Primary elections determine which candidates will represent political parties in general elections, playing a crucial role in shaping the political landscape. Voters participate in selecting their preferred candidate, influencing the policies and leadership that will affect their community and country. Explore the rest of this article to understand how primary elections impact your future and voter engagement.
Table of Comparison
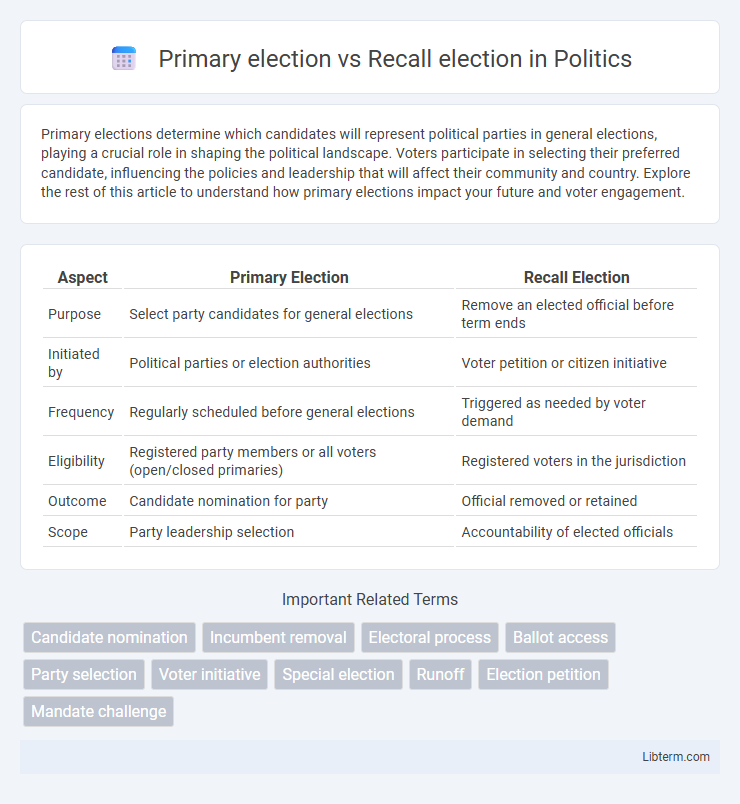
| Aspect | Primary Election | Recall Election |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Select party candidates for general elections | Remove an elected official before term ends |
| Initiated by | Political parties or election authorities | Voter petition or citizen initiative |
| Frequency | Regularly scheduled before general elections | Triggered as needed by voter demand |
| Eligibility | Registered party members or all voters (open/closed primaries) | Registered voters in the jurisdiction |
| Outcome | Candidate nomination for party | Official removed or retained |
| Scope | Party leadership selection | Accountability of elected officials |
Introduction to Primary and Recall Elections
Primary elections serve as the preliminary voting process where political parties select their candidates for general elections, enabling party members to influence candidate nominations directly. Recall elections allow voters to remove elected officials from office before their term ends, providing a mechanism for accountability and public response to dissatisfaction. Both elections play crucial roles in democratic governance, empowering citizens to shape leadership and policy direction effectively.
Defining Primary Elections
Primary elections are preliminary voting processes where party members select their candidates for upcoming general elections, playing a critical role in shaping party representation. These elections determine which candidates advance to the general election ballot, focusing on party nominations rather than policy recall. Unlike recall elections, which aim to remove an elected official before their term ends, primary elections are centered on candidate selection within political parties.
Understanding Recall Elections
Recall elections empower voters to remove elected officials before their term ends, serving as a direct democratic tool to hold politicians accountable. Unlike primary elections that select candidates for upcoming general elections, recall elections focus on the potential dismissal of a current officeholder based on voter dissatisfaction. The process typically requires a petition with a specified number of signatures, followed by a vote where the official can be replaced if the majority supports the recall.
Key Differences Between Primary and Recall Elections
Primary elections select party candidates for general elections, allowing registered party members or voters to choose who will represent their party. Recall elections enable voters to remove elected officials from office before their term ends, typically triggered by a petition with sufficient signatures. The key difference lies in purpose: primaries determine candidates for upcoming elections, while recalls focus on holding current officeholders accountable.
Purpose and Objectives of Primary Elections
Primary elections serve to select a party's candidate for the general election, ensuring voter participation in the nomination process and strengthening democratic representation. Their purpose is to identify the most popular and viable candidate within a political party, allowing the electorate to influence candidate selection directly rather than leaving the decision solely to party officials. Recall elections, in contrast, aim to remove an elected official from office before the end of their term, reflecting a mechanism for voter accountability and officials' responsiveness to public dissatisfaction.
Reasons and Processes Behind Recall Elections
Recall elections serve as a democratic tool allowing voters to remove elected officials before their term ends, primarily driven by reasons such as misconduct, corruption, or failure to perform duties. The process begins with a petition phase where a specified number of voter signatures is required, followed by verification, and if successful, a special election is held to decide whether the official should be recalled. Unlike primary elections that select party nominees for general elections, recall elections directly challenge the incumbent's legitimacy based on public dissatisfaction or loss of trust.
Legal Framework Governing Both Elections
The legal framework governing primary elections is typically established by state election laws and party rules, defining candidate eligibility, voter participation, and ballot procedures, ensuring a structured process for selecting party nominees. Recall elections are regulated by specific statutes that outline the grounds for removal, petition requirements, and procedural safeguards to protect the rights of elected officials and voters. Both election types involve statutory deadlines and signature thresholds, but recall elections demand stricter scrutiny to balance accountability with electoral stability.
Impact on Political Parties and Candidates
Primary elections empower political parties by enabling them to select candidates who reflect the party's platform, fostering unity and strategic positioning ahead of general elections. Recall elections introduce unpredictability, pressuring incumbents to maintain voter approval and potentially disrupting party cohesion if popular officials are removed mid-term. These mechanisms influence candidate behavior and party strategy, with primaries focusing on internal party competition while recalls highlight accountability to the broader electorate.
Historical Examples of Primary and Recall Elections
The 1912 U.S. presidential primary marked a pivotal shift by allowing voters to directly influence candidate selection, contrasting with earlier party-dominated processes. The 2003 California recall election, which removed Governor Gray Davis and installed Arnold Schwarzenegger, exemplifies the recall mechanism as a tool for voter accountability outside regular election cycles. These historical cases highlight the primary election's role in candidate nomination and the recall election's function in holding elected officials accountable through direct voter intervention.
Conclusion: Significance in Democratic Systems
Primary elections empower political parties to select candidates, fostering intra-party democracy and reflecting voter preferences early in the electoral process. Recall elections serve as a direct democratic tool, enabling constituents to remove elected officials before their term ends, enhancing governmental accountability. Both mechanisms are vital for maintaining responsive and representative governance in democratic systems.
Primary election Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com