Traditional diplomacy relies on face-to-face negotiations, official state representatives, and formal protocols to manage international relations and resolve conflicts. It emphasizes state sovereignty, respect for diplomatic immunity, and long-established channels of communication. Explore the rest of the article to understand how traditional diplomacy shapes global politics and impacts your country's foreign policy.
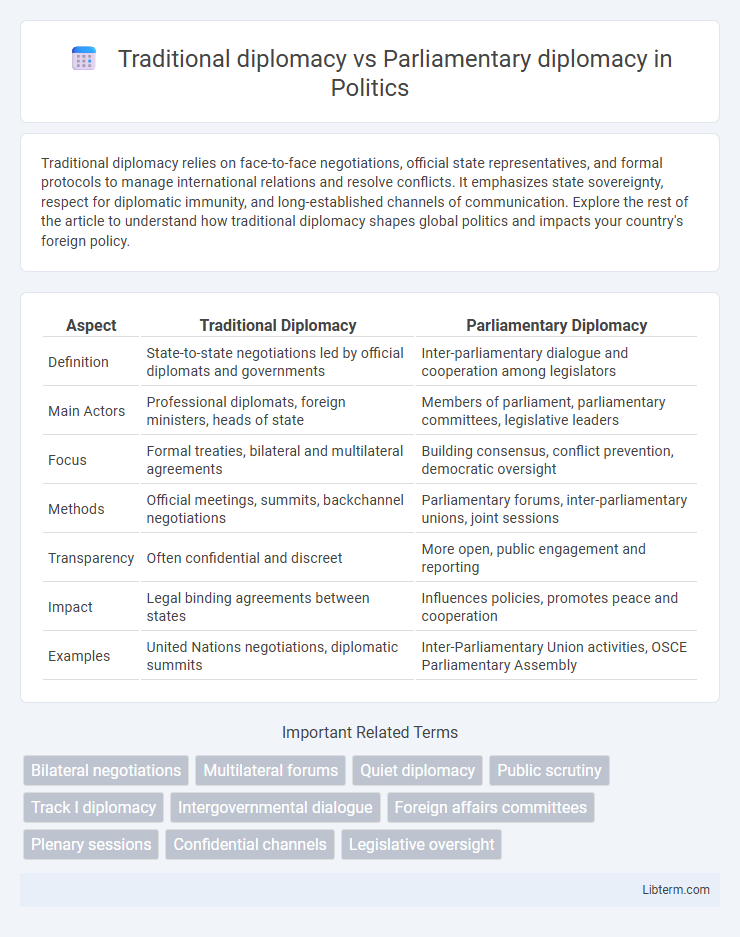
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Diplomacy | Parliamentary Diplomacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State-to-state negotiations led by official diplomats and governments | Inter-parliamentary dialogue and cooperation among legislators |
| Main Actors | Professional diplomats, foreign ministers, heads of state | Members of parliament, parliamentary committees, legislative leaders |
| Focus | Formal treaties, bilateral and multilateral agreements | Building consensus, conflict prevention, democratic oversight |
| Methods | Official meetings, summits, backchannel negotiations | Parliamentary forums, inter-parliamentary unions, joint sessions |
| Transparency | Often confidential and discreet | More open, public engagement and reporting |
| Impact | Legal binding agreements between states | Influences policies, promotes peace and cooperation |
| Examples | United Nations negotiations, diplomatic summits | Inter-Parliamentary Union activities, OSCE Parliamentary Assembly |
Defining Traditional Diplomacy
Traditional diplomacy involves formal, state-centered negotiations conducted by professional diplomats representing national governments through official channels. It emphasizes confidentiality, protocol, and the use of embassies and consulates to manage international relations and treaties. This approach is characterized by direct communication between heads of state or foreign ministers, aiming to resolve conflicts, forge alliances, and safeguard national interests.
Understanding Parliamentary Diplomacy
Parliamentary diplomacy involves interactions between legislators and parliamentary bodies across nations to promote dialogue, mutual understanding, and conflict resolution, complementing traditional state-to-state diplomacy conducted by executive branches. It emphasizes transparency, citizen representation, and multilateral engagement, often addressing global issues such as human rights, security, and development through forums like the Inter-Parliamentary Union. Understanding parliamentary diplomacy requires recognizing its role in fostering democratic governance, influencing foreign policy from within legislatures, and enhancing diplomatic networks beyond formal diplomatic channels.
Historical Evolution of Diplomatic Practices
Traditional diplomacy, rooted in the Age of Absolutism, relied on secret negotiations and formal envoys representing sovereign monarchs, with a focus on bilateral state-to-state interactions. Parliamentary diplomacy emerged prominently in the 20th century as democratic institutions gained influence, emphasizing transparent multilateral dialogue and the growing role of legislative bodies in international relations. The historical evolution reflects a shift from exclusive elite bargaining towards inclusive, representative processes accommodating global governance complexities.
Key Actors in Traditional Diplomacy
Key actors in traditional diplomacy primarily include state leaders such as presidents and prime ministers, foreign ministers, and accredited ambassadors who represent their countries in bilateral and multilateral negotiations. These actors operate within formal government institutions and rely on established diplomatic protocols to communicate and negotiate international agreements. Traditional diplomacy emphasizes state sovereignty and direct government-to-government interactions, often conducted through embassies and official diplomatic channels.
The Rise of Parliamentary Diplomacy in Global Affairs
Parliamentary diplomacy has emerged as a significant force in global affairs, complementing traditional diplomacy by involving elected representatives in international dialogue and decision-making processes. This form of diplomacy enhances transparency and democratic legitimacy, allowing parliaments to influence foreign policy through interparliamentary unions and regional parliamentary assemblies such as the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) and the European Parliament. The rise of parliamentary diplomacy reflects a trend toward multi-actor engagement in global governance, emphasizing collaboration, accountability, and people-centered approaches.
Structural Differences Between the Two Approaches
Traditional diplomacy relies on centralized authority with professional diplomats conducting state-to-state negotiations in closed environments, while parliamentary diplomacy involves elected representatives engaging in open dialogue and multilateral forums to influence international relations. The structural framework of traditional diplomacy emphasizes confidentiality, hierarchy, and executive control, whereas parliamentary diplomacy is characterized by transparency, legislative participation, and broader public accountability. These structural differences impact decision-making processes, with traditional diplomacy often prioritizing state interests and secrecy, contrasting with the inclusive and deliberative nature of parliamentary diplomacy.
Communication Strategies: Confidential vs. Transparent
Traditional diplomacy relies on confidential communication strategies, emphasizing discreet negotiations and private dialogues to protect national interests and maintain strategic advantages. Parliamentary diplomacy prioritizes transparent communication, enabling public scrutiny and accountability through open debates and information sharing among elected representatives. The contrast in communication styles reflects differing goals: confidentiality fosters secrecy and control, while transparency encourages inclusiveness and democratic participation.
Influence on International Policy-Making
Traditional diplomacy relies on confidential negotiations and state-centric approaches to influence international policy-making, emphasizing formal treaties and executive decisions. Parliamentary diplomacy enhances influence by involving elected representatives in dialogue, increasing transparency and public accountability in shaping foreign policies. This approach broadens participation, allowing legislative bodies to scrutinize, amend, and legitimize international agreements beyond executive control.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Model
Traditional diplomacy excels in confidentiality and swift decision-making through direct interactions among professional diplomats, but its limitation lies in limited public accountability and reduced transparency. Parliamentary diplomacy enhances democratic legitimacy and public engagement by involving elected representatives in international discussions, yet it often suffers from slower processes and less coherence due to diverse political interests. Balancing the confidentiality and efficiency of traditional diplomacy with the inclusiveness and transparency of parliamentary diplomacy remains a key challenge for modern international relations.
Future Trends in Diplomatic Engagement
Future trends in diplomatic engagement indicate a shift from traditional diplomacy, which relies heavily on formal state-to-state negotiations, towards parliamentary diplomacy that enhances legislative bodies' roles in foreign policy dialogue and decision-making. The rise of digital communication platforms facilitates real-time interaction among parliamentarians across nations, promoting transparency and inclusiveness in diplomatic efforts. Emerging practices emphasize multi-level governance, increased public participation, and issue-specific coalitions, reshaping diplomatic norms and expanding the scope of international cooperation.
Traditional diplomacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com