Collaborative politics emphasizes teamwork and consensus-building among diverse stakeholders to address complex societal challenges effectively. This approach fosters mutual understanding, reduces conflicts, and promotes sustainable, inclusive decision-making processes. Explore the rest of the article to discover how collaborative politics can transform governance and empower your role in shaping public policy.
Table of Comparison
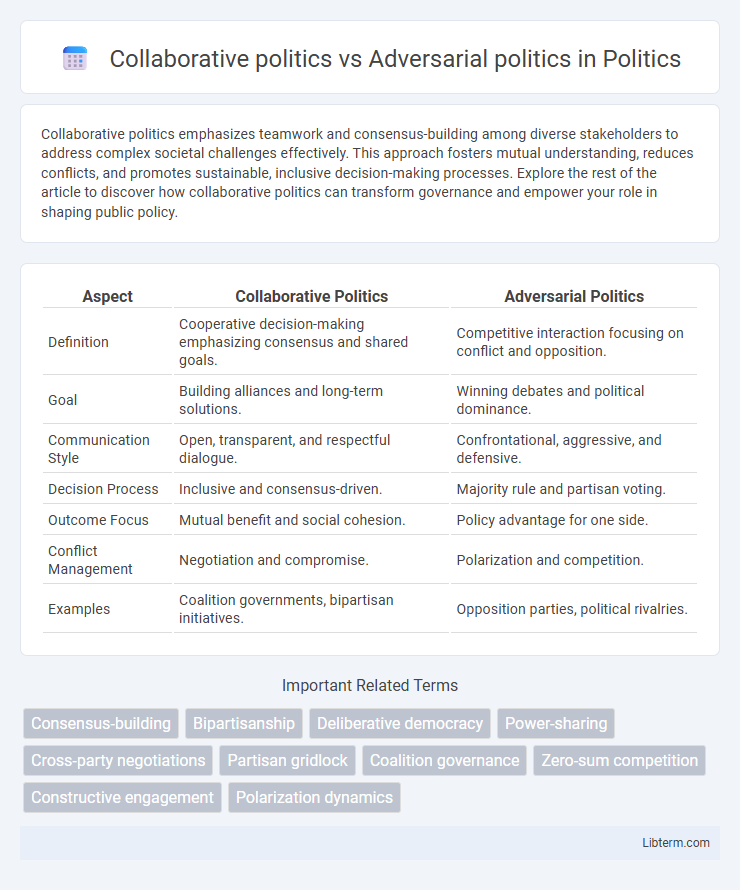
| Aspect | Collaborative Politics | Adversarial Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooperative decision-making emphasizing consensus and shared goals. | Competitive interaction focusing on conflict and opposition. |
| Goal | Building alliances and long-term solutions. | Winning debates and political dominance. |
| Communication Style | Open, transparent, and respectful dialogue. | Confrontational, aggressive, and defensive. |
| Decision Process | Inclusive and consensus-driven. | Majority rule and partisan voting. |
| Outcome Focus | Mutual benefit and social cohesion. | Policy advantage for one side. |
| Conflict Management | Negotiation and compromise. | Polarization and competition. |
| Examples | Coalition governments, bipartisan initiatives. | Opposition parties, political rivalries. |
Understanding Collaborative Politics
Collaborative politics emphasizes cooperation, dialogue, and consensus-building among stakeholders to achieve shared goals, contrasting sharply with adversarial politics that often rely on conflict and competition. This approach fosters inclusivity and mutual respect, enabling more sustainable and effective policy outcomes by integrating diverse perspectives. Studies show that collaborative politics can reduce polarization and enhance problem-solving in complex governance environments.
Defining Adversarial Politics
Adversarial politics is characterized by a competitive, zero-sum approach where opposing parties prioritize defeating their rivals rather than seeking common ground. This model emphasizes conflict, confrontation, and polarization, often resulting in legislative gridlock and reduced cooperation. Unlike collaborative politics, adversarial politics discourages compromise and fosters division within political systems.
Historical Contexts of Political Approaches
Collaborative politics emerged prominently during the Progressive Era in the early 20th century, emphasizing bipartisan cooperation to address complex social issues through negotiation and consensus-building. In contrast, adversarial politics has roots in the foundational years of American democracy, exemplified by the Federalist and Anti-Federalist debates, where opposing parties fiercely contested ideological visions to shape government structures. Historical contexts reveal that collaborative approaches often surface during periods demanding reform and unity, while adversarial politics intensify in times of ideological polarization and power struggles.
Key Principles of Collaborative Governance
Collaborative politics emphasizes shared decision-making, mutual trust, and inclusive stakeholder engagement as key principles of collaborative governance, fostering consensus-building and long-term partnerships. It prioritizes transparency, accountability, and collective problem-solving to address complex public issues effectively, contrasting with adversarial politics that often rely on competition and conflict. This approach enhances policy durability and public trust by integrating diverse perspectives and promoting cooperative institution-building.
Core Features of Adversarial Political Systems
Adversarial political systems are characterized by a clear division between competing parties that seek to gain power through opposition and conflict rather than cooperation. These systems emphasize competition, winner-takes-all outcomes, and often feature intense partisan rivalry, limiting consensus-building efforts. The core features include a zero-sum approach to policy-making, adversarial debates, and a focus on electoral victories rather than collaborative problem-solving.
Impacts on Policy-Making and Implementation
Collaborative politics fosters consensus-building, resulting in more inclusive and sustainable policy-making by encouraging stakeholder participation and reducing partisan gridlock. Adversarial politics often leads to polarization and slower policy implementation, as conflicting interests and zero-sum approaches create legislative deadlock and hinder effective governance. The efficiency of policy outcomes in collaborative systems typically surpasses adversarial models due to enhanced communication and mutual compromise among policymakers.
Public Perception and Trust in Governance
Collaborative politics fosters higher public trust in governance by emphasizing transparency, shared decision-making, and consensus-building, which enhances citizens' perception of inclusivity and accountability. In contrast, adversarial politics often leads to polarization and skepticism, reducing public confidence due to frequent conflicts and perceived partisanship. Empirical studies indicate that governments practicing collaborative approaches report increased citizen engagement and perceived legitimacy compared to those dominated by adversarial tactics.
Case Studies: Collaborative vs Adversarial Outcomes
Case studies highlight how collaborative politics foster consensus-building and effective policy implementation, as seen in the Nordic countries' welfare reforms that emphasize stakeholder engagement and broad agreement. In contrast, adversarial politics often result in gridlock and polarized outcomes, exemplified by the U.S. legislative stalemates on healthcare reform, where partisan conflicts impeded progress. Empirical evidence from these case studies indicates that collaborative approaches yield more sustainable solutions and higher public trust compared to the frequent deadlocks and volatility associated with adversarial systems.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Collaborative politics often faces challenges related to slower decision-making processes and potential dilution of core values due to the need for compromise among diverse stakeholders. Adversarial politics is criticized for fostering polarization, obstructing consensus-building, and prioritizing party interests over effective governance. Both approaches struggle to balance efficiency and inclusivity, impacting public trust and policy outcomes.
Pathways Toward Effective Political Collaboration
Pathways toward effective political collaboration emphasize open dialogue, mutual respect, and shared goals to bridge divides between differing parties. Establishing trust through transparent communication and inclusive decision-making processes enhances policy consensus and implementation success. Leveraging collaborative frameworks and bipartisan committees fosters durable solutions that address diverse stakeholder interests in both local and national governance contexts.
Collaborative politics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com