A coalition of principle unites individuals or groups around shared core values rather than temporary interests, fostering long-term collaboration and trust. Such alliances prioritize integrity and common goals, strengthening collective impact in political or social movements. Discover how your participation in a coalition of principle can drive meaningful change by reading the full article.
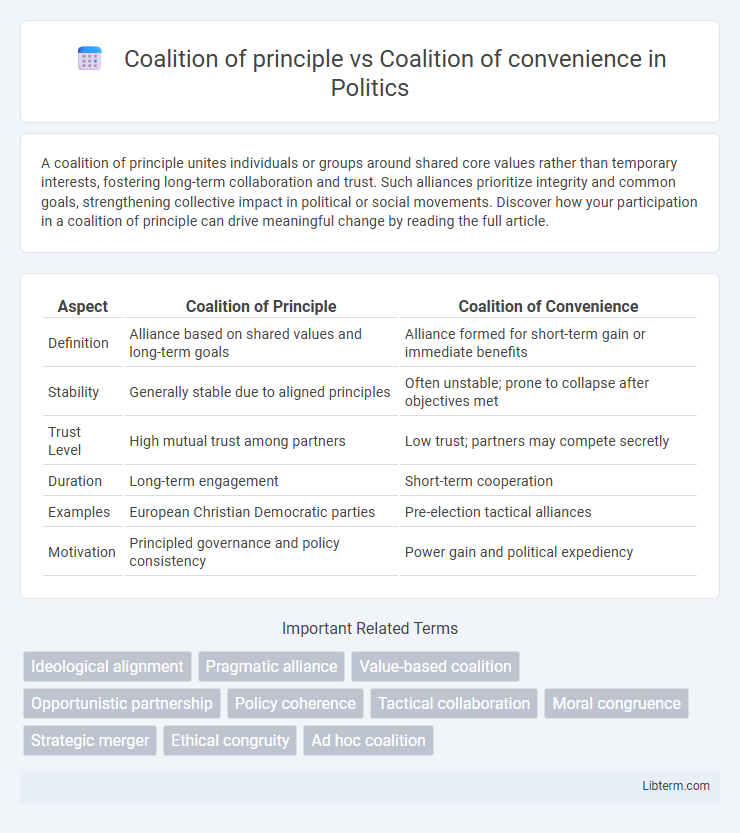
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Coalition of Principle | Coalition of Convenience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alliance based on shared values and long-term goals | Alliance formed for short-term gain or immediate benefits |
| Stability | Generally stable due to aligned principles | Often unstable; prone to collapse after objectives met |
| Trust Level | High mutual trust among partners | Low trust; partners may compete secretly |
| Duration | Long-term engagement | Short-term cooperation |
| Examples | European Christian Democratic parties | Pre-election tactical alliances |
| Motivation | Principled governance and policy consistency | Power gain and political expediency |
Defining Coalitions of Principle
Coalitions of principle are alliances formed based on shared core values, long-term goals, and mutual trust between parties, emphasizing ideological alignment over short-term benefits. These coalitions prioritize consistent policy objectives and commitment to a common vision, fostering stability and cooperation in governance or advocacy. In contrast, coalitions of convenience are temporary and driven by immediate advantages, often lacking deep ideological unity.
Understanding Coalitions of Convenience
Coalitions of convenience form when parties temporarily unite based on shared, short-term interests rather than deep ideological alignment, often prioritizing immediate strategic advantages over long-term goals. Understanding coalitions of convenience involves analyzing the motivations behind such alliances, where pragmatic compromises and situational benefits drive cooperation despite underlying differences. These coalitions tend to be fragile and subject to dissolution once the common advantage dissipates or conflicting priorities resurface.
Key Differences Between Principle and Convenience Coalitions
Coalitions of principle are formed based on shared values, ideologies, or long-term goals, fostering strong internal cohesion and consistent policy agendas. Coalitions of convenience arise from temporary alliances driven by immediate benefits or strategic gains, often resulting in fragile partnerships prone to conflict once the objective is achieved. The key differences lie in the durability, motivation, and ideological alignment, with principle-based coalitions emphasizing trust and shared vision, while convenience coalitions prioritize pragmatic, short-term advantages.
Historical Examples of Principle-Based Coalitions
Principle-based coalitions prioritize shared values and long-term goals over short-term gains, as exemplified by the Allied Powers during World War II, who united to defeat totalitarian regimes and promote democracy. Another significant example is the anti-apartheid coalition in South Africa, where diverse groups joined forces based on the principle of racial equality and human rights. These coalitions tend to have greater resilience and enduring impact due to their foundational commitment to core principles.
Notable Cases of Convenience-Driven Alliances
Convenience-driven alliances often emerge in geopolitical contexts where temporary objectives override ideological differences, such as the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union in 1939. Another notable case includes the U.S.-Soviet cooperation during World War II to defeat Nazi Germany despite profound ideological opposition. These coalitions highlight strategic expediency as the primary factor, rather than shared principles or long-term alignment.
Motivations Behind Coalition Building
Motivations behind coalition building differ significantly between a coalition of principle, which is driven by shared ideology, values, and long-term policy goals, and a coalition of convenience, formed primarily for short-term gains, such as winning elections or achieving specific legislative outcomes. Coalitions of principle prioritize ideological compatibility and trust, ensuring stability and coherence, whereas coalitions of convenience prioritize pragmatic alliances, often compromising principles for immediate strategic advantage. Understanding these motivations is crucial for analyzing political stability, policy consistency, and governance effectiveness in various political systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Coalition Type
A Coalition of Principle offers stability and long-term commitment by uniting parties with shared ideologies, which enhances policy coherence and voter trust, but it may limit flexibility and slow decision-making due to ideological rigidity. A Coalition of Convenience allows for pragmatic alliances based on short-term goals, increasing adaptability and faster consensus on specific issues, yet it risks internal conflicts and diminished public credibility due to divergent agendas. Both types impact political dynamics differently: principle-based coalitions foster consistent governance, while convenience coalitions emphasize tactical advantage but face potential instability.
Impact on Political Stability and Policy Outcomes
Coalitions of principle typically enhance political stability by fostering long-term alliances rooted in shared ideologies, which facilitate consistent and coherent policy outcomes. In contrast, coalitions of convenience often result in fragile governments prone to breakdowns, causing policy inconsistency and frequent shifts that undermine effective governance. The durability and ideological alignment of coalitions significantly influence both the steadiness of political environments and the quality of legislative decisions.
Challenges in Sustaining Coalition Unity
Coalitions of principle often struggle with maintaining unity due to rigid ideological stances that limit compromise, increasing the risk of internal conflicts over core values. In contrast, coalitions of convenience face challenges in sustaining commitment once the immediate shared interest is achieved, as differing agendas may lead to fragmentation. Both types encounter difficulties in balancing individual member goals with the coalition's collective objectives, affecting long-term cohesion and effectiveness.
Future Trends in Coalition Formation
Future trends in coalition formation indicate a rise in coalitions of convenience, driven by short-term policy goals and shifting political landscapes rather than shared core values. Advances in data analytics and real-time communication technologies enable more dynamic and flexible coalition-building strategies, allowing actors to rapidly adapt partnerships based on immediate interests. However, the durability and effectiveness of coalitions of principle, grounded in ideological alignment, may become increasingly vital for long-term governance stability amid growing political polarization.
Coalition of principle Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com