Libertarianism champions individual freedom, limited government, and free-market principles, emphasizing personal responsibility and minimal state intervention. This political philosophy advocates for maximizing autonomy in both personal and economic decisions, valuing property rights and voluntary exchange. Discover how libertarian ideals shape policies and impact your daily life by reading the full article.
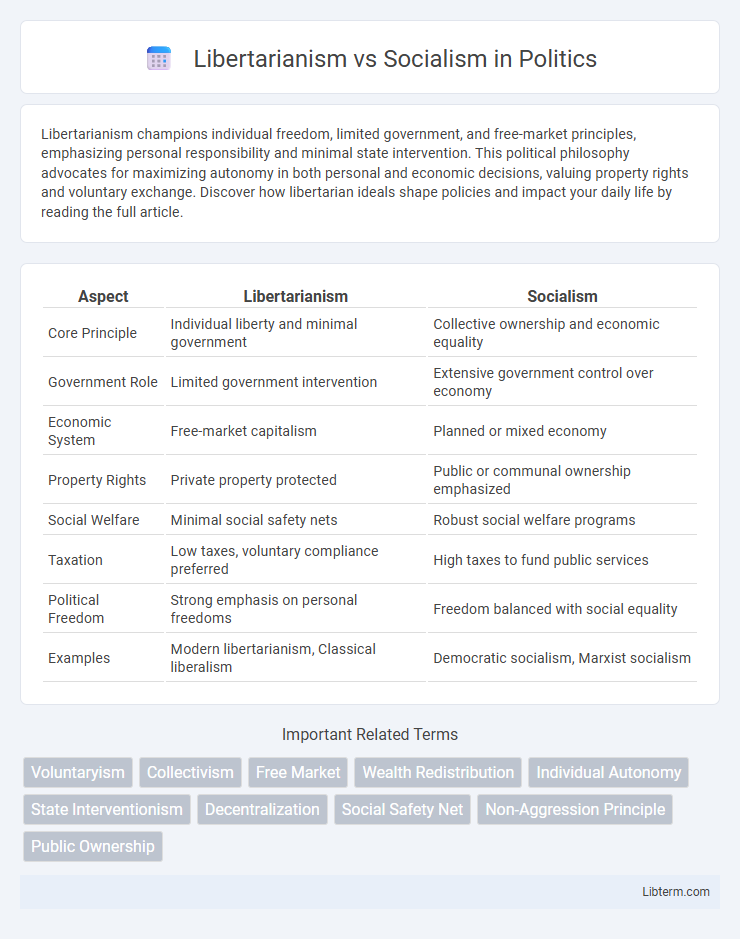
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Libertarianism | Socialism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Individual liberty and minimal government | Collective ownership and economic equality |
| Government Role | Limited government intervention | Extensive government control over economy |
| Economic System | Free-market capitalism | Planned or mixed economy |
| Property Rights | Private property protected | Public or communal ownership emphasized |
| Social Welfare | Minimal social safety nets | Robust social welfare programs |
| Taxation | Low taxes, voluntary compliance preferred | High taxes to fund public services |
| Political Freedom | Strong emphasis on personal freedoms | Freedom balanced with social equality |
| Examples | Modern libertarianism, Classical liberalism | Democratic socialism, Marxist socialism |
Understanding Libertarianism and Socialism
Libertarianism emphasizes individual freedom, limited government intervention, and free markets, advocating for personal autonomy and minimal state control over economic and social life. Socialism prioritizes collective ownership, wealth redistribution, and social equality, supporting government involvement to reduce economic disparities and provide public services. Understanding these ideologies involves analyzing their differing views on property rights, economic management, and the role of the state in society.
Core Philosophies and Principles
Libertarianism emphasizes individual liberty, limited government, and free-market capitalism, advocating minimal state intervention to maximize personal freedom and economic choice. Socialism centers on collective ownership, social equality, and wealth redistribution, aiming to reduce economic disparities through government regulation and public control of resources. Both philosophies differ fundamentally in their views on property rights, the role of the state, and economic organization, reflecting contrasting approaches to freedom and social justice.
Views on Individual Freedom
Libertarianism places individual freedom as the paramount principle, advocating minimal government intervention to maximize personal autonomy and property rights. Socialism emphasizes collective well-being, supporting state or communal control over resources to reduce inequality, sometimes prioritizing social equity over absolute individual freedom. The fundamental tension lies in libertarianism prioritizing personal liberty, while socialism balances freedom with social justice and economic redistribution.
Role of Government in Society
Libertarianism advocates for minimal government intervention, emphasizing individual freedom and free markets as the primary drivers of societal progress. In contrast, Socialism supports a significant government role in regulating the economy, redistributing wealth, and providing social services to promote equality and protect workers. The debate centers on the extent and nature of government involvement required to balance personal liberty with social welfare.
Economic Systems and Property Rights
Libertarianism emphasizes free-market capitalism with minimal government intervention, advocating for private property rights as fundamental to individual freedom and economic efficiency. Socialism supports collective or state ownership of production means, promoting wealth redistribution to achieve economic equality and reduce social disparities. The core conflict lies in Libertarianism prioritizing individual property rights and market mechanisms, while Socialism centers on communal ownership and state regulation to address societal needs.
Approaches to Social Welfare
Libertarianism emphasizes minimal government intervention in social welfare, advocating for individual responsibility and voluntary private charity to address social needs. Socialism promotes extensive government involvement to ensure equitable distribution of resources, providing universal access to healthcare, education, and social security as fundamental rights. These contrasting approaches reflect differing priorities on economic freedom versus social equality in welfare policy design.
Taxation and Redistribution Policies
Libertarianism advocates for minimal taxation and opposes extensive redistribution policies, emphasizing individual property rights and voluntary exchange as core economic principles. Socialism supports progressive taxation and extensive wealth redistribution to reduce economic inequality and fund public services, aiming to ensure a more equitable allocation of resources. The ideological divide centers on the role of government intervention, with libertarians favoring limited state involvement while socialists endorse robust fiscal policies to achieve social equity.
Historical Case Studies and Outcomes
Libertarianism and socialism have been tested through historical case studies such as the Spanish Civil War, where anarchist libertarian collectives in Catalonia emphasized decentralized governance and direct worker control, resulting in early social and economic mobilization but ultimately faltering against centralized nationalist forces. Contrastingly, socialist experiments in the Soviet Union and Cuba centralized economic planning and state control, achieving rapid industrialization and social welfare improvements while facing criticism for authoritarian governance and economic inefficiencies. These outcomes highlight the divergent impacts of libertarian emphasis on individual freedoms and decentralized power versus socialist focus on state-led equality and planned economies.
Contemporary Debates and Critiques
Contemporary debates on Libertarianism vs Socialism emphasize contrasting views on individual freedom and economic equality, with Libertarianism advocating minimal government intervention and Socialism promoting state control to reduce inequality. Critics of Libertarianism argue it risks exacerbating social disparities by prioritizing market freedom over social welfare, while detractors of Socialism highlight potential inefficiencies and constraints on personal liberties caused by extensive government regulation. Recent discourse often centers on policy outcomes in healthcare, taxation, and social services, reflecting divergent priorities in balancing liberty and collective responsibility.
Future Prospects in a Changing World
Libertarianism envisions a future with expanded individual freedoms, decentralized governance, and minimal state intervention, promising innovation through free markets and personal responsibility. Socialism emphasizes equitable resource distribution, social welfare, and collective ownership, aiming to address systemic inequalities intensified by technological change and globalization. As automation and climate challenges accelerate, hybrid models integrating libertarian flexibility with socialist social safety nets could redefine governance and economic structures globally.
Libertarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com