Technocracy emphasizes governance by experts and scientists, prioritizing data-driven decision-making for efficient societal management. This system aims to replace political influence with specialized knowledge to solve complex problems objectively. Explore the rest of the article to understand how technocracy could impact your future.
Table of Comparison
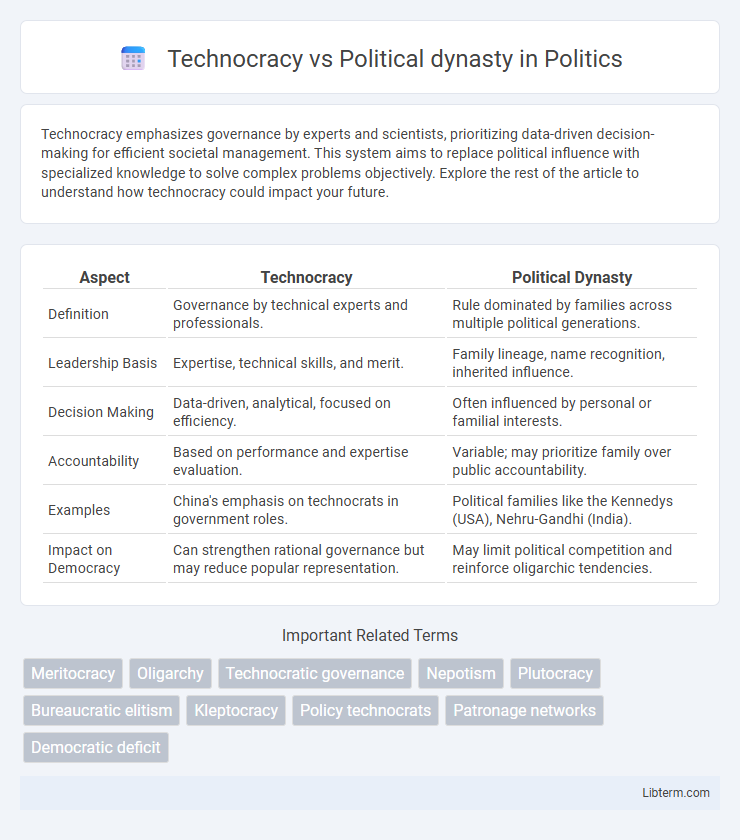
| Aspect | Technocracy | Political Dynasty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance by technical experts and professionals. | Rule dominated by families across multiple political generations. |
| Leadership Basis | Expertise, technical skills, and merit. | Family lineage, name recognition, inherited influence. |
| Decision Making | Data-driven, analytical, focused on efficiency. | Often influenced by personal or familial interests. |
| Accountability | Based on performance and expertise evaluation. | Variable; may prioritize family over public accountability. |
| Examples | China's emphasis on technocrats in government roles. | Political families like the Kennedys (USA), Nehru-Gandhi (India). |
| Impact on Democracy | Can strengthen rational governance but may reduce popular representation. | May limit political competition and reinforce oligarchic tendencies. |
Introduction to Technocracy and Political Dynasties
Technocracy is a system of governance where decision-makers are selected based on their technical expertise and specialized knowledge, emphasizing efficiency and data-driven policies. Political dynasties refer to families that maintain political power across generations, often prioritizing personal or familial interests over meritocratic governance. Contrasting these models highlights the tension between expertise-based leadership and inherited political influence in shaping public administration.
Historical Context: Origins and Evolution
Technocracy emerged during the early 20th century as a movement advocating for governance by experts and engineers, emphasizing efficiency and scientific management, notably gaining traction during the Great Depression. Political dynasties trace back to ancient monarchies and feudal systems, evolving into contemporary family-based power structures where political influence is passed down through generations. The contrasting origins highlight technocracy's basis in meritocratic principles versus political dynasties' reliance on hereditary authority and social capital accumulation.
Defining Features of Technocracy
Technocracy is characterized by governance led by experts and specialists who base decisions on scientific data, technical knowledge, and empirical evidence. Unlike political dynasties that emphasize familial ties and inherited power, technocracy prioritizes meritocracy, expertise, and efficiency in policy-making. This system aims to depoliticize government functions by relying on objective analysis and professional competence rather than political influence or nepotism.
Characteristics of Political Dynasties
Political dynasties are characterized by the concentration of political power within a few influential families, often leading to inherited positions across generations and reduced political competition. These dynasties typically leverage name recognition, established networks, and economic resources to maintain control and influence electoral outcomes. The entrenchment of political families can hinder democratic processes by limiting opportunities for diverse leadership and perpetuating patronage systems.
Governance Approaches: Expertise vs. Inheritance
Technocracy emphasizes governance driven by specialized expertise, where decision-makers are selected based on technical knowledge and skills to implement evidence-based policies that enhance efficiency and innovation. Political dynasties rely on inherited authority, often prioritizing familial loyalty and tradition over merit, which can undermine transparency and democratic accountability. The contrast between these approaches highlights the tension between meritocratic competence and entrenched power structures in shaping effective governance.
Impact on Policy and Decision-Making
Technocracy emphasizes expertise-driven policy and data-informed decision-making, often resulting in more efficient and technically sound governance. Political dynasties tend to prioritize familial loyalty and political legacy, which can lead to decisions influenced by personal interests rather than objective analysis. The contrast between technocratic governance and political dynasties significantly affects policy outcomes, with technocracy promoting innovation and accountability while dynasties may perpetuate entrenched power structures.
Societal Perceptions and Public Trust
Societal perceptions of technocracy often emphasize expertise, efficiency, and merit-based governance, fostering higher public trust in policy decisions driven by specialized knowledge. Political dynasties, conversely, may evoke skepticism due to associations with nepotism, power concentration, and potential corruption, which can erode public confidence and civic engagement. The contrast in trust levels profoundly impacts governance legitimacy, where technocratic leadership is perceived as impartial and capable, while dynastic rule is frequently linked to elitism and patronage networks.
Case Studies: Global Examples
Global case studies reveal stark contrasts between technocracy and political dynasty governance models, as seen in Singapore's technocratic leadership driving sustainable development versus the entrenched political dynasties entrenched in the Philippines undermining policy continuity. In Mexico, the dominance of the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) exemplifies how political dynasties can perpetuate corruption and hinder democratic progress, while Germany's technocracy, particularly through its reliance on expert administrators and evidence-based policy, facilitates efficient governance. These examples emphasize the efficacy of technocratic systems in promoting innovation and stability compared to political dynasties, which often prioritize family interests over national welfare.
Challenges and Criticisms
Technocracy faces criticism for potentially lacking democratic representation as experts prioritize technical solutions over popular opinion, creating a perceived disconnect from the electorate. Political dynasties often encounter challenges related to nepotism, perpetuating power within families and limiting political diversity and meritocracy. Both systems risk undermining democratic principles: technocracy through elitism and political dynasties through entrenched patronage and decreased political competition.
Future Prospects: Navigating Governance Models
Technocracy offers data-driven decision-making and specialized expertise that can enhance policy efficiency and long-term planning in governance models. Political dynasties, while leveraging established influence and networks, may face challenges in promoting innovation and broader representation in future political landscapes. Balancing technocratic innovation with democratic inclusivity is crucial to navigating effective governance models going forward.
Technocracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com