Party voting occurs when members of a political party consistently vote in alignment with their party's platform rather than personal beliefs or constituent interests. This behavior strengthens party cohesion and influences legislative outcomes, often impacting policy decisions at various government levels. Explore the full article to understand how party voting shapes political dynamics and what it means for your representation.
Table of Comparison
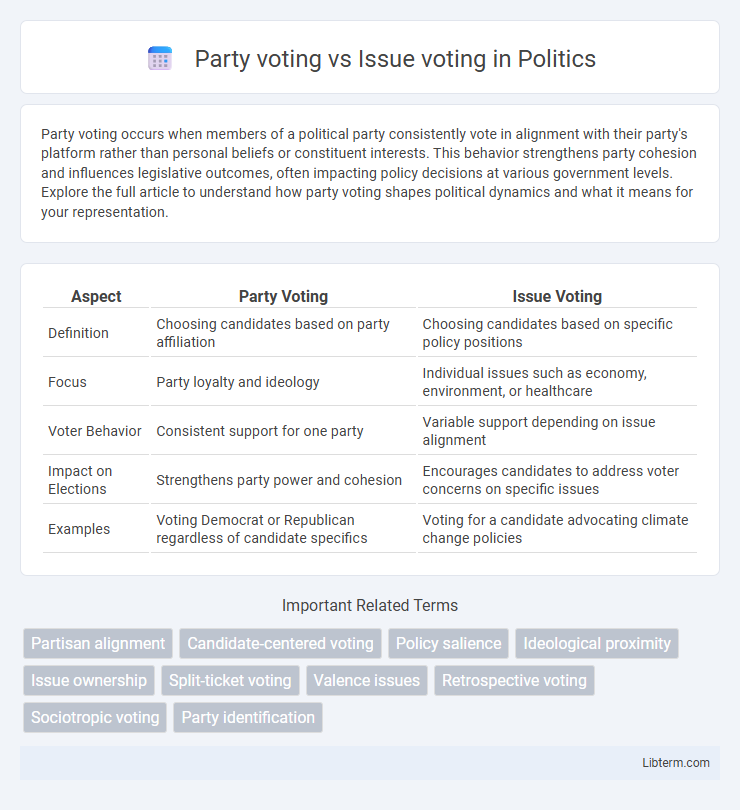
| Aspect | Party Voting | Issue Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Choosing candidates based on party affiliation | Choosing candidates based on specific policy positions |
| Focus | Party loyalty and ideology | Individual issues such as economy, environment, or healthcare |
| Voter Behavior | Consistent support for one party | Variable support depending on issue alignment |
| Impact on Elections | Strengthens party power and cohesion | Encourages candidates to address voter concerns on specific issues |
| Examples | Voting Democrat or Republican regardless of candidate specifics | Voting for a candidate advocating climate change policies |
Understanding Party Voting: Definition and Characteristics
Party voting refers to the tendency of voters to consistently support candidates from a specific political party based on party identification rather than individual issues or candidate attributes. Characteristics of party voting include loyalty to party platforms, alignment with party ideology, and reliance on party cues to simplify decision-making. This form of voting often reinforces partisan loyalty and contributes to electoral stability by maintaining consistent support for established parties.
What is Issue Voting? Key Features and Examples
Issue voting refers to voters making electoral decisions based on specific policy issues rather than party loyalty, emphasizing informed choices tied to individual stances on topics like healthcare, immigration, or climate change. Key features include voters' evaluation of candidates' positions on salient issues, prioritization of policy alignment over party affiliation, and responsiveness to current socio-political debates. Examples of issue voting include environmental advocates supporting candidates with strong climate action plans and economic conservatives favoring candidates who promote tax cuts or deregulation.
Historical Trends: Party Voting vs Issue Voting
Historical trends indicate a gradual shift from party voting, where voters align consistently with a political party, toward issue voting, where decisions are based on specific policies or candidate positions. Throughout the 20th century, strong party loyalty dominated electoral behavior in the United States, but increasing political polarization and information availability have enhanced voter focus on issues such as the economy, healthcare, and civil rights. Data from recent elections show a rising number of independents and split-ticket voters, reflecting this transition toward issue-driven electoral choices.
Factors Influencing Party Voting Behavior
Party voting behavior is primarily influenced by party identification, ideological alignment, and long-standing loyalty, which often serve as strong predictors of electoral choices. Sociodemographic factors such as age, race, education, and socioeconomic status further shape party affiliation, reinforcing voter commitment through social and cultural group membership. Campaign strategies and media framing also affect party voting by amplifying partisan cues and emotional resonance, strengthening the psychological attachment to a political party.
Drivers of Issue-Based Voting Decisions
Issue-based voting decisions are primarily driven by voters' personal values, policy preferences, and the perceived impact of specific issues on their lives, such as healthcare, the economy, or climate change. Cognitive factors such as political awareness and information processing also play a crucial role, enabling voters to evaluate candidates based on issue competence rather than party loyalty. Emotional responses and social influences further shape issue voting by reinforcing or challenging individual beliefs through community discourse and media exposure.
Impact of Party Identification on Election Outcomes
Party identification significantly influences election outcomes by shaping voter loyalty and reducing electoral volatility, often guiding choices even when voters disagree with specific issues. This psychological attachment to a party creates a heuristic shortcut, simplifying complex political decisions and increasing predictability in election results. The strength of party identification can overshadow issue voting, leading voters to prioritize party allegiance over policy preferences during candidate selection.
The Role of Media in Shaping Voting Preferences
Media outlets significantly influence party voting by consistently framing political parties through partisan biases and agenda-setting techniques, which reinforce voters' loyalty to established party lines. Issue voting is shaped as media selectively highlight specific policy debates and emphasize candidate stances, providing voters with targeted information to make issue-based decisions. The growing presence of social media platforms amplifies echo chambers, intensifying partisan polarization and altering the impact of both party and issue voting patterns.
Case Studies: Party Voting vs Issue Voting in Recent Elections
Recent elections in the United States and Germany highlight the distinctions between party voting and issue voting. In the 2020 U.S. presidential election, voter alignment largely followed party identification, evidenced by strong partisan turnout, whereas Germany's 2021 federal election displayed greater issue voting as environmental policies influenced shifts toward the Green Party. These case studies demonstrate how contextual factors like political polarization and salient policy issues affect the prevalence of party versus issue-based electoral decisions.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Voting Approach
Party voting offers the advantage of simplifying decision-making by aligning with established party platforms, ensuring consistency and predictability for voters, but it may limit individual policy consideration and reinforce partisan polarization. Issue voting allows voters to focus on specific policies or candidate positions, promoting informed choices tailored to personal priorities, although it requires greater political knowledge and may lead to fragmented electoral outcomes. Both approaches impact democratic engagement differently, with party voting fostering collective identity and issue voting encouraging nuanced evaluation of complex topics.
The Future of Voting Patterns: Emerging Trends and Predictions
Emerging trends in voting patterns indicate a growing shift from traditional party voting to more nuanced issue voting, driven by increased access to information and social media influence. Voters increasingly prioritize specific policy issues such as climate change, healthcare, and economic inequality over party loyalty, reshaping electoral dynamics and candidate strategies. Predictive models suggest this shift will lead to more fragmented political landscapes and the rise of independent or issue-based political movements in future elections.
Party voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com