Abstention occurs when individuals deliberately refrain from voting or participating in a decision-making process, often reflecting dissatisfaction or indecision. Understanding the reasons behind abstention can provide valuable insights into public opinion and democratic engagement. Explore the article to learn how abstention impacts elections and what it means for your civic involvement.
Table of Comparison
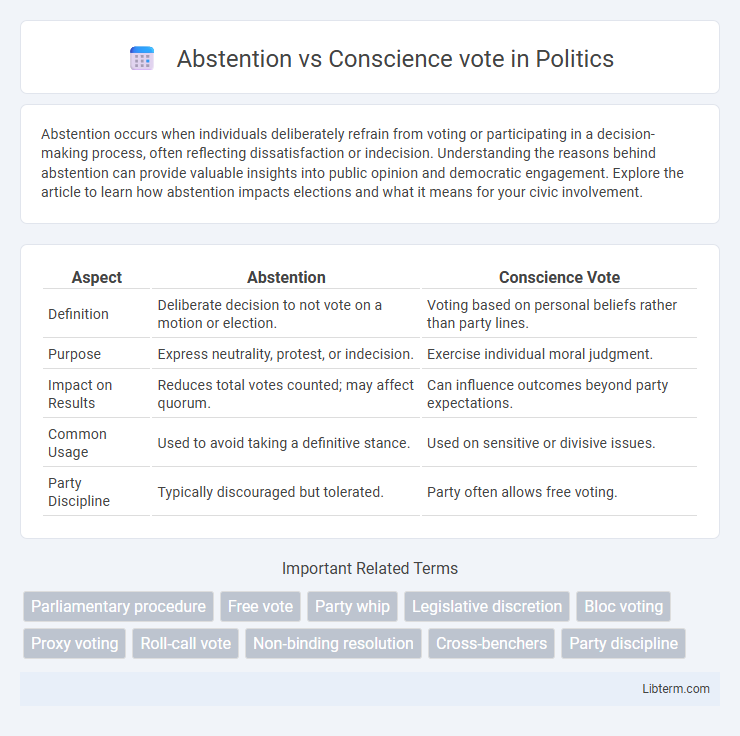
| Aspect | Abstention | Conscience Vote |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate decision to not vote on a motion or election. | Voting based on personal beliefs rather than party lines. |
| Purpose | Express neutrality, protest, or indecision. | Exercise individual moral judgment. |
| Impact on Results | Reduces total votes counted; may affect quorum. | Can influence outcomes beyond party expectations. |
| Common Usage | Used to avoid taking a definitive stance. | Used on sensitive or divisive issues. |
| Party Discipline | Typically discouraged but tolerated. | Party often allows free voting. |
Understanding Abstention: Definition and Context
Abstention occurs when a member deliberately chooses not to cast a vote either in favor or against a proposal, reflecting neutrality or indecision in parliamentary or decision-making contexts. It differs from a conscience vote, where members vote based on personal beliefs rather than party lines. Understanding abstention is crucial as it can influence the outcome of decisions by reducing the total number of active votes, often signaling political strategy or ethical considerations without direct opposition or support.
What Is a Conscience Vote?
A conscience vote allows legislators to vote according to their personal beliefs rather than following party lines, often on morally or ethically sensitive issues such as same-sex marriage or euthanasia. Unlike abstention, where a member chooses not to participate in the vote at all, a conscience vote actively reflects individual convictions and prioritizes autonomy over party discipline. This voting method highlights the significance of personal ethics in parliamentary decision-making processes.
Historical Overview: Abstention and Conscience Votes
Abstention and conscience votes have played distinct roles in parliamentary history, with abstentions historically signaling neutrality or indecision on contentious legislation. Conscience votes, emerging prominently in the 19th century, allow legislators to vote according to personal beliefs rather than party lines, especially on ethical or moral issues such as abortion or capital punishment. Over time, these voting types have shaped legislative dynamics by reflecting individual legislator autonomy and political strategy within democratic institutions.
Key Differences Between Abstention and Conscience Vote
Abstention refers to a deliberate decision by a member to not cast a vote either in favor or against a motion, often to remain neutral or avoid conflict. A conscience vote, also known as a free vote, allows members to vote according to their personal beliefs rather than following party lines, emphasizing individual ethical judgment. Key differences include that abstention is an act of non-participation in voting, while a conscience vote actively engages personal morality in decision-making processes.
Motivations Behind Abstaining in Legislative Decisions
Abstention in legislative decisions often stems from a desire to remain neutral when lawmakers face conflicting interests or insufficient information, reflecting a cautious approach to policy impact. Motivations behind abstaining include avoiding political backlash, expressing dissent without outright opposition, or signaling indecision on complex or controversial issues. This strategic choice contrasts with conscience votes, where representatives openly prioritize personal or ethical beliefs, highlighting the nuanced role abstention plays in legislative behavior.
The Role of Conscience Votes in Democratic Process
Conscience votes empower legislators to cast decisions aligned with personal beliefs rather than party lines, enhancing ethical representation in democratic processes. They differ from abstentions, where lawmakers neither support nor oppose a measure, usually signifying neutrality or indecision. By facilitating genuine moral deliberation, conscience votes promote transparency and trust between elected officials and constituents, strengthening democratic legitimacy.
Political Implications of Abstention vs Conscience Voting
Abstention in legislative voting often signals political neutrality or strategic avoidance, allowing lawmakers to sidestep controversial issues without explicit opposition, which can impact party cohesion and public perception of accountability. Conscience voting empowers legislators to vote based on personal beliefs rather than party lines, reflecting democratic principles and individual moral judgment, but potentially causing intra-party conflicts or weakening collective agenda enforcement. Both abstention and conscience votes influence political dynamics by shaping legislative outcomes, signaling political stances to constituents, and affecting the balance of power within parliamentary systems.
Case Studies: Famous Abstentions and Conscience Votes
Famous abstentions in political history include the 2016 United Nations vote on the Paris Climate Agreement, where several countries abstained to express neutrality or strategic ambiguity. Notable conscience votes include the UK's 1967 Abortion Act, where MPs voted based on personal moral beliefs rather than party lines, demonstrating individual ethical decision-making. These case studies highlight the impact of abstention as a diplomatic tool and conscience voting as a reflection of personal conviction in legislative processes.
Pros and Cons: Evaluating Each Voting Method
Abstention allows members to refrain from voting, preserving neutrality and avoiding direct opposition, but it can dilute the clarity of majority decisions and reduce accountability. Conscience votes empower legislators to vote based on personal beliefs rather than party lines, promoting authentic representation and moral integrity while risking party cohesion and legislative predictability. Evaluating these methods requires balancing the benefits of individual expression against the need for clear, consistent policy outcomes.
Impacts on Governance and Public Trust
Abstention in voting can create ambiguity in legislative outcomes, often diluting decision-making clarity and weakening governance effectiveness. Conscience votes empower representatives to act according to personal or ethical beliefs, fostering authentic policymaking but potentially fragmenting party unity, which impacts public trust differently. Both practices influence public perception by either raising concerns about accountability through abstentions or enhancing legitimacy when conscience drives transparent, value-based decisions.
Abstention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com