Loyalists were American colonists who remained steadfastly supportive of the British Crown during the Revolutionary War, often facing social ostracism and property confiscation. Their complex motivations ranged from economic interests to cultural ties and fear of instability. Discover how Loyalists influenced the outcome of the revolution and shaped early American society in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
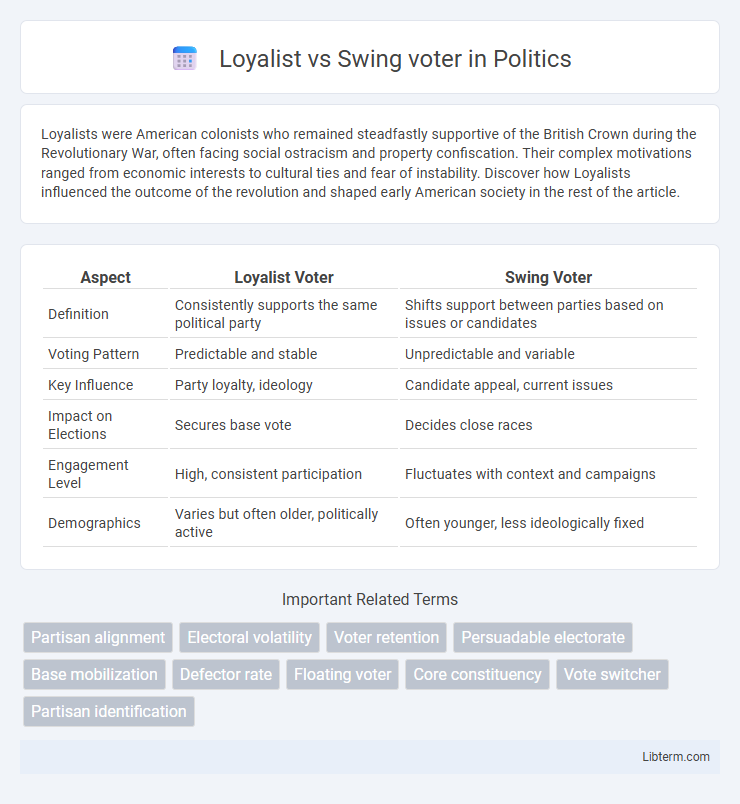
| Aspect | Loyalist Voter | Swing Voter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistently supports the same political party | Shifts support between parties based on issues or candidates |
| Voting Pattern | Predictable and stable | Unpredictable and variable |
| Key Influence | Party loyalty, ideology | Candidate appeal, current issues |
| Impact on Elections | Secures base vote | Decides close races |
| Engagement Level | High, consistent participation | Fluctuates with context and campaigns |
| Demographics | Varies but often older, politically active | Often younger, less ideologically fixed |
Understanding Loyalist Voters
Loyalist voters consistently support a single political party or candidate due to strong ideological alignment, emotional attachment, or long-standing loyalty. These voters tend to prioritize party identity and policies that reinforce their values, making them less susceptible to campaign swings or temporary political trends. Understanding loyalist voters involves analyzing demographic patterns, voting history, and core issues that solidify their unwavering support, which is crucial for targeted campaign strategies.
Defining Swing Voters
Swing voters, also known as undecided or floating voters, do not consistently align with a single political party and often decide their vote based on current issues or candidate appeal. They represent a crucial segment in elections, typically ranging from 10% to 20% of the electorate, capable of swinging the outcome in tightly contested races. Unlike loyalist voters, who exhibit strong, habitual support for a particular party, swing voters' preferences are fluid and influenced by campaign dynamics, media coverage, and real-time political events.
Key Characteristics of Loyalists
Loyalist voters consistently support the same political party across multiple election cycles, demonstrating strong party identification and high voter turnout rates. They exhibit resistance to changing their preferred candidate or party despite shifts in political climate or policy platforms, reflecting deep ideological alignment. Their voting patterns provide predictive insights for party base reliability and long-term electoral strategy planning.
Traits of Swing Voters
Swing voters exhibit high electoral volatility, often undecided until close to elections, reflecting their openness to multiple political perspectives. Their demographic diversity includes younger adults, suburban residents, and moderate-income groups who prioritize current issues over party loyalty. Behavioral traits emphasize issue-based decision-making, susceptibility to campaign influence, and fluctuating political engagement levels.
Voting Patterns: Loyalist vs Swing Voter
Loyalist voters consistently support the same political party across multiple election cycles, demonstrating predictable voting patterns influenced by long-term party identification and ideological alignment. Swing voters, however, exhibit fluctuating voting behavior, shifting their support based on candidate appeal, issue salience, and current political climate, making them critical in determining election outcomes. Understanding the distinct motivations and demographic profiles of loyalist versus swing voters is essential for targeted campaign strategies and accurate electoral forecasting.
Influence on Election Outcomes
Loyalist voters consistently support a particular political party, providing a stable base that candidates rely on to secure initial votes and maintain core support throughout election campaigns. Swing voters, who do not have a fixed party allegiance, play a crucial role in determining election outcomes by shifting their votes based on current issues, candidate appeal, and campaign effectiveness. The influence of swing voters is amplified in closely contested districts, where their decisions can tip the balance and ultimately decide which party wins control.
Campaign Strategies for Each Group
Campaign strategies targeting loyalist voters emphasize reinforcing party loyalty through personalized communication, consistent messaging, and engagement in core issues that resonate deeply with this group. For swing voters, campaigns prioritize data-driven outreach, focusing on persuasive messaging that highlights moderate policies, candidate trustworthiness, and addressing pivotal local concerns to shift undecided opinions. Tailoring outreach efforts using voter segmentation and behavioral analytics maximizes influence on each group's voting decisions.
Psychological Motivations Behind Voting
Loyalist voters are driven primarily by strong party identification and emotional attachment, which provides a sense of identity and consistency in their political choices. Swing voters exhibit more flexible psychological motivations, often influenced by issue salience, candidate evaluations, and situational factors that trigger rational and affective responses. Cognitive biases like confirmation bias and motivated reasoning shape how both groups process political information, but swing voters demonstrate greater susceptibility to changing attitudes based on campaign dynamics and current events.
Historical Shifts: Loyalists and Swing Voters
Historical shifts reveal that loyalist voters consistently support their preferred party due to strong ideological alignment and identity, whereas swing voters display variable preferences influenced by socio-economic changes and pivotal political events. Data from multiple U.S. elections indicate swing voter percentages fluctuate between 15-30%, playing a decisive role in election outcomes. Studies show that demographic shifts, such as urbanization and education levels, significantly impact the size and behavior of swing voter groups compared to stable loyalist bases.
The Future of Voter Loyalty and Volatility
Voter loyalty is expected to decline as swing voters grow in influence, driven by increasing access to diverse information sources and shifting socio-political dynamics. Political parties must adapt strategies by targeting volatile voter segments through personalized messaging and data analytics to secure election outcomes. The future landscape will emphasize fluid voter behavior, making predictive modeling and real-time engagement critical for maintaining electoral advantage.
Loyalist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com