Parliamentary initiative empowers members of parliament to propose new legislation, shaping policies directly through their submissions. This process enhances democratic engagement by allowing representatives to address constituents' concerns proactively. Explore the full article to understand how your parliamentary initiative can influence lawmaking effectively.
Table of Comparison
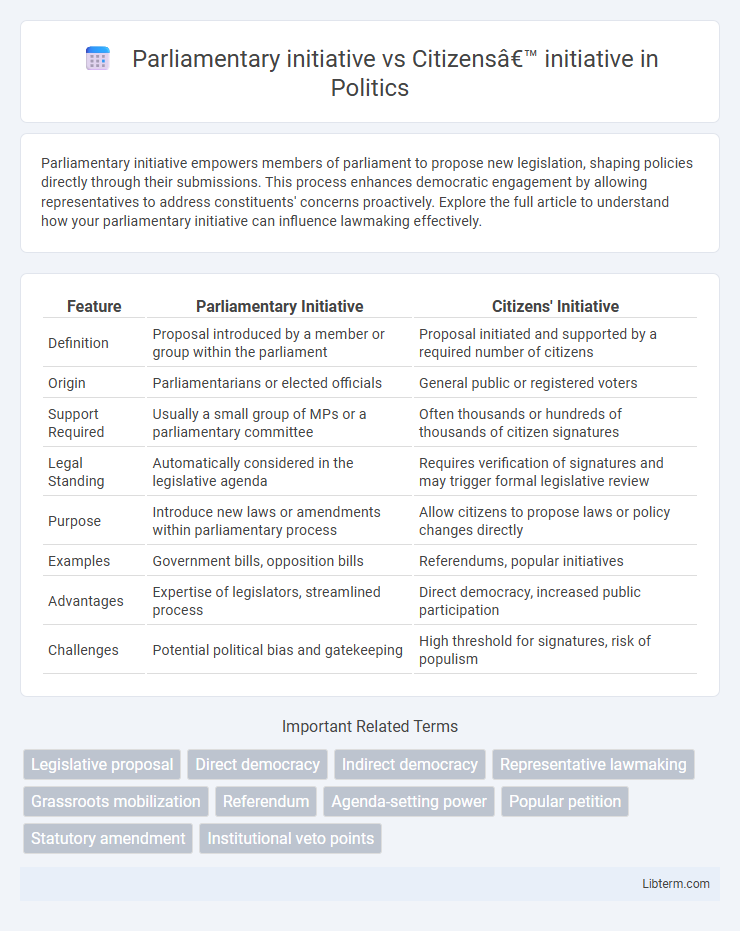
| Feature | Parliamentary Initiative | Citizens' Initiative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proposal introduced by a member or group within the parliament | Proposal initiated and supported by a required number of citizens |
| Origin | Parliamentarians or elected officials | General public or registered voters |
| Support Required | Usually a small group of MPs or a parliamentary committee | Often thousands or hundreds of thousands of citizen signatures |
| Legal Standing | Automatically considered in the legislative agenda | Requires verification of signatures and may trigger formal legislative review |
| Purpose | Introduce new laws or amendments within parliamentary process | Allow citizens to propose laws or policy changes directly |
| Examples | Government bills, opposition bills | Referendums, popular initiatives |
| Advantages | Expertise of legislators, streamlined process | Direct democracy, increased public participation |
| Challenges | Potential political bias and gatekeeping | High threshold for signatures, risk of populism |
Overview of Parliamentary Initiatives
Parliamentary initiatives allow legislators to propose new laws or amendments, reflecting the priorities and expertise of elected representatives. These initiatives typically undergo rigorous scrutiny and debate within parliamentary committees, ensuring detailed examination before voting. The process strengthens representative democracy by enabling parliamentarians to address complex policy issues on behalf of their constituents.
Understanding Citizens’ Initiatives
Citizens' initiatives empower the public to propose legislation by collecting a required number of signatures, fostering direct democratic participation outside parliamentary channels. Unlike parliamentary initiatives, which are introduced solely by elected representatives, citizens' initiatives reflect grassroots priorities and can influence legislative agendas. Understanding citizens' initiatives is crucial for recognizing their role in enhancing civic engagement and accountability in democratic governance.
Historical Context and Development
Parliamentary initiatives originated in European legislative traditions, allowing elected representatives to propose laws as a key democratic function since the 19th century. Citizens' initiatives emerged more recently, gaining prominence in the 20th century as a tool for direct democracy, enabling the electorate to propose legislation or constitutional amendments through petitions. Both instruments have evolved to balance representative and participatory governance, with parliamentary initiatives reflecting institutional authority and citizens' initiatives emphasizing grassroots involvement.
Legal Framework and Requirements
Parliamentary initiatives require sponsorship by one or more members of the legislature and must adhere to procedural rules established by the parliamentary body, often including formal submission and committee review. Citizens' initiatives demand a minimum number of valid signatures from eligible voters, varying by jurisdiction, and are subject to stringent verification processes to qualify for ballot consideration or legislative response. Legal frameworks typically set distinct timelines, scope of subjects, and administrative oversight for both types of initiatives to ensure compliance with democratic and constitutional standards.
Initiation and Proposal Processes
Parliamentary initiatives are proposed and introduced by elected representatives within the legislative body, following formal parliamentary procedures and internal committee reviews. Citizens' initiatives originate from the general public, requiring a specified number of registered voter signatures to qualify for legislative consideration or a referendum. Both processes aim to influence lawmaking but differ in origin, with parliamentary initiatives reflecting political agendas and citizens' initiatives emphasizing direct democratic participation.
Scope and Limitations of Each Initiative
Parliamentary initiatives typically have broader scope and access to legislative processes, allowing elected representatives to propose laws or amendments with procedural support but are limited to parliamentary approval and political dynamics. Citizens' initiatives enable direct public participation by requiring a minimum number of signatures to propose legislation or amendments; however, they often face restrictions on eligible subjects, geographic applicability, and are subject to strict validation and possible parliamentary or referendum hurdles. Both initiatives serve as democratic tools but differ in accessibility, procedural complexity, and influence, with parliamentary initiatives embedded in formal legislative systems and citizens' initiatives offering grassroots influence within legal constraints.
Role of Public Participation
Parliamentary initiatives allow elected representatives to propose legislation, ensuring professional input while incorporating indirect public influence through their electoral accountability. Citizens' initiatives enable direct public participation by allowing voters to propose laws or amendments, empowering grassroots democracy and increasing civic engagement. Both mechanisms enhance democratic processes, but citizens' initiatives provide a more direct channel for public involvement in lawmaking.
Impact on Legislative Outcomes
Parliamentary initiatives often result in higher legislative success rates due to direct backing from elected representatives who hold decision-making power, enabling streamlined proposal adoption. Citizens' initiatives, while fostering greater public engagement and democratic legitimacy, generally face more challenges in influencing legislation because they require additional parliamentary approval and are subject to political negotiation. Statistical analyses reveal that parliamentary initiatives influence approximately 70% of enacted laws, whereas citizens' initiatives contribute to around 15%, highlighting the disparity in legislative impact between the two mechanisms.
Advantages and Challenges
Parliamentary initiatives benefit from clearer legislative framing and greater political support, enabling efficient discussion and potential implementation, while challenges include possible partisan bias and limited public engagement. Citizens' initiatives empower direct democracy by allowing voters to propose laws, enhancing public participation and accountability, but face hurdles such as stringent signature requirements, lack of expert drafting, and slower legislative progress. Both mechanisms provide valuable means for lawmaking, balancing representative authority with grassroots input, yet each involves trade-offs in legitimacy, feasibility, and inclusiveness.
Case Studies and Comparative Analysis
Parliamentary initiatives, exemplified by the UK's Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011, showcase how elected representatives propose legislation reflecting institutional priorities, while citizens' initiatives, such as Switzerland's use of popular referendums, demonstrate direct democratic engagement allowing voters to shape policies. Comparative analysis reveals that parliamentary initiatives often ensure expert scrutiny and political feasibility, whereas citizens' initiatives enhance public participation but may face challenges in complexity and implementation. Case studies from Germany and California highlight varied success rates and political impacts, emphasizing the balance between representative decision-making and grassroots influence in legislative processes.
Parliamentary initiative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com