Liberal beliefs emphasize individual freedoms, equal rights, and social justice, promoting policies that support diversity and inclusion. This political philosophy values open-mindedness and progressive reforms aimed at improving society for all citizens. Explore the rest of the article to understand how liberal ideals impact modern governance and your everyday life.
Table of Comparison
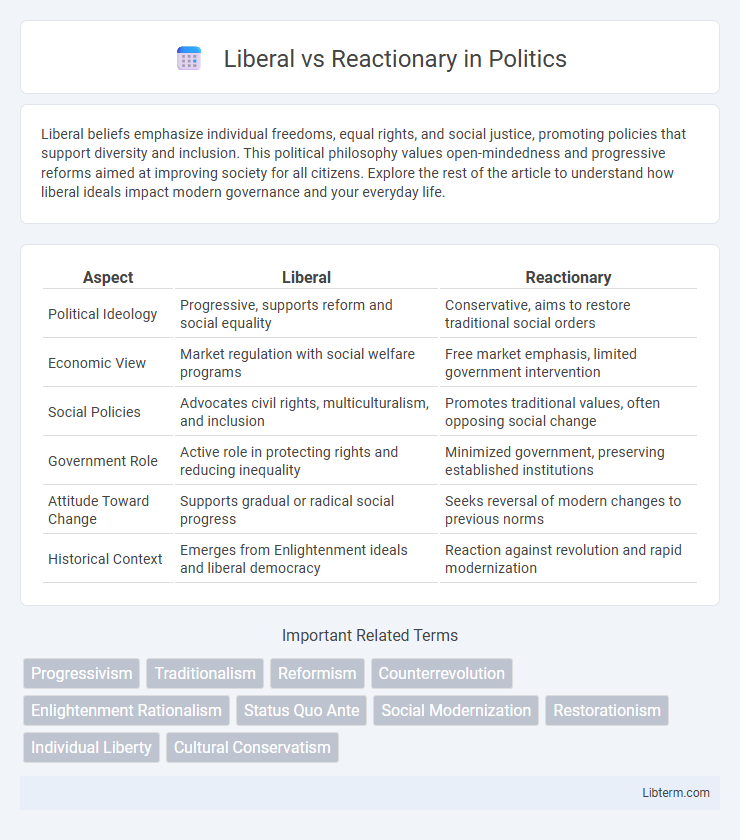
| Aspect | Liberal | Reactionary |
|---|---|---|
| Political Ideology | Progressive, supports reform and social equality | Conservative, aims to restore traditional social orders |
| Economic View | Market regulation with social welfare programs | Free market emphasis, limited government intervention |
| Social Policies | Advocates civil rights, multiculturalism, and inclusion | Promotes traditional values, often opposing social change |
| Government Role | Active role in protecting rights and reducing inequality | Minimized government, preserving established institutions |
| Attitude Toward Change | Supports gradual or radical social progress | Seeks reversal of modern changes to previous norms |
| Historical Context | Emerges from Enlightenment ideals and liberal democracy | Reaction against revolution and rapid modernization |
Understanding Liberalism: Core Principles
Liberalism centers on individual freedom, equality, and the protection of civil rights through democratic governance and rule of law. It emphasizes social progress, open markets, and government intervention to promote social justice and economic opportunity. Key principles include tolerance, pluralism, and the belief in rational debate to resolve conflicts within society.
Defining Reactionary Thought
Reactionary thought seeks to preserve or restore traditional social orders and hierarchies, opposing progressive reforms and liberal principles of individual rights and equality. It often idealizes a past era perceived as more stable or morally grounded, rejecting rapid change and modernity. Reactionaries emphasize authority, tradition, and social cohesion as essential to societal well-being, contrasting with the liberal emphasis on freedom, equality, and social progress.
Historical Origins of Liberal and Reactionary Movements
The historical origins of liberal movements trace back to the Enlightenment era, emphasizing individual rights, constitutional government, and economic freedom against absolute monarchies. Reactionary movements emerged as a counterforce during the 19th century, seeking a return to traditional social orders, monarchy, and established hierarchies disrupted by revolutionary changes. Key events like the French Revolution highlighted the clash, with liberals advocating progressive reforms and reactionaries resisting rapid social and political upheaval.
Key Differences: Liberal vs Reactionary Ideologies
Liberal ideologies emphasize individual freedoms, equality, and progressive social reforms aimed at expanding rights and opportunities within democratic frameworks. Reactionary ideologies seek to preserve or revive traditional social orders, often opposing rapid change and advocating a return to previous political, cultural, or moral norms. The key difference lies in liberals promoting change for social progress, while reactionaries resist change to maintain established hierarchies.
Social Change: Progress vs Preservation
Liberals advocate for social change by promoting progressive policies that emphasize equality, individual rights, and social justice to address systemic inequalities. Reactionaries resist social change, aiming to preserve traditional social structures, cultural norms, and hierarchical orders believed to sustain societal stability. The tension between liberal progress and reactionary preservation fundamentally shapes debates on civil rights, government intervention, and cultural values.
Economic Perspectives: Reform vs Tradition
Liberals advocate for economic reforms that promote free markets, innovation, and social progress, emphasizing policies such as deregulation, progressive taxation, and social welfare programs to reduce inequality. Reactionaries emphasize preserving traditional economic structures, supporting protectionist policies, strict regulation, and maintaining hierarchies believed to ensure social stability and continuity. The fundamental divide centers on whether economic change fosters growth and equity or threatens established order and cultural values.
Political Influence of Liberals and Reactionaries
Liberals champion progressive reforms, advocating for democratic governance, individual rights, and social equality, which significantly shape modern political landscapes through policy innovations and expanded civil liberties. Reactionaries strive to restore traditional institutions and social orders, often resisting rapid change by promoting conservative values and hierarchical power structures, thereby influencing political discourse toward preservation of established norms. The dynamic tension between liberal activism and reactionary resistance drives political evolution, influencing election outcomes, legislative priorities, and public attitudes worldwide.
Modern Examples: Global Case Studies
Liberal ideologies in modern global contexts often emphasize individual rights, democratic governance, and economic freedom, as seen in countries like Canada and Sweden promoting progressive social policies and open markets. Reactionary movements, exemplified by nations such as Russia under Vladimir Putin or Turkey under Recep Tayyip Erdogan, prioritize traditional values, national sovereignty, and centralized authority to counter perceived liberal overreach. These contrasting approaches influence policy-making, international relations, and societal structures, shaping the contemporary political landscape worldwide.
Criticisms and Controversies
Liberals face criticism for promoting progressive social policies that some argue undermine traditional values and lead to excessive government intervention in the economy. Reactionaries are often criticized for their resistance to social change and perceived nostalgia for authoritarian or elitist regimes, which can hinder democratic progress and civil rights advancements. Both ideologies spark controversies regarding the balance between individual freedoms and societal order, with debates over issues like immigration, economic regulation, and cultural identity intensifying political polarization.
The Ongoing Debate: Future of Liberal and Reactionary Ideas
Liberal ideas emphasize individual freedoms, equality, and progressive reforms, advocating for social justice and inclusive governance as essential for future societal development. Reactionary perspectives resist rapid change, favoring a return to traditional values and established hierarchies, arguing that preserving cultural continuity ensures social stability. The ongoing debate centers on balancing innovation with tradition, as societies grapple with how to integrate change while maintaining foundational structures.
Liberal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com