A grand coalition unites major political parties to form a majority government, often during times of crisis or political deadlock. This alliance aims to stabilize governance and implement broad policy agendas by combining diverse perspectives. Explore the rest of the article to understand how grand coalitions impact your country's political landscape.
Table of Comparison
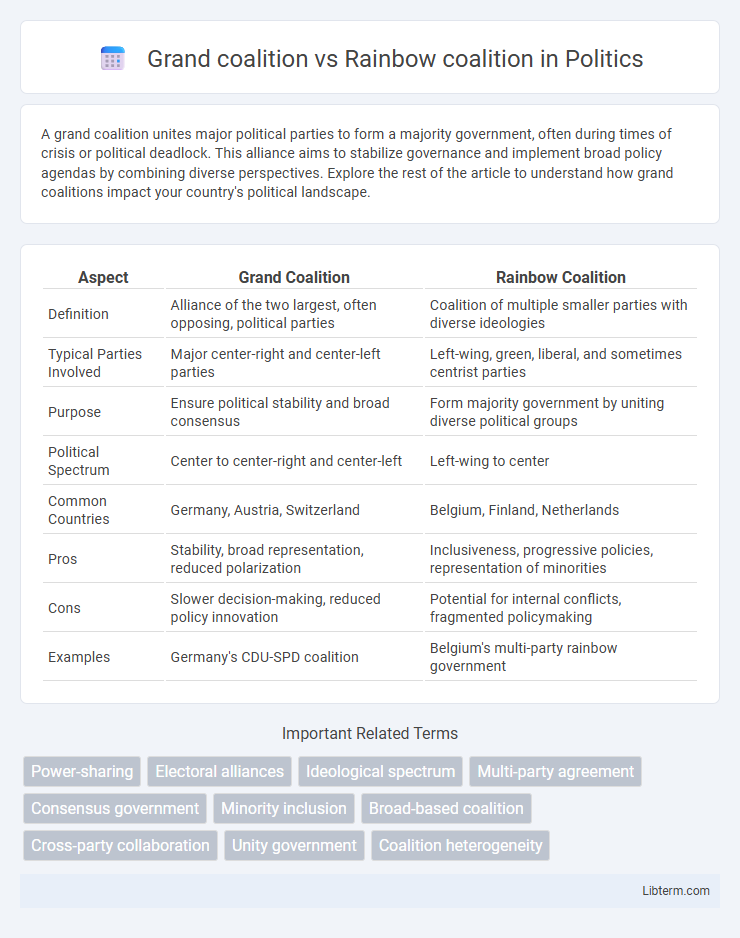
| Aspect | Grand Coalition | Rainbow Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alliance of the two largest, often opposing, political parties | Coalition of multiple smaller parties with diverse ideologies |
| Typical Parties Involved | Major center-right and center-left parties | Left-wing, green, liberal, and sometimes centrist parties |
| Purpose | Ensure political stability and broad consensus | Form majority government by uniting diverse political groups |
| Political Spectrum | Center to center-right and center-left | Left-wing to center |
| Common Countries | Germany, Austria, Switzerland | Belgium, Finland, Netherlands |
| Pros | Stability, broad representation, reduced polarization | Inclusiveness, progressive policies, representation of minorities |
| Cons | Slower decision-making, reduced policy innovation | Potential for internal conflicts, fragmented policymaking |
| Examples | Germany's CDU-SPD coalition | Belgium's multi-party rainbow government |
Definition of Grand Coalition
A Grand coalition refers to a political alliance formed by the two or more major parties, typically encompassing the largest political groups in a legislature to establish a stable government. This coalition often includes parties with differing ideologies that agree to cooperate for broad national interests, especially during times of crisis or political deadlock. In contrast, a Rainbow coalition brings together multiple smaller parties with diverse political backgrounds to create a more ideologically varied governing body.
Definition of Rainbow Coalition
The Rainbow coalition is a political alliance of diverse groups representing various ethnic, social, and ideological backgrounds united by common goals, typically emphasizing progressive policies and social justice. Unlike a Grand coalition, which consists of major parties across the political spectrum, the Rainbow coalition prioritizes inclusivity and minority representation. This coalition seeks to amplify marginalized voices by fostering cooperation among different communities and activists.
Historical Context of Both Coalitions
The Grand coalition, typically formed by major political parties from opposing sides, emerged prominently in post-World War II Germany to stabilize governance and prevent extremist resurgence. In contrast, the Rainbow coalition, notably used in the United States during the late 20th century, brought together diverse political groups and minorities aiming to challenge dominant party structures and promote social inclusion. Both coalitions reflect strategic responses to historical political fragmentation and social challenges within their respective countries.
Key Players in Grand Coalitions
Key players in grand coalitions typically include major political parties from opposing spectrums, such as the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and the Social Democratic Party (SPD) in Germany, who collaborate to form a stable government. These parties share policy-making responsibilities to address national challenges by combining their parliamentary majorities. The collaboration of dominant parties in a grand coalition contrasts with rainbow coalitions, which involve multiple smaller parties across a broader ideological spectrum.
Key Players in Rainbow Coalitions
Rainbow coalitions consist of diverse political parties, social movements, and minority groups united by common goals such as social justice, civil rights, and environmental protection. Key players often include progressive parties, labor unions, immigrant organizations, environmental advocates, and civil rights groups, each contributing unique perspectives and grassroots support. This coalition's strength lies in its ability to mobilize a broad spectrum of communities to influence policy and enact inclusive reforms.
Political Objectives and Motivations
Grand coalitions merge major rival parties aiming to ensure political stability and governance during crises or fragmented parliaments, emphasizing compromise on broad, centrist policies. Rainbow coalitions unite diverse parties across the ideological spectrum, often prioritizing social inclusion, minority representation, and progressive reforms to counterbalance dominant political forces. Both coalitions leverage collective strength to achieve legislative goals but differ in their strategic focus: stability and unity in grand coalitions versus diversity and change in rainbow coalitions.
Advantages of Grand Coalitions
Grand coalitions unify major political parties to create stable governments capable of passing significant legislation efficiently. This arrangement reduces partisan gridlock by fostering collaboration between leading parties, thereby promoting policy continuity and economic confidence. The broad-based support in grand coalitions also enhances political legitimacy and social cohesion during periods of national crisis or transition.
Advantages of Rainbow Coalitions
Rainbow coalitions offer diverse representation by including multiple political parties or groups, enhancing inclusivity and reflecting a broader spectrum of societal interests. This diversity fosters innovative policy solutions and improves democratic legitimacy by integrating varied perspectives. Their collaborative nature often leads to stronger grassroots support and increased political stability through consensus-building.
Challenges and Criticisms
Grand coalitions often face challenges related to ideological compromise, which can lead to diluted policy agendas and voter dissatisfaction due to perceived lack of clear opposition. Rainbow coalitions encounter difficulties in maintaining cohesion among diverse parties with varying priorities, risking instability and inconsistent governance. Both coalition types face criticism for potential inefficiency and undermining democratic accountability by blurring political distinctions.
Impact on Governance and Policy
Grand coalitions, typically formed between the largest parties across the political spectrum, often lead to more stable governance by reducing political fragmentation but may slow policy innovation due to the need for consensus among diverse ideologies. Rainbow coalitions, consisting of multiple smaller parties with varied agendas, increase representational diversity and policy experimentation but can cause governance challenges like legislative gridlock and unstable majorities. The impact on policy is thus shaped by the trade-off between stability and inclusiveness, influencing the government's ability to implement coherent and sustained reforms.
Grand coalition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com