A closed primary is an election process where only registered party members can vote to choose their party's candidate. This system helps maintain party integrity by ensuring that only loyal members influence candidate selection. Learn how closed primaries impact your voting rights and the democratic process in the full article.
Table of Comparison
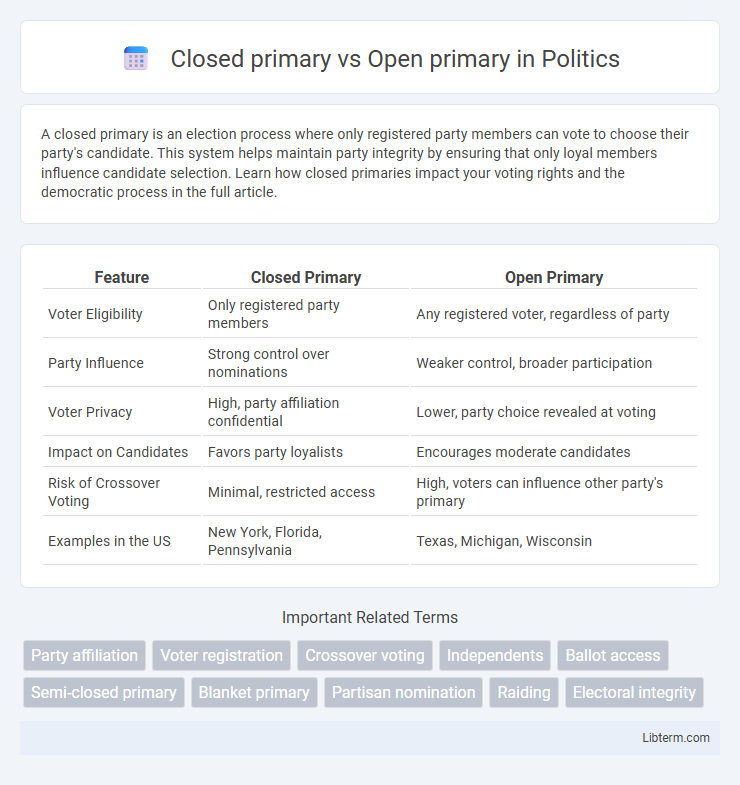
| Feature | Closed Primary | Open Primary |
|---|---|---|
| Voter Eligibility | Only registered party members | Any registered voter, regardless of party |
| Party Influence | Strong control over nominations | Weaker control, broader participation |
| Voter Privacy | High, party affiliation confidential | Lower, party choice revealed at voting |
| Impact on Candidates | Favors party loyalists | Encourages moderate candidates |
| Risk of Crossover Voting | Minimal, restricted access | High, voters can influence other party's primary |
| Examples in the US | New York, Florida, Pennsylvania | Texas, Michigan, Wisconsin |
Understanding Primary Elections: An Overview
Closed primaries restrict voting to registered party members, ensuring only loyal party affiliates influence candidate selection and maintaining stronger party cohesion. Open primaries allow any registered voter to participate regardless of party affiliation, promoting broader voter engagement and potentially more moderate candidate choices. Understanding these differences is crucial for analyzing how states balance party control with inclusive democratic participation in primary elections.
Defining Closed Primaries
Closed primaries restrict voting rights exclusively to registered party members, ensuring that only individuals aligned with a political party can participate in selecting that party's candidates. This system enhances party loyalty and prevents members of opposing parties from influencing candidate nominations. States like New York and Florida implement closed primaries to maintain party integrity and limit crossover voting.
Defining Open Primaries
Open primaries allow voters to participate in any party's primary regardless of their registered affiliation, enabling broader voter engagement and flexibility. Unlike closed primaries, which restrict voting to registered party members only, open primaries can increase turnout by giving independents and members of other parties the chance to influence candidate selection. This system supports a more inclusive electoral process by allowing wider access to primary elections.
Key Differences Between Closed and Open Primaries
Closed primaries restrict voting to registered party members, ensuring only affiliates influence candidate selection, while open primaries allow any registered voter to participate regardless of party affiliation, increasing voter inclusivity. Closed primaries enhance party control and reduce crossover voting, which can skew results, whereas open primaries encourage broader voter participation and candidate appeal across party lines. The key differences lie in voter eligibility rules, impact on party strategy, and influence on electoral outcomes.
Advantages of Closed Primaries
Closed primaries enhance party unity by ensuring that only registered party members participate in candidate selection, reducing the influence of opposing party voters and independents. This system increases the likelihood of candidates representing the core values and priorities of the party base, leading to stronger, more cohesive platforms. Voter identification in closed primaries also minimizes strategic voting and crossover interference, maintaining the integrity of the nomination process.
Advantages of Open Primaries
Open primaries increase voter participation by allowing all registered voters, regardless of party affiliation, to vote in any party's primary. They promote broader candidate appeal and encourage moderation, as candidates must address a wider electorate beyond party loyalists. Open primaries also enhance democratic inclusivity and reduce partisan polarization by enabling independent and crossover voting.
Criticisms of Closed Primaries
Closed primaries face criticism for limiting voter participation to registered party members, excluding independents and potentially reducing overall voter turnout. This system can reinforce party polarization by preventing crossover voting and discouraging moderate candidates from emerging. Critics argue that closed primaries undermine democratic inclusivity and restrict broader political engagement.
Criticisms of Open Primaries
Open primaries face criticism for allowing voters unaffiliated with a party to influence candidate selection, potentially diluting party ideology and cohesion. This system can encourage strategic voting, where opponents may cast ballots to weaken a rival's chances, undermining genuine electoral preferences. Consequently, open primaries may reduce party accountability and shift candidate platforms toward more centrist positions to attract a broader electorate.
Impact on Voter Participation and Party Influence
Closed primaries restrict voting to registered party members, often leading to lower voter participation as independents and non-affiliated voters are excluded. This system increases party influence by ensuring candidates align closely with party platforms and member preferences. In contrast, open primaries allow all registered voters to participate, boosting turnout but potentially diluting party control over candidate selection and encouraging more moderate nominees.
Which Primary System is More Democratic?
Closed primaries limit voting participation to registered party members, promoting party cohesion and preventing cross-party interference, but they exclude independent voters and decrease overall electoral inclusivity. Open primaries allow any registered voter to participate regardless of party affiliation, fostering broader democratic engagement and reflecting a wider spectrum of voter preferences. The open primary system is generally considered more democratic because it enhances voter participation and reduces partisan polarization by empowering independent and unaffiliated voters.
Closed primary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com