The ruling party holds the majority of power within a government, shaping national policies and legislative priorities to influence economic growth and social development. Their governance impacts every sector, from healthcare to education, and plays a critical role in international relations. Discover how the ruling party's decisions affect Your daily life and the broader political landscape in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
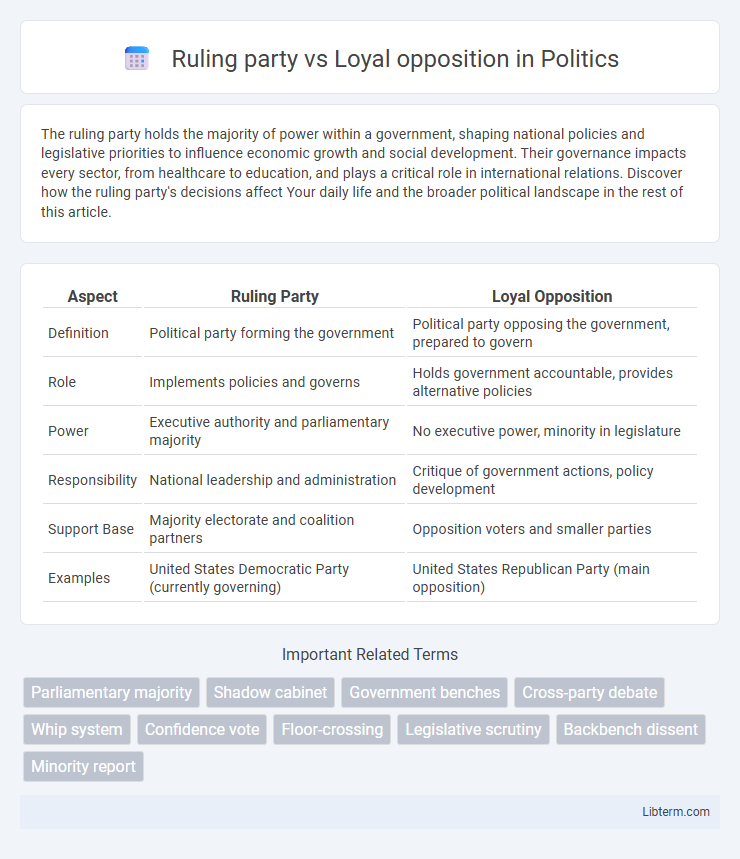
| Aspect | Ruling Party | Loyal Opposition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political party forming the government | Political party opposing the government, prepared to govern |
| Role | Implements policies and governs | Holds government accountable, provides alternative policies |
| Power | Executive authority and parliamentary majority | No executive power, minority in legislature |
| Responsibility | National leadership and administration | Critique of government actions, policy development |
| Support Base | Majority electorate and coalition partners | Opposition voters and smaller parties |
| Examples | United States Democratic Party (currently governing) | United States Republican Party (main opposition) |
Definition of Ruling Party and Loyal Opposition
The ruling party is the political group that holds the majority of seats in a legislative body and controls the executive branch, responsible for forming the government and implementing policies. Loyal opposition consists of political parties or members who do not hold power but actively monitor and challenge the ruling party's decisions while respecting the democratic system. Both roles are essential for balanced governance, ensuring accountability and representation in a parliamentary democracy.
Historical Context of Political Rivalry
The historical context of political rivalry between the ruling party and the loyal opposition traces back to the development of parliamentary democracy in the 18th century, particularly in Britain. This dynamic emerged as formalized parties began to structure government and challenged its authority while respecting constitutional frameworks. The loyal opposition played a critical role in holding the ruling party accountable, shaping policies through debate, and ensuring a balance of power in evolving democratic systems.
Core Functions of the Ruling Party
The ruling party primarily focuses on formulating and implementing government policies, managing public administration, and maintaining national security. It holds executive power, oversees the budget allocation, and ensures law enforcement aligns with legislative priorities. This party drives political stability by responding to public needs and guiding socio-economic development programs.
Essential Roles of the Loyal Opposition
The loyal opposition plays a critical role in a functioning democracy by holding the ruling party accountable through scrutinizing policies and offering alternative solutions. It ensures government transparency and prevents the abuse of power by challenging decisions and representing diverse public interests. This balance fosters healthy political debate and strengthens the democratic process by encouraging continuous improvement and responsiveness.
Balance of Power in Democratic Systems
The ruling party holds executive authority, implementing policies and managing government operations, while the loyal opposition scrutinizes decisions to ensure accountability and represent alternative views. This dynamic creates a balance of power essential for preventing authoritarianism and fostering transparent governance in democratic systems. Effective checks and balances between these entities promote political stability and protect citizens' rights by encouraging continuous dialogue and responsiveness.
Policy-Making: Collaboration vs. Conflict
The ruling party drives policy-making by setting legislative agendas and mobilizing support to implement their priorities, while the loyal opposition scrutinizes proposals, offering alternative solutions to influence or challenge policies. Collaboration between both entities can lead to more comprehensive and balanced legislation, fostering democratic accountability and effective governance. Persistent conflict, however, may result in gridlock, undermining policy effectiveness and public trust in government institutions.
Accountability and Political Responsibility
The ruling party holds the primary responsibility for governance and policy implementation, making it accountable to the electorate for its decisions and actions. The loyal opposition plays a crucial role in scrutinizing government performance, offering alternative policies, and holding the ruling party accountable through informed debate and oversight. Effective political responsibility relies on this dynamic balance, ensuring transparency, responsiveness, and democratic integrity within the political system.
Impact on Governance and Stability
The ruling party typically drives governance by setting policies and implementing legislation that reflects their electoral mandate, ensuring governmental functionality and decision-making continuity. The loyal opposition plays a critical role in scrutinizing government actions, providing alternative policies, and holding the ruling party accountable, which strengthens democratic processes and prevents abuses of power. This dynamic balance fosters political stability by enabling constructive debate while maintaining institutional checks and balances essential for effective governance.
Challenges Facing Ruling Parties and Oppositions
Ruling parties face challenges such as maintaining public trust, managing diverse internal factions, and effectively implementing policies amidst economic or social crises. Loyal oppositions grapple with the difficulty of presenting viable alternatives while holding the government accountable without appearing obstructive or opportunistic. Both entities must navigate complex media landscapes and shifting voter expectations to sustain political relevance.
Future Trends in Party Dynamics
Future trends in party dynamics indicate an increasing fluidity between the ruling party and loyal opposition, driven by shifting voter demographics and evolving policy priorities. Technological advancements and social media platforms enhance real-time engagement, compelling both entities to adopt more transparent and responsive strategies. Fragmentation and coalition-building are expected to redefine traditional roles, challenging the binary nature of governing and opposition parties.
Ruling party Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com