The Challenger was a pivotal spacecraft in NASA's space shuttle program, known for its seven successful missions before its tragic disaster in 1986. Its legacy highlights critical advancements in space exploration technology and the importance of rigorous safety protocols. Discover the detailed history and lessons learned from the Challenger to better understand its impact on space travel.
Table of Comparison
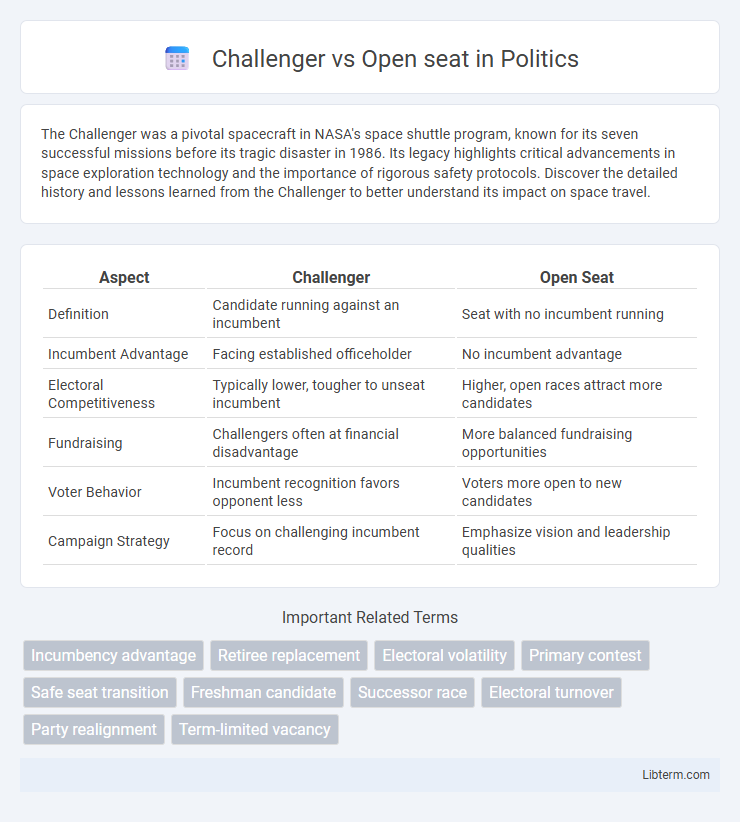
| Aspect | Challenger | Open Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Candidate running against an incumbent | Seat with no incumbent running |
| Incumbent Advantage | Facing established officeholder | No incumbent advantage |
| Electoral Competitiveness | Typically lower, tougher to unseat incumbent | Higher, open races attract more candidates |
| Fundraising | Challengers often at financial disadvantage | More balanced fundraising opportunities |
| Voter Behavior | Incumbent recognition favors opponent less | Voters more open to new candidates |
| Campaign Strategy | Focus on challenging incumbent record | Emphasize vision and leadership qualities |
Introduction to Challenger vs Open Seat
A Challenger seat refers to an electoral contest where an incumbent seeks re-election against a rival, often reflecting voter satisfaction and the strength of the current officeholder. An Open seat occurs when no incumbent is running, creating a more competitive environment typically leading to higher candidate turnout and increased campaign investment. Understanding the dynamics between Challenger and Open seats is crucial for analyzing election strategies and predicting electoral outcomes.
Defining Challenger Races
Challenger races occur when a candidate contests an incumbent holding an elected office, aiming to unseat them during an election. These races often involve higher competition levels and increased campaign spending due to the incumbent's name recognition and established voter base. Understanding the dynamics of challenger races is crucial for analyzing electoral strategies and predicting election outcomes.
Understanding Open Seat Contests
Open seat contests occur when no incumbent is running, creating a highly competitive race with greater unpredictability and increased candidate diversity. These contests often attract more campaign funding and voter interest due to the absence of established political advantages. Understanding open seat dynamics is crucial for analyzing election strategies and forecasting potential shifts in legislative power.
Key Differences Between Challenger and Open Seats
Challenger seats involve incumbents facing opposition, often with established voter bases and fundraising networks, whereas open seats lack an incumbent, creating a more competitive environment with higher candidate turnover. The presence of an incumbent in challenger races typically leads to higher campaign spending and strategic voter targeting compared to open seats. Open seats provide greater opportunities for new candidates due to the absence of an incumbent advantage, often resulting in unpredictable election outcomes.
Historical Success Rates: Challenger vs Open Seat
Historical success rates reveal that challengers face significantly tougher odds, with win percentages often below 30%, reflecting the inherent advantages of incumbency such as name recognition and established fundraising networks. Open seats generally see higher success rates for new candidates, typically exceeding 50%, as the absence of an incumbent levels the playing field and increases electoral competitiveness. Data from past congressional elections consistently demonstrate that party turnover is more frequent in open-seat races than in contests featuring challengers against incumbents.
Strategic Approaches for Candidates
Challengers prioritize targeted voter outreach and issue-based campaigning to overcome incumbent advantages in open seat races. They leverage data analytics to identify swing districts and tailor messages that resonate with undecided voters. Open seat candidates focus on building broad coalitions early, capitalizing on the absence of an incumbent to establish name recognition and secure key endorsements.
Voter Behavior in Each Scenario
Voter behavior in challenger races often leans toward preference for incumbency due to name recognition and perceived experience, while open seat elections exhibit higher volatility as voters evaluate candidates without established loyalty. Data from multiple election cycles show that incumbents typically receive a 5-10% advantage in voter turnout and support compared to challengers. Open seat contests tend to increase campaign spending and voter engagement as both parties see greater opportunity to influence electoral outcomes.
Impact on Party Dynamics
Challenger candidates often invigorate party dynamics by introducing fresh ideas and competitive energy, potentially reshaping voter loyalties and campaign strategies. Open seat races typically lead to intense intra-party contests, encouraging broader candidate selection and fostering strategic alliances within the party. Both scenarios significantly influence party cohesion, resource allocation, and long-term electoral strength.
Media Coverage and Public Perception
Media coverage of challengers often emphasizes their fresh perspectives and policy alternatives, shaping public perception by highlighting their potential to disrupt the status quo. Open seat races attract intense media attention due to the unpredictability and heightened competition, which influences voters by framing these contests as pivotal and highly consequential. Public perception in both scenarios is significantly molded by the narratives constructed through news outlets and social media platforms, affecting candidate viability and voter engagement.
Case Studies: Notable Elections
The 2018 U.S. House elections showcased key case studies where challengers unseated incumbents, such as in New York's 14th District, defeating long-term representatives by leveraging grassroots support and shifting demographics. Open seat races like the 2020 Georgia Senate runoff demonstrated intense competition, with candidates benefiting from the absence of an incumbent to capitalize on voter mobilization strategies. These examples highlight the strategic differences in campaign approaches essential for success in elections involving challengers versus open seats.
Challenger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com