Proportional representation ensures that political parties gain seats in proportion to the number of votes they receive, creating a fairer and more inclusive electoral system. This method encourages diverse viewpoints and reduces the dominance of major parties, leading to a more representative government. Discover how proportional representation can impact your voting experience and the broader political landscape in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
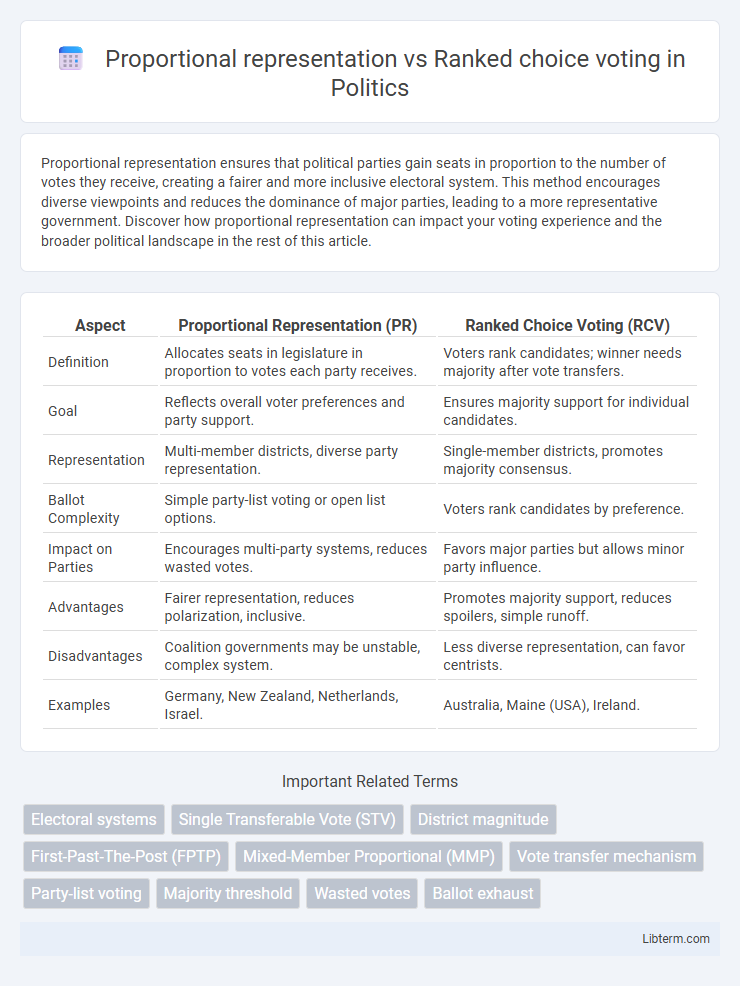
| Aspect | Proportional Representation (PR) | Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocates seats in legislature in proportion to votes each party receives. | Voters rank candidates; winner needs majority after vote transfers. |
| Goal | Reflects overall voter preferences and party support. | Ensures majority support for individual candidates. |
| Representation | Multi-member districts, diverse party representation. | Single-member districts, promotes majority consensus. |
| Ballot Complexity | Simple party-list voting or open list options. | Voters rank candidates by preference. |
| Impact on Parties | Encourages multi-party systems, reduces wasted votes. | Favors major parties but allows minor party influence. |
| Advantages | Fairer representation, reduces polarization, inclusive. | Promotes majority support, reduces spoilers, simple runoff. |
| Disadvantages | Coalition governments may be unstable, complex system. | Less diverse representation, can favor centrists. |
| Examples | Germany, New Zealand, Netherlands, Israel. | Australia, Maine (USA), Ireland. |
Introduction to Electoral Systems
Proportional representation allocates legislative seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring a more accurate reflection of voter preferences in multi-member districts. Ranked choice voting allows voters to rank candidates by preference, promoting majority support and reducing the spoiler effect in single-winner elections. Both systems aim to enhance democratic fairness but differ fundamentally in structure and electoral outcomes.
What is Proportional Representation?
Proportional representation is an electoral system designed to allocate seats in a legislature in proportion to the number of votes each party receives, ensuring fair and diverse political representation. Unlike winner-takes-all models, this system allows smaller parties to gain seats reflective of their actual support within the electorate. Proportional representation enhances voter engagement and leads to multi-party coalitions, promoting consensus-driven governance.
Understanding Ranked Choice Voting
Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) allows voters to rank candidates by preference, ensuring that the winning candidate has majority support through a series of vote redistributions. Unlike Proportional Representation, which allocates seats based on party vote share, RCV enhances individual voter choice and minimizes vote splitting within single-winner elections. This voting method increases election competitiveness and encourages more moderate candidates by requiring a majority rather than a simple plurality to secure victory.
Key Differences Between the Two Systems
Proportional representation allocates seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring diverse political representation in legislatures, while ranked choice voting allows voters to rank candidates by preference, determining a winner through successive rounds of vote counting until a candidate surpasses the majority threshold. Proportional representation promotes multiparty systems and coalition governments, whereas ranked choice voting encourages majority support for individual candidates and reduces the spoiler effect. The two systems differ fundamentally in their approach to vote counting, representation outcomes, and impact on electoral competitiveness.
Advantages of Proportional Representation
Proportional representation enhances electoral fairness by allocating seats in legislature based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring minority voices gain representation. This system fosters political diversity and reduces wasted votes, increasing voter turnout and engagement. It encourages coalition-building and policy compromise, leading to more stable and inclusive governance.
Benefits of Ranked Choice Voting
Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) enhances electoral fairness by allowing voters to rank candidates in order of preference, reducing the spoiler effect and promoting majority support for winners. It encourages positive campaigning and voter engagement by incentivizing candidates to appeal to a broader electorate, rather than just a base. RCV often results in more diverse representation and reduces the likelihood of costly and divisive runoff elections.
Common Criticisms of PR and RCV
Common criticisms of Proportional Representation (PR) include the potential for fragmented legislatures and coalition governments that may lead to political instability and slow decision-making. Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) often faces criticism for its complexity, which can confuse voters and complicate ballot counting processes. Both systems also spark debate over whether they truly enhance voter representation or simply shift power dynamics without addressing underlying electoral concerns.
Global Examples and Case Studies
Proportional representation (PR) systems, utilized in countries like Germany, Sweden, and New Zealand, ensure legislative seats reflect each party's share of the vote, promoting multi-party representation and coalition governments. Ranked choice voting (RCV), implemented in places such as Australia (Instant-runoff Voting) and Maine in the United States, allows voters to rank candidates by preference, enhancing majority support and reducing the spoiler effect in single-member districts. Comparative case studies reveal that PR tends to increase party diversity and voter turnout, while RCV improves electoral competitiveness and voter satisfaction in candidate-centered races.
Impact on Voter Representation and Fairness
Proportional representation enhances voter representation by allocating seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring minority groups gain fair legislative presence. Ranked choice voting improves fairness by allowing voters to rank candidates in order of preference, reducing vote splitting and increasing the likelihood of majority support for elected officials. Both systems aim to rectify disproportional outcomes but differ in approach: proportional representation focuses on party-based fairness, while ranked choice voting emphasizes candidate preference and consensus.
Choosing the Right System for Your Community
Choosing the right voting system for your community depends on its size, diversity, and goals for fair representation. Proportional representation ensures that political parties gain seats in proportion to the total votes they receive, promoting multi-party inclusivity. Ranked choice voting allows voters to rank candidates by preference, often leading to majority support for elected officials and reducing the risk of vote splitting in single-winner districts.
Proportional representation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com