A consultative assembly serves as an advisory body that provides recommendations and feedback to decision-makers without holding legislative power. These assemblies often play a crucial role in shaping policies through expert insights and public consultations. Discover how consultative assemblies influence governance and what impact they may have on Your community by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
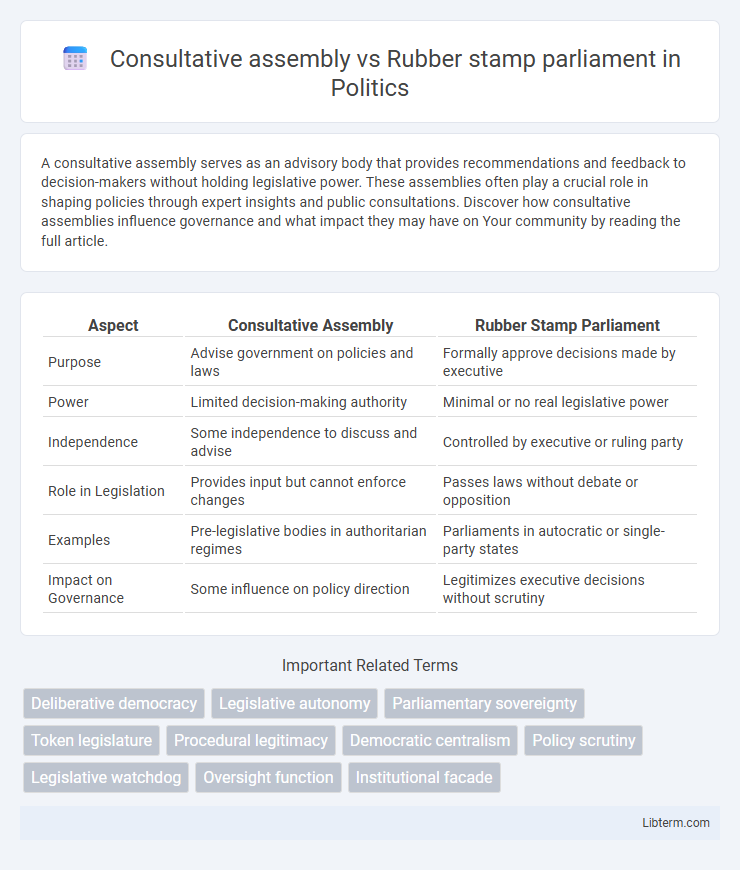
| Aspect | Consultative Assembly | Rubber Stamp Parliament |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Advise government on policies and laws | Formally approve decisions made by executive |
| Power | Limited decision-making authority | Minimal or no real legislative power |
| Independence | Some independence to discuss and advise | Controlled by executive or ruling party |
| Role in Legislation | Provides input but cannot enforce changes | Passes laws without debate or opposition |
| Examples | Pre-legislative bodies in authoritarian regimes | Parliaments in autocratic or single-party states |
| Impact on Governance | Some influence on policy direction | Legitimizes executive decisions without scrutiny |
Introduction to Legislative Bodies
Consultative assemblies primarily serve as advisory bodies that provide expert opinions and feedback without holding legislative power, often influencing policy through recommendations rather than direct decision-making. Rubber stamp parliaments, by contrast, function as nominal legislative bodies that formally approve decisions made by an authoritative executive or ruling party without genuine debate or opposition. Understanding these distinctions highlights the varying degrees of legislative autonomy and democratic governance within different political systems.
Defining Consultative Assemblies
Consultative assemblies serve as advisory bodies that provide expert opinions and recommendations to governments or parliaments, without possessing legislative power. These assemblies facilitate participatory governance by incorporating diverse stakeholder perspectives, enhancing policy deliberation and transparency. In contrast, a rubber stamp parliament lacks genuine deliberative function, merely formalizing decisions made by the executive without meaningful debate or opposition.
Understanding Rubber Stamp Parliaments
Rubber stamp parliaments are legislative bodies that approve decisions made by the executive without meaningful debate or opposition, serving primarily as formalities rather than forums for genuine policy discussion. Unlike consultative assemblies, which engage in dialogue and offer advice or feedback on governance, rubber stamp parliaments lack genuine legislative power and fail to hold the executive accountable. This erosion of legislative independence undermines democratic processes and concentrates power within the ruling authority.
Key Features of Consultative Assemblies
Consultative assemblies are advisory bodies that provide expert opinions and represent diverse stakeholders without holding legislative authority, focusing on dialogue and consensus-building. These assemblies prioritize transparency, stakeholder participation, and informed decision-making, often addressing social, economic, or policy issues to guide government actions. Unlike rubber stamp parliaments, consultative assemblies emphasize genuine deliberation and influence rather than merely endorsing predetermined decisions.
Characteristics of Rubber Stamp Parliaments
Rubber stamp parliaments primarily serve to endorse decisions made by the executive branch without genuine debate or opposition, reflecting limited legislative independence. These assemblies lack meaningful scrutiny, with members typically agreeing unanimously or by overwhelming majorities without critical evaluation of policies. The absence of diverse political dialogue and the predetermined approval of government proposals characterize the rubber stamp nature of such parliaments.
Comparative Analysis: Powers and Functions
Consultative assemblies primarily serve an advisory role, offering recommendations without binding legislative authority, whereas rubber stamp parliaments merely approve decisions made by the executive without genuine debate or modification. The powers of consultative assemblies often include reviewing policies and providing expert opinions, while rubber stamp parliaments lack independent legislative functions, limiting their impact on governance. Functionally, consultative assemblies engage in limited oversight and dialogue, contrasting with rubber stamp parliaments that act as formalities to legitimize pre-decided executive actions.
Impact on Governance and Policy-making
Consultative assemblies primarily serve as advisory bodies, offering expert opinions and facilitating dialogue without binding legislative power, which can slow policy implementation and limit direct impact on governance. Rubber stamp parliaments formally endorse decisions made by the executive branch, diminishing genuine debate and weakening checks and balances, often leading to policies that reflect centralized authority rather than diverse public interests. The effectiveness of governance and policy-making depends on the degree of legislative independence, with consultative assemblies providing some input and rubber stamp parliaments largely reinforcing executive dominance.
Case Studies: Real-world Examples
The Consultative Assembly of Saudi Arabia exemplifies a consultative body with limited legislative authority, providing recommendations without binding power, shaping policy through advisory roles. In contrast, the Russian State Duma during the early 2000s acted as a rubber stamp parliament, passing legislation aligned strictly with executive directives, exemplifying constrained parliamentary autonomy. Case studies of these bodies highlight differences in political influence, where consultative assemblies engage in dialogue but lack enforcement power, whereas rubber stamp parliaments legitimize executive decisions with minimal scrutiny.
Challenges and Criticisms
Consultative assemblies often face criticism for lacking genuine legislative power, limiting their role to advisory functions without the authority to enact or amend laws, which undermines democratic governance and effective policymaking. Rubber stamp parliaments are challenged by their inability to provide meaningful checks and balances, as they routinely approve decisions made by the executive branch without substantive debate or opposition, leading to questions about transparency and accountability. Both institutions struggle with limited political autonomy and reduced public trust, hindering their capacity to represent diverse interests and ensure robust democratic processes.
Conclusion: The Significance of Legislative Independence
Legislative independence ensures that a parliament functions as a genuine representative body, enabling meaningful debate and the creation of laws reflective of public interest. In contrast, a consultative assembly or rubber stamp parliament lacks autonomy, often merely endorsing executive decisions without scrutiny. The distinction underscores the vital role of independent legislatures in upholding democratic governance and accountability.
Consultative assembly Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com