Supranationalism empowers multiple countries to collaborate under a unified authority, transcending national borders for collective decision-making. This approach enhances global cooperation on economic, political, and social issues, promoting stability and shared prosperity. Discover how supranationalism influences international relations and impacts Your world by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
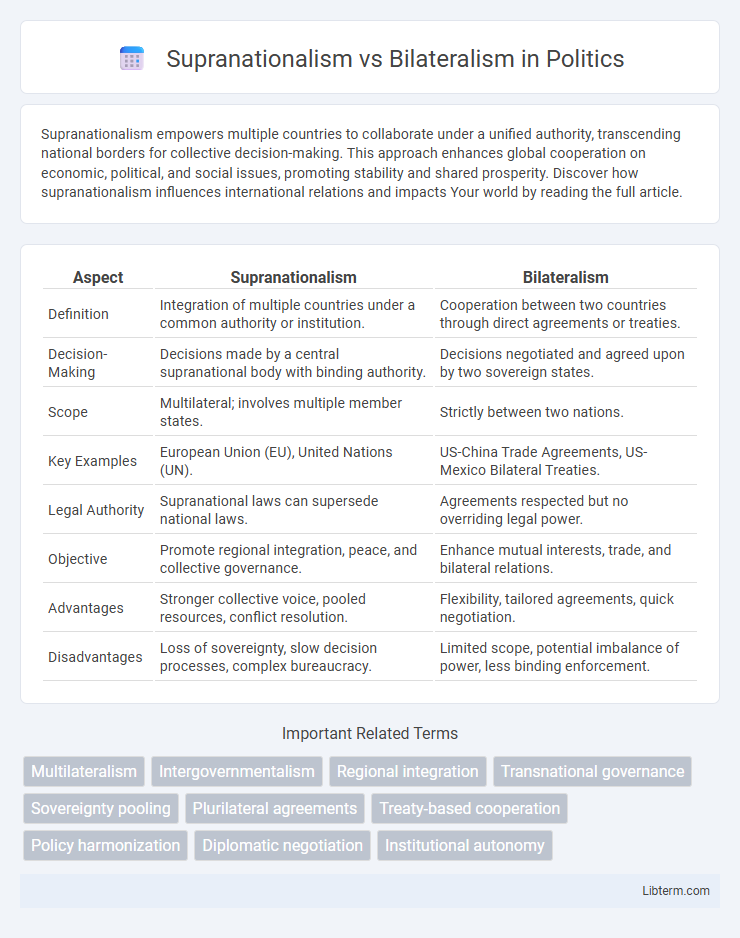
| Aspect | Supranationalism | Bilateralism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of multiple countries under a common authority or institution. | Cooperation between two countries through direct agreements or treaties. |
| Decision-Making | Decisions made by a central supranational body with binding authority. | Decisions negotiated and agreed upon by two sovereign states. |
| Scope | Multilateral; involves multiple member states. | Strictly between two nations. |
| Key Examples | European Union (EU), United Nations (UN). | US-China Trade Agreements, US-Mexico Bilateral Treaties. |
| Legal Authority | Supranational laws can supersede national laws. | Agreements respected but no overriding legal power. |
| Objective | Promote regional integration, peace, and collective governance. | Enhance mutual interests, trade, and bilateral relations. |
| Advantages | Stronger collective voice, pooled resources, conflict resolution. | Flexibility, tailored agreements, quick negotiation. |
| Disadvantages | Loss of sovereignty, slow decision processes, complex bureaucracy. | Limited scope, potential imbalance of power, less binding enforcement. |
Understanding Supranationalism: Definition and Key Features
Supranationalism refers to a form of multinational cooperation where independent states delegate authority to an overarching organization with the power to make decisions binding on member states. Key features include shared sovereignty, collective decision-making, and institutional mechanisms that enforce compliance and enable integration beyond national borders. This contrasts with bilateralism, which involves direct, two-party agreements without broader institutional involvement or binding authority over multiple states.
Bilateralism Explained: Foundations and Characteristics
Bilateralism is a diplomatic approach where two countries engage in direct negotiations and agreements to address specific issues, fostering mutual benefits and tailored cooperation. Its foundations lie in sovereignty preservation, enabling states to maintain control over their foreign policies without external interference. Key characteristics include exclusivity, flexibility, and a focus on pragmatic solutions tailored to the unique interests and circumstances of the involved parties.
Historical Evolution of Supranational Organizations
Supranationalism emerged after World War II as a response to the failures of bilateral agreements, with organizations like the European Coal and Steel Community laying the foundation for deeper political and economic integration among multiple states. The historical evolution of supranational organizations is marked by milestones such as the formation of the European Union, which exemplifies pooled sovereignty aimed at promoting peace, stability, and economic cooperation beyond bilateral treaties. This shift from bilateralism to supranational governance reflects a growing emphasis on collective decision-making and shared authority to address transnational challenges.
The Role of Bilateral Agreements in Global Politics
Bilateral agreements play a crucial role in global politics by allowing two countries to negotiate terms tailored specifically to their mutual interests, ranging from trade to security cooperation. These agreements enable more flexible and direct diplomacy, bypassing the complexities and slower decision-making processes often associated with supranational organizations. By fostering targeted partnerships, bilateralism can complement broader multilateral frameworks and address specific geopolitical priorities effectively.
Comparative Analysis: Supranationalism vs Bilateralism
Supranationalism involves multiple countries ceding authority to an overarching institution, enhancing collective decision-making on regional or global issues, while bilateralism centers on direct agreements between two nations prioritizing tailored cooperation. Supranational entities like the European Union enable binding policies that promote integration and collective benefits, contrasting with bilateral agreements that offer flexibility and specificity but may lack broader regional impact. The comparative analysis highlights supranationalism's strength in multilateral coordination versus bilateralism's advantage in customized, direct diplomatic relations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Supranationalism
Supranationalism offers advantages such as enhanced cooperation among multiple nations, leading to collective decision-making and stronger political and economic integration, which can improve regional stability and promote shared prosperity. However, its disadvantages include the potential loss of national sovereignty, slower decision-making processes due to the need for consensus, and the risk of disproportionate influence by more powerful member states. This contrasts with bilateralism, where agreements between two countries allow for more tailored and flexible arrangements but may lack the broader benefits of multilateral collaboration.
Strengths and Limitations of Bilateralism
Bilateralism offers tailored agreements between two nations, enabling precise negotiation on trade, security, or environmental issues that reflect each country's unique interests and policy frameworks. Its strength lies in fostering strong diplomatic relations and quicker decision-making processes due to the limited number of actors involved. However, bilateral agreements may lack broader regional or global impact, can result in inconsistent standards, and risk excluding smaller or less powerful nations from critical international discussions.
Case Studies: Successful Supranational Initiatives
The European Union exemplifies successful supranationalism by enabling member states to delegate sovereignty for common economic and political goals, illustrated by the creation of the Eurozone and Schengen Area. The ASEAN Economic Community demonstrates regional integration through policy harmonization and dispute resolution mechanisms, enhancing trade and investment flows among Southeast Asian nations. These cases highlight how pooling authority beyond bilateral agreements fosters comprehensive cooperation and sustainable development.
Notable Bilateral Pacts: Examples and Impacts
Notable bilateral pacts such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the US-China Phase One Trade Deal demonstrate the strategic importance of direct state-to-state agreements in enhancing economic cooperation and addressing specific bilateral issues. These pacts often result in tailored trade benefits, dispute resolution mechanisms, and enhanced diplomatic ties, providing flexibility that supranational agreements may lack. The impacts include increased trade volumes, investment flows, and sometimes geopolitical shifts, highlighting bilateralism's role in shaping international relations.
Future Prospects: The Balance Between Supranationalism and Bilateralism
The future prospects of international relations hinge on balancing supranationalism's collective decision-making with bilateralism's targeted diplomacy, offering both unified policy frameworks and tailored agreements. Supranational institutions like the European Union facilitate comprehensive regulatory standards and economic integration, while bilateral agreements enable flexibility and specificity in addressing unique national interests. Navigating the interplay between these models will determine the effectiveness of global governance amid evolving geopolitical challenges and economic interdependence.
Supranationalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com