viability of candidates, influenced by social identity, cognitive biases, and fear of marginalizing their political preferences. The psychological need for efficacy and meaningful participation drives the tension between sincere and strategic voting behavior.
The Role of Minor Parties in Vote Allocation
Strategic voting often arises when voters support minor parties to influence policy indirectly or signal dissatisfaction, despite low chances of winning, contrasting with wasted votes cast for candidates unlikely to impact outcomes. Minor parties play a crucial role in vote allocation by shaping electoral dynamics, pushing major parties to adopt diverse platforms to capture these strategic voters. Their presence can alter election results by redistributing votes and affecting coalition-building efforts within proportional representation systems.
Consequences for Democracy: Strategic vs Wasted Voting
Strategic voting can distort true voter preferences by encouraging individuals to support less preferred but more viable candidates, potentially undermining the principle of representative democracy. Wasted votes, often cast for candidates with little chance of winning, may discourage voter participation and weaken the legitimacy of election outcomes. Both phenomena impact democratic health by influencing voter behavior, election results, and the overall responsiveness of political systems.
Navigating Your Vote: Making an Informed Choice
Strategic voting involves selecting a candidate with a realistic chance of winning to maximize electoral impact, while wasted votes occur when ballots support candidates with little to no chance of success, effectively diluting voter influence. Understanding the dynamics of your voting district, including candidate viability and historical election outcomes, helps optimize your vote's effectiveness. Accessing reliable election analytics and polling data empowers voters to make informed choices that align with their preferences and strategic goals.
Strategic vote Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com