Government effectiveness measures the ability of public institutions to implement policies, deliver public services, and maintain order efficiently. High government effectiveness is crucial for fostering economic growth, enhancing public trust, and improving citizens' quality of life. Explore the rest of the article to understand how government effectiveness impacts your daily life and global development.
Table of Comparison
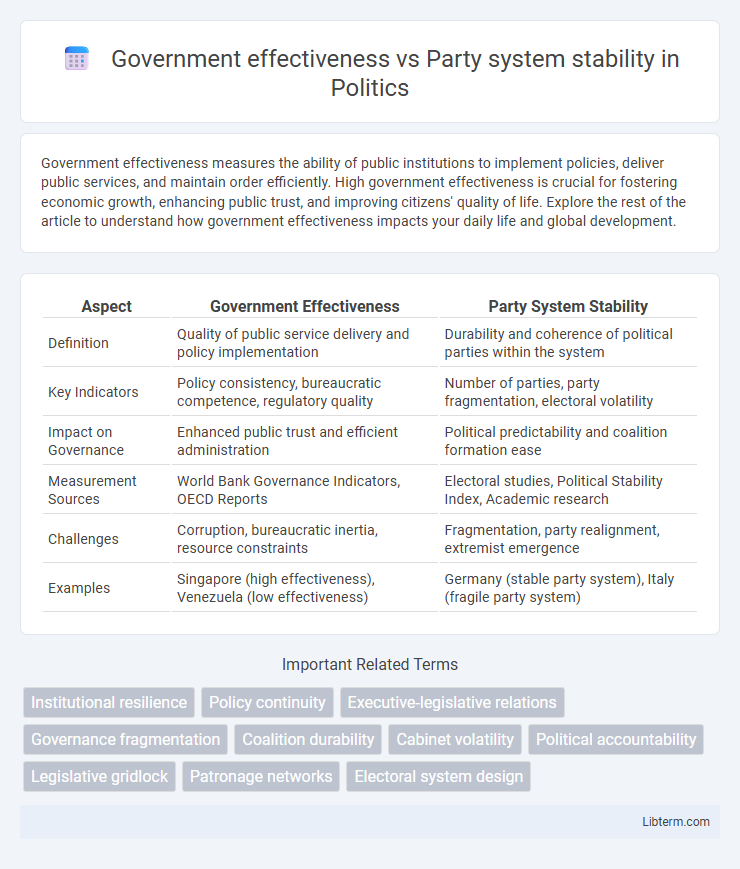
| Aspect | Government Effectiveness | Party System Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Quality of public service delivery and policy implementation | Durability and coherence of political parties within the system |
| Key Indicators | Policy consistency, bureaucratic competence, regulatory quality | Number of parties, party fragmentation, electoral volatility |
| Impact on Governance | Enhanced public trust and efficient administration | Political predictability and coalition formation ease |
| Measurement Sources | World Bank Governance Indicators, OECD Reports | Electoral studies, Political Stability Index, Academic research |
| Challenges | Corruption, bureaucratic inertia, resource constraints | Fragmentation, party realignment, extremist emergence |
| Examples | Singapore (high effectiveness), Venezuela (low effectiveness) | Germany (stable party system), Italy (fragile party system) |
Defining Government Effectiveness and Party System Stability
Government effectiveness measures the quality of public services, policy formulation, and implementation, reflecting the state's ability to meet citizens' needs efficiently. Party system stability refers to the durability and consistency of political parties in maintaining governance and public trust without frequent fragmentation or volatility. Both concepts are critical for political science, as effective governments rely on stable party systems to ensure coherent policy-making and societal order.
The Relationship Between Effective Governance and Political Parties
Effective governance enhances public trust, which strengthens party system stability by promoting consistent policy implementation and reducing political fragmentation. Stable party systems facilitate coordinated decision-making and institutional continuity, essential for sustained government effectiveness. The dynamic interplay between governance quality and party stability directly influences political legitimacy and democratic consolidation.
Historical Trends in Party System Stability
Historical trends in party system stability reveal that effective government institutions often contribute to prolonged party system endurance by fostering public trust and policy continuity. Empirical studies demonstrate that nations with high government effectiveness experience fewer abrupt party realignments and less electoral volatility, reinforcing stable partisan structures. Conversely, weak governance tends to coincide with fragmented party systems and frequent shifts in party dominance, undermining political stability and consistent policymaking.
Measuring Government Performance Across Party Systems
Measuring government performance across party systems requires analyzing indicators such as policy implementation efficiency, public service quality, and institutional responsiveness within both dominant and multiparty frameworks. Research shows that government effectiveness often correlates with the stability of the party system, as stable party coalitions enable consistent policymaking and long-term planning. Quantitative metrics like the Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGI) and the Varieties of Democracy (V-Dem) Project provide robust tools to assess these dynamics in comparative politics.
Multiparty Systems vs. Two-party Systems: Impact on Governance
Multiparty systems often face challenges in government effectiveness due to coalition complexities and policy compromises, whereas two-party systems typically benefit from clearer accountability and streamlined decision-making processes. The stability of party systems influences legislative efficiency, with multiparty frameworks risking fragmentation and frequent government changes, while two-party regimes tend to sustain more consistent governance and policy implementation. Empirical studies indicate that countries with two-party systems generally exhibit higher government effectiveness metrics, although multiparty systems can enhance representational diversity at the cost of institutional stability.
Case Studies: Countries with High Government Effectiveness
Countries with high government effectiveness, such as Singapore and Germany, demonstrate strong institutional frameworks that enhance public service delivery and policy implementation, contributing to political stability. In these cases, the presence of a stable and dominant party system, like the People's Action Party in Singapore, supports consistent governance and long-term planning. Empirical data highlights that effective governments with stable party systems tend to achieve higher socioeconomic development and public trust, illustrating the interdependence between administrative capacity and political continuity.
Party Fragmentation and Its Effect on Policy Implementation
Party fragmentation often weakens government effectiveness by diluting legislative consensus, leading to unstable coalitions and delayed policy implementation. High fragmentation in multiparty systems complicates decision-making processes, reducing the government's capacity to enforce coherent and timely policies. Empirical studies reveal that countries with lower party system stability frequently experience inconsistent policy outcomes and administrative inefficiencies due to fragmented parliamentary structures.
Electoral Systems and Their Influence on Party Stability
Electoral systems significantly impact party system stability by shaping the number and strength of political parties within a government. Proportional representation tends to foster multiparty systems, enhancing inclusivity but often complicating government effectiveness through coalition dynamics. Conversely, majoritarian systems typically produce fewer dominant parties, promoting clearer governance but risking underrepresentation of diverse political preferences.
Challenges to Government Effectiveness in Unstable Party Systems
Unstable party systems present significant challenges to government effectiveness by causing frequent changes in leadership and policy inconsistency, which hinder long-term planning and implementation. Fragmented or polarized parties lead to weak coalition governments, reducing the ability to pass legislation and execute policies efficiently. These dynamics often result in gridlock, eroding public trust and undermining institutional capacity.
Strategies to Enhance Both Government Effectiveness and Party Stability
Implementing transparent policy-making processes and strengthening institutional checks and balances enhances government effectiveness while fostering party system stability. Promoting inclusive political dialogue and internal party democracy mitigates factionalism, ensuring cohesive policy support and long-term governance continuity. Investing in capacity building for civil servants and party officials improves administrative competence and aligns party agendas with national development goals.
Government effectiveness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com