Voter suppression refers to tactics and laws that aim to prevent or discourage certain groups from voting, often targeting minorities, the elderly, and low-income populations. By imposing strict ID requirements, purging voter rolls, or limiting early voting, these measures undermine democratic participation and equity. Explore the article to understand how voter suppression affects your right to vote and what can be done to protect it.
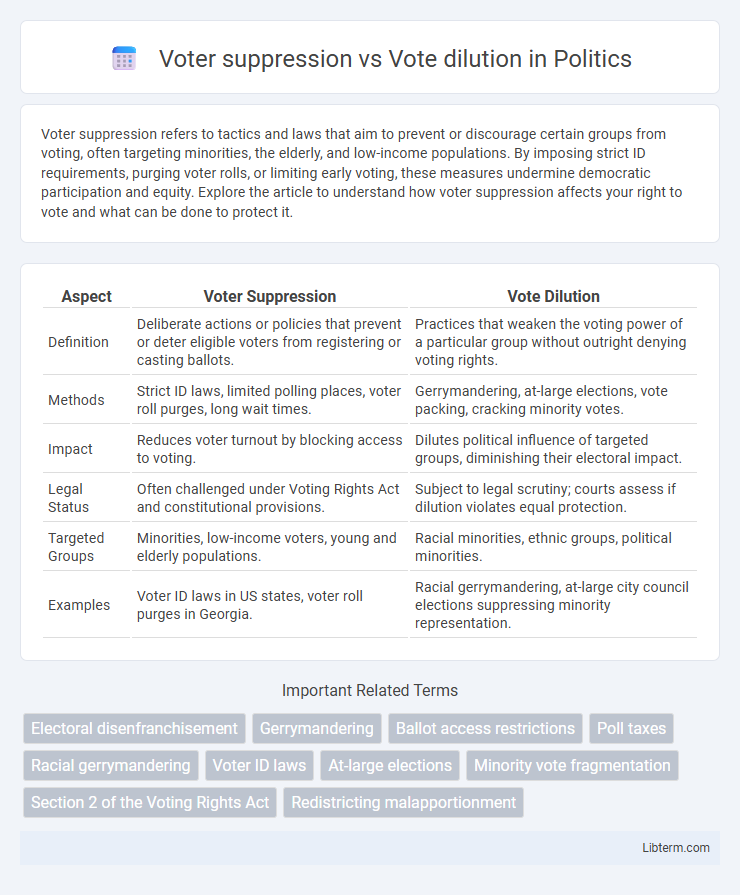
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Voter Suppression | Vote Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate actions or policies that prevent or deter eligible voters from registering or casting ballots. | Practices that weaken the voting power of a particular group without outright denying voting rights. |
| Methods | Strict ID laws, limited polling places, voter roll purges, long wait times. | Gerrymandering, at-large elections, vote packing, cracking minority votes. |
| Impact | Reduces voter turnout by blocking access to voting. | Dilutes political influence of targeted groups, diminishing their electoral impact. |
| Legal Status | Often challenged under Voting Rights Act and constitutional provisions. | Subject to legal scrutiny; courts assess if dilution violates equal protection. |
| Targeted Groups | Minorities, low-income voters, young and elderly populations. | Racial minorities, ethnic groups, political minorities. |
| Examples | Voter ID laws in US states, voter roll purges in Georgia. | Racial gerrymandering, at-large city council elections suppressing minority representation. |
Understanding Voter Suppression: Definition and Tactics
Voter suppression involves deliberate strategies and policies designed to prevent eligible voters from casting their ballots, including strict voter ID laws, limited polling locations, and purging voter rolls. Unlike vote dilution, which diminishes the weight of a vote through redistricting or at-large elections, suppression directly obstructs voting access and participation. Understanding these tactics is crucial for recognizing legal and systemic barriers that disproportionately affect minority and marginalized communities in elections.
What Is Vote Dilution? Key Concepts Explained
Vote dilution occurs when the voting power of a particular group is weakened, typically by redistricting or at-large elections that reduce their influence. It differs from voter suppression, which directly restricts access to voting through barriers like ID laws or limited polling locations. Key concepts of vote dilution include racial gerrymandering and vote cracking or packing, which scatter or concentrate minority voters to minimize their electoral impact.
Historical Context: Voter Suppression in the United States
Voter suppression in the United States has a deep-rooted historical context marked by systemic efforts to disenfranchise African Americans and marginalized groups, particularly through Jim Crow laws, literacy tests, and poll taxes post-Reconstruction. These tactics aimed to significantly reduce voter turnout by creating high barriers to voting access, influencing electoral outcomes. In contrast, vote dilution involves practices such as gerrymandering and at-large voting systems that weaken the electoral power of specific groups without outright denying the right to vote.
Evolution of Vote Dilution: From Gerrymandering to Redistricting
Vote dilution has evolved significantly, transitioning from traditional gerrymandering tactics aimed at weakening the power of specific demographic groups to more sophisticated redistricting strategies that subtly reshape electoral boundaries to influence political outcomes. Modern redistricting efforts manipulate district lines using advanced data analytics and geographic information systems (GIS) to fragment or concentrate voter populations, thereby minimizing their electoral impact without overt disenfranchisement. This evolution poses complex legal challenges under the Voting Rights Act and highlights ongoing debates about the fairness and transparency of electoral processes in representative democracies.
Legal Framework: Laws Governing Voter Suppression and Vote Dilution
The legal framework addressing voter suppression and vote dilution is primarily governed by the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which prohibits practices that deny or abridge the right to vote based on race or ethnicity. Courts apply the Fifteenth Amendment alongside Section 2 of the Act to evaluate cases of vote dilution, such as gerrymandering that weakens minority voting strength, and voter suppression tactics like strict ID laws or purging voter rolls. State-level laws and federal judiciary rulings continue to shape the enforcement landscape, balancing election integrity with the protection of voting rights under constitutional and statutory provisions.
Modern Methods of Voter Suppression and Their Impacts
Modern methods of voter suppression include strict voter ID laws, purging voter rolls, reducing polling locations, and implementing discriminatory voter registration requirements, which disproportionately affect minority and low-income communities. These tactics limit access to voting and contribute to significant vote dilution by minimizing the electoral influence of targeted populations. The impact undermines democratic participation, skewing election outcomes and weakening representative governance.
Analyzing the Effects of Vote Dilution on Minority Representation
Vote dilution significantly undermines minority representation by fragmenting or consolidating minority votes to prevent them from influencing election outcomes effectively. Techniques such as at-large voting, redistricting, and absorption of minority populations into larger electoral districts dilute the voting strength of minority groups, resulting in fewer elected officials who represent their interests. This systemic marginalization diminishes political power and access to resources, perpetuating disparities in policy-making and community investment.
Case Studies: Notable Examples of Voter Suppression vs. Vote Dilution
In the case of Shelby County v. Holder (2013), the Supreme Court struck down key provisions of the Voting Rights Act, leading to increased voter suppression tactics such as strict voter ID laws and reduced early voting in states with histories of discrimination. The 2018 North Carolina congressional redistricting case highlighted vote dilution, where district boundaries were redrawn to weaken the voting power of African American communities, undermining fair representation. Both instances demonstrate how legal and electoral strategies can either overtly disenfranchise voters or subtly diminish the influence of minority votes.
Combating Voter Suppression and Vote Dilution: Policies and Solutions
Combating voter suppression and vote dilution requires robust policies such as implementing automatic voter registration, expanding early voting access, and enforcing the Voting Rights Act to prevent discriminatory practices. Redistricting reforms and independent redistricting commissions can help address vote dilution by ensuring fair representation without racial gerrymandering. Enhanced federal oversight and transparency measures increase accountability and protect voting rights across all jurisdictions.
The Future of Voting Rights: Ensuring Fair Representation
Voter suppression involves tactics that directly prevent eligible voters from casting ballots, whereas vote dilution weakens the impact of certain votes through unfair districting or discriminatory practices. Ensuring fair representation requires robust enforcement of voting rights laws and reforms aimed at protecting equal access to the ballot. The future of voting rights hinges on combating both suppression and dilution to uphold democratic principles and guarantee every vote carries equal weight.
Voter suppression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com