Sanctions are powerful tools used by countries or international organizations to influence the behavior of governments, entities, or individuals by restricting trade, financial transactions, or travel. These measures can target specific sectors, aiming to pressure compliance with international laws or human rights standards while minimizing broader economic impacts. Explore the rest of the article to understand how sanctions work and their implications for your business or global relations.
Table of Comparison
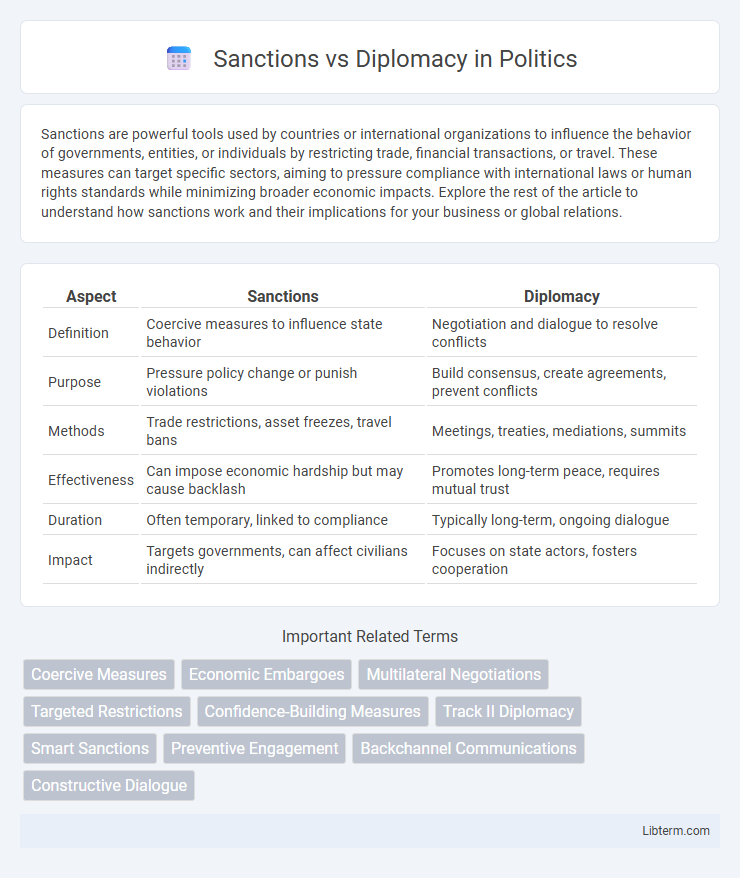
| Aspect | Sanctions | Diplomacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coercive measures to influence state behavior | Negotiation and dialogue to resolve conflicts |
| Purpose | Pressure policy change or punish violations | Build consensus, create agreements, prevent conflicts |
| Methods | Trade restrictions, asset freezes, travel bans | Meetings, treaties, mediations, summits |
| Effectiveness | Can impose economic hardship but may cause backlash | Promotes long-term peace, requires mutual trust |
| Duration | Often temporary, linked to compliance | Typically long-term, ongoing dialogue |
| Impact | Targets governments, can affect civilians indirectly | Focuses on state actors, fosters cooperation |
Understanding Sanctions and Diplomacy
Sanctions represent coercive measures imposed by countries or international bodies to influence state behavior without resorting to military conflict, targeting economies, individuals, or specific sectors to create political or economic pressure. Diplomacy involves dialogue, negotiation, and compromise between nations aimed at resolving disputes, establishing agreements, and maintaining peaceful relations through mutual understanding. Understanding the strategic application of sanctions alongside diplomacy is crucial for policymakers seeking to balance pressure and engagement to achieve foreign policy objectives.
Historical Overview of Sanctions and Diplomacy
Sanctions and diplomacy have served as pivotal tools in international relations, with sanctions historically employed to coerce or punish states by restricting trade, financial transactions, or military activities. Diplomacy, rooted in ancient practices, relies on negotiation and dialogue to resolve conflicts and build alliances, often complementing sanctions to achieve geopolitical objectives. Throughout history, examples such as the League of Nations' sanctions on Italy (1935) and Cold War-era diplomatic engagements illustrate the dynamic interplay between these strategies in shaping global political outcomes.
Key Differences Between Sanctions and Diplomacy
Sanctions involve the use of economic, trade, or financial restrictions imposed by one country or group to influence the behavior of another, often serving as a punitive measure. Diplomacy relies on negotiation, dialogue, and cooperation between nations to resolve conflicts and build mutual agreements. While sanctions exert pressure through coercion, diplomacy emphasizes collaboration and compromise to achieve strategic objectives.
Effectiveness of Sanctions in Global Politics
Sanctions serve as a strategic tool in global politics to pressure governments or entities without direct military intervention, often targeting economic sectors or key political figures to influence behavior. Their effectiveness depends on multilateral enforcement, the targeted nation's economic resilience, and the availability of alternative partnerships that can mitigate impact. While sanctions can isolate regimes and signal international disapproval, their impact varies, with some cases showing limited change in policies and unintended humanitarian effects.
The Role of Diplomacy in International Conflict Resolution
Diplomacy plays a crucial role in international conflict resolution by facilitating dialogue, negotiation, and compromise between conflicting parties, preventing escalation and fostering peaceful solutions. Unlike sanctions, which often serve as punitive measures to coerce behavior, diplomacy emphasizes communication and mutual understanding to address underlying issues effectively. Effective diplomatic engagement can bridge differences, build trust, and create frameworks for sustainable peace.
Case Studies: Sanctions vs Diplomacy in Action
Sanctions and diplomacy have played contrasting roles in resolving geopolitical conflicts, exemplified by Iran's nuclear program, where multilateral sanctions pressured Tehran into negotiations leading to the 2015 JCPOA agreement. In contrast, North Korea's persistent nuclear development despite repeated sanctions highlights diplomacy's challenges and underscores the importance of nuanced, continuous dialogue alongside punitive measures. Case studies reveal that while sanctions can compel initial engagement, sustainable conflict resolution often requires integrating diplomatic strategies tailored to the specific political landscape.
Economic Impacts of Sanctions vs Diplomatic Solutions
Economic sanctions often lead to significant disruptions in trade, investment, and financial flows, causing inflation, unemployment, and reduced economic growth in targeted countries. Diplomatic solutions, by contrast, promote stability and open markets through negotiation, fostering long-term economic cooperation and development. While sanctions impose short-term economic pain, diplomacy tends to create sustainable economic benefits by resolving conflicts and enabling mutually beneficial agreements.
Humanitarian Consequences: Sanctions and Diplomacy
Sanctions often aim to pressure governments but can inadvertently exacerbate humanitarian crises by restricting access to essential goods such as food, medicine, and clean water, impacting vulnerable populations the most. Diplomacy prioritizes negotiation and cooperation to resolve conflicts, reducing the risk of collateral damage to civilians and maintaining humanitarian aid channels. Effective diplomatic efforts can mitigate the negative consequences of sanctions by fostering dialogue and enabling targeted measures that minimize harm to non-combatants.
Balancing Sanctions and Diplomacy for Peacebuilding
Balancing sanctions and diplomacy is crucial for effective peacebuilding, as sanctions can pressure conflicting parties to negotiate without escalating violence. Targeted sanctions, such as asset freezes and travel bans, minimize humanitarian impacts while maintaining leverage. Diplomatic engagement ensures dialogue channels remain open, facilitating conflict resolution and sustainable peace agreements.
Future Trends: Integrating Sanctions and Diplomacy
Future trends in international relations emphasize integrating sanctions and diplomacy as complementary tools to address global challenges effectively. Leveraging targeted sanctions alongside proactive diplomatic engagement enhances conflict resolution and promotes compliance with international norms. Innovations in data analytics and multilateral coordination are expected to optimize the strategic application of sanctions within diplomatic frameworks.
Sanctions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com