National unity government fosters collaboration among diverse political parties to address pressing national challenges and promote stability. This coalition often emerges during crises, ensuring collective decision-making and shared responsibility for the country's welfare. Discover how such governments impact your nation's political landscape and what that means for your future.
Table of Comparison
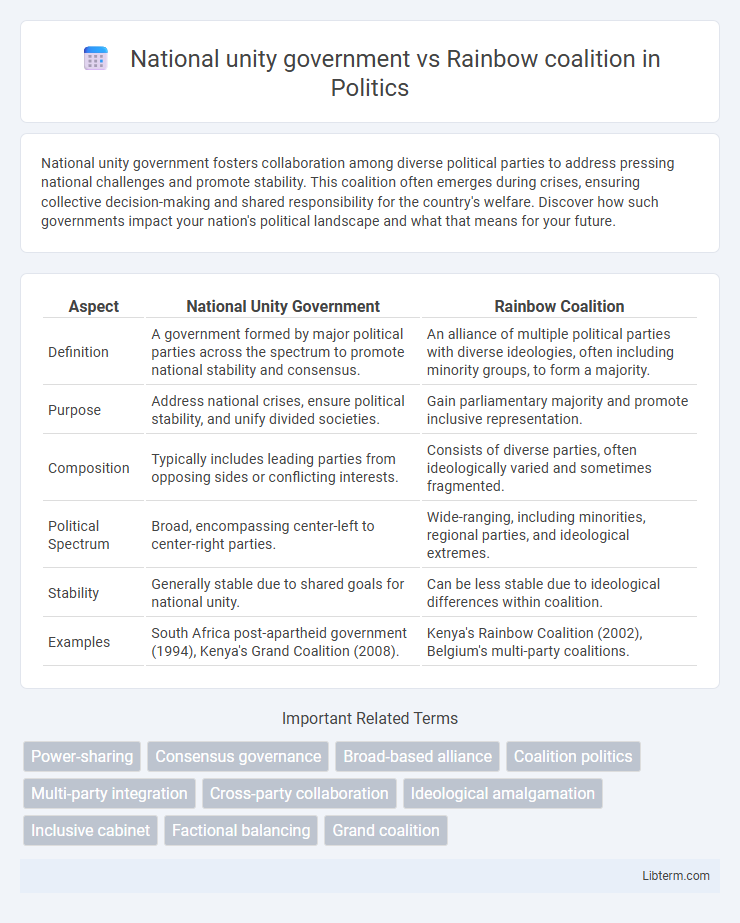
| Aspect | National Unity Government | Rainbow Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A government formed by major political parties across the spectrum to promote national stability and consensus. | An alliance of multiple political parties with diverse ideologies, often including minority groups, to form a majority. |
| Purpose | Address national crises, ensure political stability, and unify divided societies. | Gain parliamentary majority and promote inclusive representation. |
| Composition | Typically includes leading parties from opposing sides or conflicting interests. | Consists of diverse parties, often ideologically varied and sometimes fragmented. |
| Political Spectrum | Broad, encompassing center-left to center-right parties. | Wide-ranging, including minorities, regional parties, and ideological extremes. |
| Stability | Generally stable due to shared goals for national unity. | Can be less stable due to ideological differences within coalition. |
| Examples | South Africa post-apartheid government (1994), Kenya's Grand Coalition (2008). | Kenya's Rainbow Coalition (2002), Belgium's multi-party coalitions. |
Defining National Unity Government
A National Unity Government is a broad coalition formed by major political parties or factions to promote stability and address national crises, often including representatives from across the political spectrum. Unlike a Rainbow Coalition, which unites diverse groups based primarily on social or ethnic diversity, a National Unity Government prioritizes political consensus and shared governance to overcome exceptional challenges. Its defining feature is collaborative decision-making aimed at national cohesion rather than partisan advantage.
Understanding the Rainbow Coalition Model
The Rainbow Coalition model emphasizes inclusive power-sharing among diverse political parties, fostering cooperation across ethnic and ideological lines to promote national stability. Unlike the National Unity Government, which typically involves major parties forming a single ruling entity during crises, the Rainbow Coalition thrives on structured multi-party collaboration with agreed policy platforms. This model enhances democratic representation and reduces ethnic polarization by institutionalizing consensus-building mechanisms within a coalition framework.
Historical Context and Origins
The National Unity Government emerged in Kenya in 2008 following the disputed 2007 presidential election, aiming to resolve ethnic tensions and political violence through power-sharing between President Mwai Kibaki and opposition leader Raila Odinga. The Rainbow Coalition, formed in 2002, united diverse political parties under Odinga's leadership to successfully end the Kenya African National Union's long-standing dominance, marking a pivotal shift toward multiparty democracy. Both formations were responses to Kenya's history of ethnic-based political rivalry and electoral conflict, reflecting efforts to promote inclusivity and stability in governance.
Key Objectives and Motivations
National unity governments aim to include major political parties to foster stability and nationwide consensus during crises or transitional periods, prioritizing cooperation and conflict resolution. Rainbow coalitions focus on uniting diverse political groups, often across ideological lines, to promote inclusive representation and address broad social, economic, and ethnic issues. Both structures emphasize collective governance but differ in scope, with national unity governments targeting crisis management and rainbow coalitions emphasizing diversity and comprehensive policy agendas.
Power Sharing Mechanisms
National unity governments typically involve formal power-sharing arrangements where major political parties, including opposition groups, share executive responsibilities to ensure inclusive governance and stability. Rainbow coalitions are often characterized by diverse political and ethnic groups forming alliances with negotiated distributions of ministerial and legislative roles to balance competing interests. Both mechanisms emphasize proportional representation and consensus-building to prevent dominance by a single party and promote political harmony.
Inclusivity and Representation
National unity governments emphasize broad inclusivity by bringing together major political parties and diverse ethnic groups to ensure balanced representation in decision-making processes, promoting stability in divided societies. Rainbow coalitions, often composed of multiple smaller parties and marginalized groups, focus on amplifying minority voices and fostering equal participation across various social and ethnic identities. Both frameworks aim to enhance political inclusivity, but national unity governments prioritize cross-party collaboration among dominant factions, whereas rainbow coalitions stress diversity and representation from a wider array of constituencies.
Political Stability and Governance
National unity governments enhance political stability by incorporating diverse political factions to foster cooperation and reduce conflict during crises. Rainbow coalitions, often comprising multiple smaller parties with varying ideologies, can face challenges in maintaining cohesive governance due to ideological differences. Effective governance under a national unity government typically benefits from unified policy agendas, whereas rainbow coalitions may require continuous negotiation to balance competing interests.
Challenges and Criticisms
National unity governments often face challenges related to ideological conflicts and power-sharing disputes among diverse parties, leading to policy gridlock and inefficiency. Rainbow coalitions encounter criticisms for lack of cohesion and stability due to their inherently diverse memberships, which can result in fragile alliances and frequent disagreements. Both models struggle with maintaining long-term consensus, impacting their ability to deliver consistent governance outcomes.
Notable Global Examples
The National Unity Government of Myanmar, formed in response to the 2021 military coup, represents a coalition of ousted lawmakers and ethnic groups aiming for democratic restoration and international recognition. Kenya's Rainbow Coalition, which led the 2002 general elections, united diverse political parties to end decades of single-party dominance, showcasing the power of multi-ethnic alliances in stabilizing governance. Both examples highlight how inclusive political coalitions can mobilize national support and challenge entrenched power structures in different global contexts.
Future Prospects and Implications
National unity governments often provide stability during crises by uniting major political parties, which can enhance policy continuity and bolster investor confidence, but they risk diluting opposition voices and slowing reform. Rainbow coalitions, composed of diverse parties with varied agendas, promote inclusive governance and broader representation, yet face challenges in maintaining cohesion and consensus. The future prospects of national unity governments hinge on their ability to balance unity with democratic vibrancy, while rainbow coalitions must strengthen institutional frameworks to ensure effective decision-making and sustainable governance.
National unity government Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com