Political cronyism undermines democratic institutions by prioritizing loyalty over merit, leading to inefficient governance and corruption. This practice often results in favoritism, where friends and allies receive undue advantages, eroding public trust and fairness. Discover how political cronyism impacts society and what you can learn to recognize and challenge it in the rest of this article.
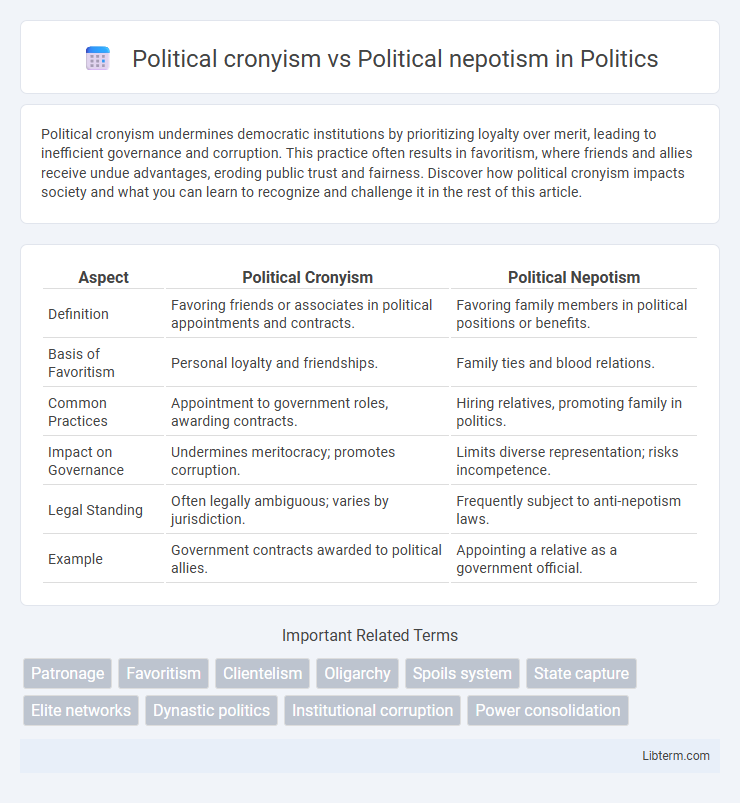
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Political Cronyism | Political Nepotism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Favoring friends or associates in political appointments and contracts. | Favoring family members in political positions or benefits. |
| Basis of Favoritism | Personal loyalty and friendships. | Family ties and blood relations. |
| Common Practices | Appointment to government roles, awarding contracts. | Hiring relatives, promoting family in politics. |
| Impact on Governance | Undermines meritocracy; promotes corruption. | Limits diverse representation; risks incompetence. |
| Legal Standing | Often legally ambiguous; varies by jurisdiction. | Frequently subject to anti-nepotism laws. |
| Example | Government contracts awarded to political allies. | Appointing a relative as a government official. |
Defining Political Cronyism and Political Nepotism
Political cronyism involves favoring friends or associates in governmental appointments or contracts without regard for qualifications, often leading to corruption and inefficiency. Political nepotism specifically refers to preferential treatment given to relatives in political positions, undermining meritocracy and transparency. Both practices erode public trust by prioritizing personal relationships over competency and fairness.
Historical Context of Cronyism and Nepotism
Political cronyism traces back to ancient Greece and Rome, where leaders appointed loyal friends to key government positions, often bypassing meritocratic principles. Nepotism, derived from the Latin word "nepos" meaning nephew, historically emerged during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, notably within the Catholic Church, where popes appointed relatives to ecclesiastical offices to consolidate power. Both practices have persisted globally, shaping political structures by privileging personal connections over competence and influencing governance and public trust throughout history.
Key Differences Between Cronyism and Nepotism
Political cronyism involves favoring close friends and associates with political power or benefits, whereas political nepotism specifically pertains to favoritism toward family members. Cronyism is generally broader, encompassing non-relatives who share personal or ideological loyalties, while nepotism is restricted to kinship ties. The key difference lies in the relationship basis: cronyism is built on friendships or alliances, nepotism on blood relations.
Notable Global Examples of Political Cronyism
Notable global examples of political cronyism include the widespread allegations in Russia, where close associates of Vladimir Putin have been granted lucrative state contracts and business monopolies. In India, the 2G spectrum case highlighted cronyism involving business leaders with political ties receiving preferential treatment, costing billions in public revenue. Brazil's Operation Car Wash scandal exposed extensive crony networks between politicians and construction firms, resulting in corruption charges against numerous high-profile figures.
High-Profile Cases of Political Nepotism
High-profile cases of political nepotism often involve leaders appointing family members to key government positions regardless of merit, undermining institutional integrity and public trust. Examples include the Marcos family in the Philippines and the Bhutto family in Pakistan, where relatives hold influential roles across generations. Such nepotism contrasts with political cronyism, which centers on favoritism toward friends and allies rather than kinship ties.
Impacts on Governance and Public Trust
Political cronyism undermines governance by promoting unqualified individuals based on loyalty rather than merit, leading to inefficiency and corruption. Political nepotism erodes public trust as it privileges family members over deserving candidates, fostering perceptions of injustice and favoritism. Both practices weaken institutional integrity and hinder transparent decision-making, damaging democratic accountability.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Political cronyism involves favoring friends or associates in government appointments and contracts, often leading to legal violations such as corruption and abuse of power statutes. Political nepotism, the practice of awarding positions or benefits to family members, raises significant ethical concerns about fairness and conflicts of interest, frequently breaching anti-nepotism laws and regulations. Both practices undermine public trust, violate principles of meritocracy, and can result in legal penalties including fines, removal from office, or criminal charges.
Strategies to Combat Cronyism and Nepotism
Strategies to combat political cronyism and nepotism include enforcing transparent recruitment processes based on meritocracy and implementing strict anti-corruption laws with independent oversight bodies. Public sector audits, whistleblower protection programs, and digital transparency platforms enhance accountability by exposing favoritism in hiring and contracting. Strengthening civil society engagement and promoting democratic norms also help reduce the influence of personal relationships in political appointments.
Role of Media in Exposing Favoritism
The media plays a crucial role in exposing political cronyism and nepotism by investigating and publicizing instances where public officials favor friends or relatives in appointments and contracts. Investigative journalism uncovers patterns of favoritism that undermine meritocracy and transparency, prompting public scrutiny and accountability. Media coverage increases awareness and pressure on political systems to implement reforms that prevent corrupt practices in governance.
Future Outlook: Reform and Accountability
Political cronyism and nepotism threaten democratic integrity by prioritizing personal connections over meritocratic governance. Future reforms emphasize transparency measures, stricter conflict-of-interest laws, and independent oversight bodies to enhance accountability in political appointments. Advancements in digital governance and civic engagement platforms contribute to monitoring and curbing these practices globally.
Political cronyism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com