Anticipatory policy involves proactive strategies designed to address future challenges before they arise, ensuring stability and adaptability. This approach helps governments and organizations mitigate risks by forecasting trends and preparing timely interventions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how anticipatory policy can safeguard your interests and shape a resilient future.
Table of Comparison
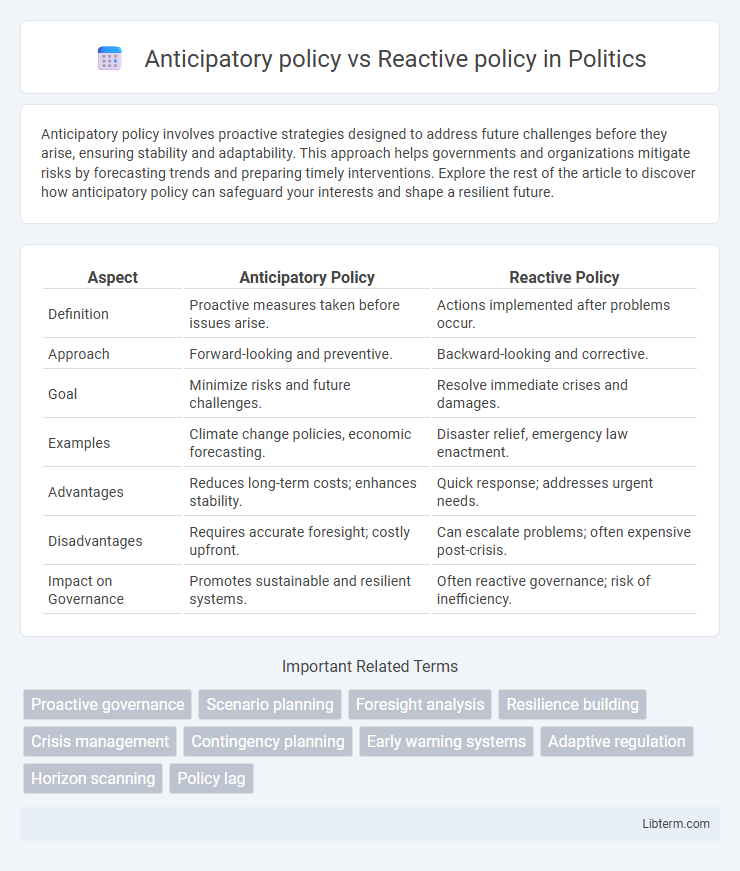
| Aspect | Anticipatory Policy | Reactive Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive measures taken before issues arise. | Actions implemented after problems occur. |
| Approach | Forward-looking and preventive. | Backward-looking and corrective. |
| Goal | Minimize risks and future challenges. | Resolve immediate crises and damages. |
| Examples | Climate change policies, economic forecasting. | Disaster relief, emergency law enactment. |
| Advantages | Reduces long-term costs; enhances stability. | Quick response; addresses urgent needs. |
| Disadvantages | Requires accurate foresight; costly upfront. | Can escalate problems; often expensive post-crisis. |
| Impact on Governance | Promotes sustainable and resilient systems. | Often reactive governance; risk of inefficiency. |
Introduction to Anticipatory and Reactive Policy
Anticipatory policy involves proactive planning and decision-making to address potential future challenges, leveraging data analytics and forecasting techniques to mitigate risks before they arise. Reactive policy, in contrast, emerges in response to events or crises, focusing on managing and resolving issues after they occur, often resulting in short-term solutions. Understanding the distinctions between anticipatory and reactive policies is critical for effective governance, crisis management, and strategic planning.
Defining Anticipatory Policy: Proactive Governance
Anticipatory policy embodies proactive governance by forecasting future challenges and implementing strategic measures before issues arise, enhancing societal resilience and resource efficiency. This approach utilizes data analysis, trend identification, and scenario planning to guide decision-making, contrasting with reactive policies that address problems post-emergence. By prioritizing prevention and long-term impact, anticipatory policy fosters sustainable development and minimizes crisis severity.
Understanding Reactive Policy: Responding to Events
Reactive policy involves responding to events after they occur, prioritizing immediate problem-solving and damage control. This approach relies on real-time data and situational analysis to address unexpected challenges, often leading to short-term fixes rather than long-term solutions. Governments and organizations implement reactive policies to manage crises such as natural disasters, economic shocks, or public health emergencies effectively.
Key Differences Between Anticipatory and Reactive Approaches
Anticipatory policies focus on proactive planning and forecasting to address potential future challenges before they occur, leveraging data analysis and trend prediction. Reactive policies respond to events after they have happened, emphasizing immediate action and problem resolution based on real-time information. The key differences lie in timing, with anticipatory strategies emphasizing early intervention, and reactive strategies prioritizing adaptability and responsiveness to crises.
Benefits of Anticipatory Policy in Modern Governance
Anticipatory policy enhances modern governance by enabling proactive decision-making that addresses potential challenges before they escalate into crises, reducing economic and social costs. It fosters innovation and resilience through data-driven insights and scenario planning, ensuring adaptive strategies that remain effective in dynamic environments. Governments benefit from improved resource allocation and increased public trust by demonstrating foresight and responsiveness to emerging issues.
Challenges and Limitations of Reactive Policies
Reactive policies often struggle with delayed responses to emerging threats, resulting in increased costs and exacerbated damages. Limited foresight impedes the ability to prevent crises, causing inefficiencies in resource allocation and emergency management. These challenges highlight the critical need for proactive frameworks that anticipate risks before they escalate.
Case Studies: Successful Anticipatory Policy Implementation
Case studies of successful anticipatory policy implementation highlight proactive measures taken by governments to address emerging challenges before they escalate. For example, Singapore's Smart Nation initiative uses big data analytics and IoT technology to predict and manage urban issues like traffic congestion and environmental sustainability, significantly improving quality of life. Similarly, Finland's education reform anticipated future workforce needs by integrating digital skills and personalized learning, resulting in enhanced national competitiveness and student outcomes.
Risks and Drawbacks of Relying on Reactive Policy
Reactive policy often leads to delayed responses, increasing vulnerability to crises by addressing problems only after they have escalated. This approach risks higher costs and resource strain, as emergency interventions typically require more extensive measures than preventive actions. Relying solely on reactive policies undermines long-term planning and resilience, potentially exacerbating socioeconomic and environmental impacts.
Integrating Anticipatory Strategies into Policy-Making
Integrating anticipatory strategies into policy-making enhances governance by enabling proactive identification and mitigation of emerging risks through data analytics, scenario planning, and foresight techniques. This approach fosters resilience and adaptive capacity by aligning policy frameworks with future trends, technological advancements, and social dynamics. Emphasizing anticipatory policies over reactive responses reduces crisis impact and supports sustainable development goals across sectors.
Future Trends: Shifting from Reactive to Anticipatory Policy
Future trends indicate a significant shift from reactive policy frameworks to anticipatory policy approaches, emphasizing proactive measures to address emerging challenges before they escalate. Governments and organizations increasingly invest in data analytics, foresight methodologies, and scenario planning to identify potential risks and opportunities, enabling timely interventions. This transition enhances resilience, improves resource allocation, and fosters sustainable development in dynamic socio-economic and environmental landscapes.
Anticipatory policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com