Parliamentary privilege grants legislators legal immunities enabling free and open debate without fear of outside interference or legal action, ensuring the effective functioning of democratic institutions. These privileges protect members from being sued or prosecuted for statements made within parliamentary proceedings, safeguarding the legislative process from external pressures. Explore the rest of the article to understand how parliamentary privilege impacts your rights and the balance of power within government.
Table of Comparison
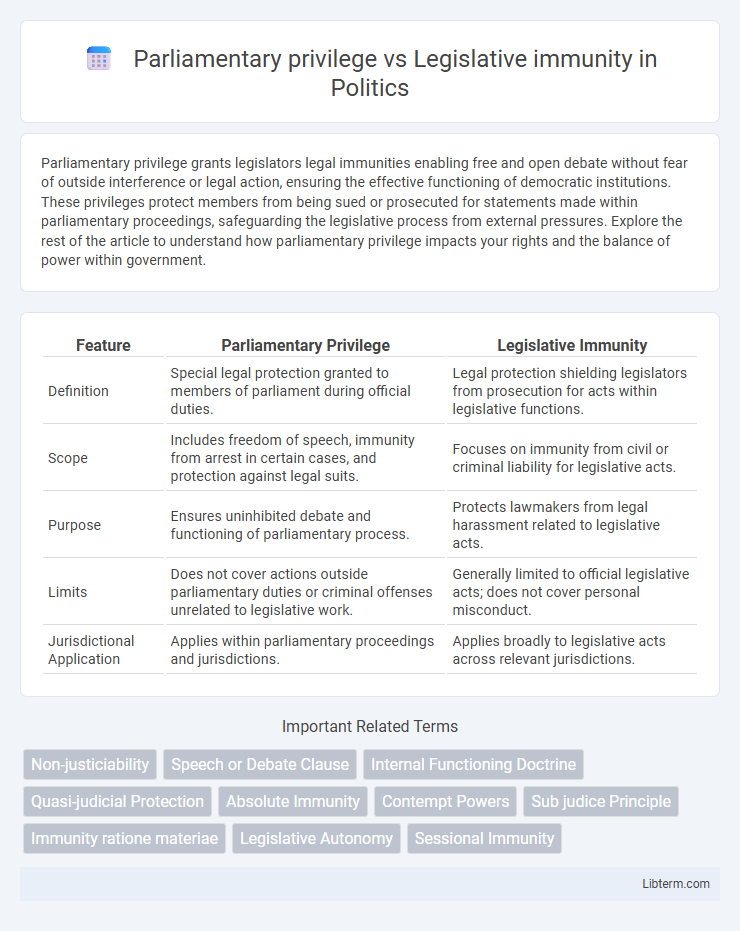
| Feature | Parliamentary Privilege | Legislative Immunity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Special legal protection granted to members of parliament during official duties. | Legal protection shielding legislators from prosecution for acts within legislative functions. |
| Scope | Includes freedom of speech, immunity from arrest in certain cases, and protection against legal suits. | Focuses on immunity from civil or criminal liability for legislative acts. |
| Purpose | Ensures uninhibited debate and functioning of parliamentary process. | Protects lawmakers from legal harassment related to legislative acts. |
| Limits | Does not cover actions outside parliamentary duties or criminal offenses unrelated to legislative work. | Generally limited to official legislative acts; does not cover personal misconduct. |
| Jurisdictional Application | Applies within parliamentary proceedings and jurisdictions. | Applies broadly to legislative acts across relevant jurisdictions. |
Introduction to Parliamentary Privilege and Legislative Immunity
Parliamentary privilege encompasses the legal immunities and rights granted to members of Parliament to ensure independent and effective legislative functions, including freedom of speech within parliamentary proceedings and protection from civil or criminal liability for actions performed as part of their duties. Legislative immunity specifically refers to the protection legislators have from prosecution or lawsuits related to official legislative acts, safeguarding the legislative process from external judicial interference. These doctrines collectively fortify the separation of powers by enabling lawmakers to perform their roles without fear of legal repercussions stemming from their legislative activities.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Parliamentary privilege originated in medieval England as a mechanism to protect legislators from monarchic interference, ensuring free debate and uninhibited lawmaking. Legislative immunity evolved from this foundation, expanding protections to legislators for acts performed within their official duties to maintain separation of powers and safeguard democratic processes. Historical developments reflect a transition from strict privileges tied to parliamentary functions towards broader immunities that balance accountability and legislative independence.
Defining Parliamentary Privilege
Parliamentary privilege refers to the rights and immunities granted to members of a legislative body, enabling them to perform their functions without interference or legal repercussions. This privilege protects actions such as speeches, debates, and votes within the parliament from being questioned or prosecuted outside the legislative context. Legislative immunity, often considered a subset of parliamentary privilege, specifically shields legislators from lawsuits or prosecution for actions directly related to their legislative duties.
Understanding Legislative Immunity
Legislative immunity protects lawmakers from legal action related to their official legislative activities, ensuring they can perform duties without fear of harassment or prosecution. This immunity covers speeches, debates, votes, and other legislative acts, safeguarding the independence and integrity of the legislative process. Unlike parliamentary privilege, which includes broader privileges like access to parliamentary premises and freedom from arrest in certain circumstances, legislative immunity specifically shields legislators from civil or criminal liability arising from their legislative functions.
Key Similarities Between Parliamentary Privilege and Legislative Immunity
Parliamentary privilege and legislative immunity both provide legal protections to legislators, ensuring freedom of speech and actions within their official duties without fear of external legal consequences. Both concepts safeguard the legislative process by allowing members to perform their roles independently, free from interference by the judiciary or executive branches. These protections enable effective lawmaking by preventing prosecution, civil suits, or arrest for acts done in the course of parliamentary functions.
Distinct Differences and Scope
Parliamentary privilege grants members of parliament specific legal protections to perform their legislative functions without external interference, including freedom of speech within debates and immunity from arrest in civil matters during sessions. Legislative immunity, often broader and applicable to various legislators, shields lawmakers from legal actions related to their official acts, extending beyond speech protections to cover actions directly connected to legislative duties. The distinct difference lies in parliamentary privilege's focus on procedural rights within parliamentary proceedings, whereas legislative immunity encompasses protection for substantive actions taken as part of legislative responsibilities.
Legal Frameworks and Jurisdictions
Parliamentary privilege grants legislators specific legal immunities within parliamentary proceedings, rooted in common law and codified in statutes like the UK's Parliamentary Privileges Act 1842 and the US Speech or Debate Clause (Article I, Section 6). Legislative immunity, often broader, protects legislators from prosecution or civil suits for actions within their official capacity, as defined by constitutional provisions such as the US Constitution or statutory frameworks in jurisdictions like Canada and Australia. Jurisdictional variations influence the scope and application of both privileges, with civil law countries typically adopting more limited immunities compared to common law systems emphasizing legislative independence and accountability.
Notable Cases and Precedents
Parliamentary privilege and legislative immunity have been defined and refined through key cases such as *Bradlaugh v. Gosset* (1884), affirming freedom of speech within Parliament, and *Kilbourn v. Thompson* (1881), which limited legislative immunity from judicial scrutiny. In *R. v. Chaytor* (2010), the UK Supreme Court clarified boundaries by ruling that parliamentary privilege does not protect members from criminal prosecution for expenses fraud. The U.S. Supreme Court case *Gravel v. United States* (1972) also significantly shaped legislative immunity by protecting legislators' speech during official proceedings from judicial intervention.
Contemporary Challenges and Criticisms
Parliamentary privilege and legislative immunity face contemporary challenges related to transparency, accountability, and potential abuse of power. Critics argue that these protections can be exploited to shield legislators from legal scrutiny, undermining public trust and democratic oversight. Ongoing debates emphasize the need to balance safeguarding legislative functions with ensuring mechanisms to prevent misuse and uphold rule of law.
Conclusion: Safeguarding Democratic Functions
Parliamentary privilege and legislative immunity both play critical roles in safeguarding democratic functions by protecting legislators from legal actions that could hinder their duties. Parliamentary privilege specifically grants members freedom of speech within parliamentary proceedings, ensuring uninhibited debate and accountability. Legislative immunity extends broader protections from prosecution for acts performed in official capacity, collectively maintaining the integrity and independence of the legislative process.
Parliamentary privilege Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com