Blank voting occurs when a voter submits a ballot without selecting any candidate or option, often signaling dissatisfaction or indecision. Understanding the implications of blank votes can help you gauge public sentiment and election dynamics more accurately. Explore the rest of the article to learn how blank voting impacts democratic processes and election outcomes.
Table of Comparison
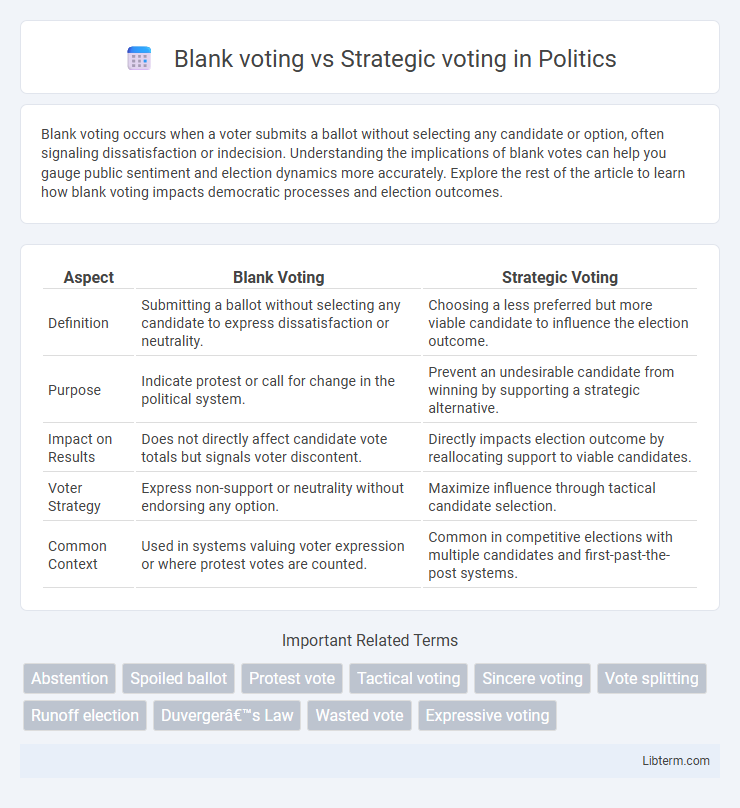
| Aspect | Blank Voting | Strategic Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Submitting a ballot without selecting any candidate to express dissatisfaction or neutrality. | Choosing a less preferred but more viable candidate to influence the election outcome. |
| Purpose | Indicate protest or call for change in the political system. | Prevent an undesirable candidate from winning by supporting a strategic alternative. |
| Impact on Results | Does not directly affect candidate vote totals but signals voter discontent. | Directly impacts election outcome by reallocating support to viable candidates. |
| Voter Strategy | Express non-support or neutrality without endorsing any option. | Maximize influence through tactical candidate selection. |
| Common Context | Used in systems valuing voter expression or where protest votes are counted. | Common in competitive elections with multiple candidates and first-past-the-post systems. |
Understanding Blank Voting
Blank voting occurs when voters submit unmarked or empty ballots, signaling indecision, protest, or dissatisfaction without endorsing any candidate, impacting election legitimacy by lowering valid vote percentages. Strategic voting involves selecting a less preferred candidate to prevent an undesirable outcome, influencing electoral results and party dynamics through tactical decision-making. Understanding blank voting is critical for assessing voter sentiment and addressing democratic engagement challenges beyond traditional vote counts.
What is Strategic Voting?
Strategic voting occurs when voters choose a candidate not because they fully support them, but to prevent an undesirable candidate from winning, often by voting for a more viable contender. This behavior contrasts with blank voting, where voters intentionally submit an empty or null ballot to express disapproval of all options. Strategic voting influences election outcomes by consolidating votes around leading candidates and minimizing wasted votes.
Key Differences Between Blank and Strategic Voting
Blank voting involves submitting a ballot without selecting any candidate, signaling voter dissatisfaction or indecision, while strategic voting entails choosing a less preferred but more viable candidate to influence the election outcome. Blank voting serves as a protest or abstention method, whereas strategic voting is a calculated decision to prevent an undesirable candidate from winning. Key differences lie in intent: blank votes express non-support, while strategic votes aim to maximize electoral impact within the constraints of the voting system.
Motivations Behind Blank Voting
Blank voting reflects voter dissatisfaction or indecision, signaling protest or disapproval without endorsing any candidate. Unlike strategic voting, where voters select a less preferred but more viable option to influence outcomes, blank voting serves as a neutral expression of disengagement or demand for better choices. This form of voting highlights underlying concerns about the candidacy, party policies, or the electoral system itself.
Why Voters Choose Strategic Voting
Voters choose strategic voting to maximize the impact of their ballots in elections with multiple candidates or parties, often selecting a less preferred but more viable option to prevent an undesirable outcome. This behavior is influenced by the desire to avoid "wasting" votes on candidates with little chance of winning, especially in plurality or first-past-the-post systems. Strategic voting aims to influence election results effectively, reflecting tactical decision-making rather than genuine preference.
Impact of Blank Votes on Election Outcomes
Blank voting can significantly affect election outcomes by increasing the percentage of non-decisive votes, which may lead to lower legitimacy for elected candidates and affect the allocation of seats in proportional representation systems. Unlike strategic voting, where voters choose a less-preferred but more viable candidate to influence the result, blank votes represent explicit voter dissatisfaction or indecision, often signaling a demand for political change or reform. High rates of blank votes can prompt electoral authorities to reconsider candidate eligibility criteria or election rules, thereby indirectly reshaping future political strategies and campaign approaches.
Effects of Strategic Voting on Democracy
Strategic voting, where voters choose candidates not to express true preferences but to influence outcomes, can distort authentic democratic representation by marginalizing minority viewpoints. It often consolidates power around major parties, weakening political pluralism and reducing incentives for policy innovation. This tactic may erode voter trust and engagement, undermining the legitimacy of electoral systems and democratic governance.
Historical Examples of Both Voting Types
Historical examples of blank voting include the 2009 European Parliament elections in Spain, where a significant number of voters submitted blank ballots to express dissatisfaction with all candidates. Strategic voting can be observed in the 2000 United States presidential election, where some voters chose to support a less preferred but more viable candidate to prevent their least favored candidate from winning. Both voting types reflect voter behavior aimed at either protest or maximizing influence under different electoral systems.
Pros and Cons: Blank vs. Strategic Voting
Blank voting allows voters to express dissatisfaction without supporting any candidate, promoting protest and highlighting flaws in the electoral system, but it can lead to wasted votes and reduced influence on election outcomes. Strategic voting involves selecting a less preferred but more viable candidate to prevent an undesired outcome, increasing the chances of a preferred result but potentially compromising genuine voter preferences. While blank voting emphasizes voter integrity, strategic voting prioritizes election efficacy and practical impact.
The Future of Voter Choice: Blank or Strategic?
Blank voting signals voter dissatisfaction or indecision, serving as a powerful statement of protest or disengagement. Strategic voting involves selecting a less preferred but more viable candidate to prevent an undesirable outcome, reflecting pragmatic decision-making in complex electoral contexts. The future of voter choice may increasingly hinge on digital platforms and enhanced voter education, potentially reshaping the balance between blank and strategic voting through data-driven insights and real-time electoral simulations.
Blank voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com