Conservative principles emphasize preserving traditional values, promoting stability, and advocating for limited government intervention in economic and social matters. This approach often prioritizes individual responsibility, free markets, and a cautious stance toward change. Explore the rest of the article to understand how conservative ideas shape policies and impact your community.
Table of Comparison
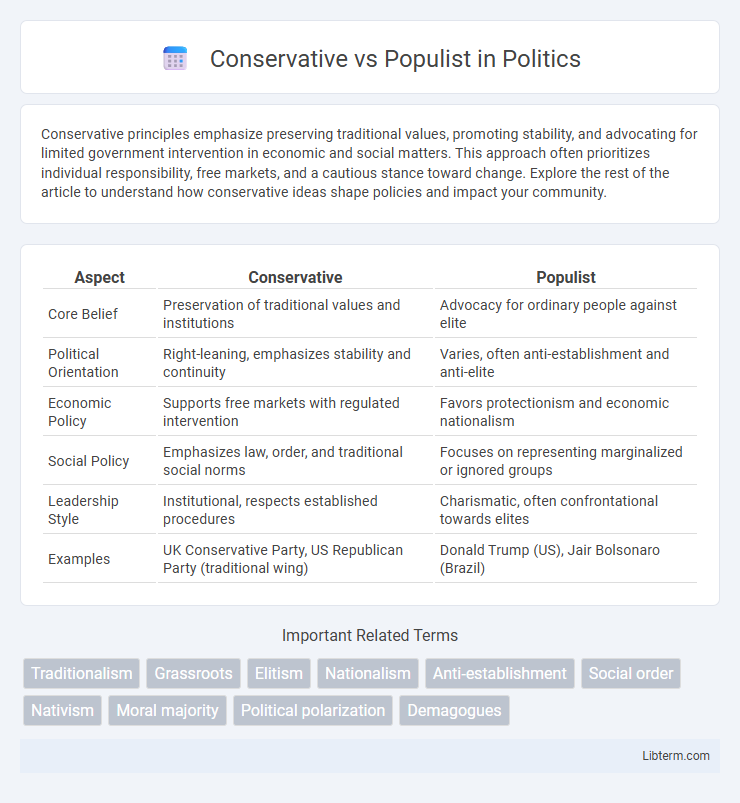
| Aspect | Conservative | Populist |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Preservation of traditional values and institutions | Advocacy for ordinary people against elite |
| Political Orientation | Right-leaning, emphasizes stability and continuity | Varies, often anti-establishment and anti-elite |
| Economic Policy | Supports free markets with regulated intervention | Favors protectionism and economic nationalism |
| Social Policy | Emphasizes law, order, and traditional social norms | Focuses on representing marginalized or ignored groups |
| Leadership Style | Institutional, respects established procedures | Charismatic, often confrontational towards elites |
| Examples | UK Conservative Party, US Republican Party (traditional wing) | Donald Trump (US), Jair Bolsonaro (Brazil) |
Defining Conservatism and Populism
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, values, and social order, promoting gradual change while resisting radical transformations. Populism centers on appealing directly to the general populace, often positioning itself against perceived elite control and advocating for the voice of "ordinary people." Both ideologies influence political dynamics but differ fundamentally in their approach to authority, social change, and governance.
Historical Roots of Conservative and Populist Movements
Conservative movements trace their historical roots to the preservation of traditional social orders and institutions, notably emerging from 18th-century European reactions to the French Revolution. Populist movements, by contrast, often arise from grassroots unrest and economic disparities, rooted in late 19th and 20th-century responses to industrialization and perceived elite corruption. While conservatism emphasizes continuity and stability, populism champions direct popular support and challenges to established elites.
Core Principles of Conservative Ideology
Conservative ideology centers on preserving traditional social institutions, advocating for limited government intervention, and emphasizing individual responsibility and free-market principles. It prioritizes stability, gradual change, and respect for established norms while upholding rule of law and national sovereignty. Core conservative values include fiscal discipline, strong defense, and the protection of personal freedoms within a structured societal framework.
Key Characteristics of Populism
Populism is characterized by a strong emphasis on representing the interests of "the common people" against a perceived corrupt elite, often employing direct and emotional rhetoric. It typically features anti-establishment sentiments, charismatic leadership, and calls for greater popular participation in political decision-making. Populist movements prioritize national identity, economic protectionism, and skepticism towards globalization and traditional political institutions.
Major Differences Between Conservatives and Populists
Conservatives emphasize preserving traditional institutions, promoting gradual change, and upholding established social norms, while populists focus on mobilizing the common people against perceived elites and advocating for rapid political or economic reform. Conservatives tend to prioritize stability, rule of law, and free-market principles, whereas populists often challenge existing power structures and support interventionist policies to address inequality. The ideological foundation of conservatism rests on maintaining continuity, contrasting with populism's emphasis on direct democracy and responsiveness to popular will.
Influential Leaders: Conservative vs Populist Figures
Conservative influential leaders like Ronald Reagan and Margaret Thatcher emphasized free-market principles, traditional values, and limited government intervention, shaping policies that prioritize stability and economic growth. Populist figures such as Donald Trump and Jair Bolsonaro galvanize mass support by challenging elite establishments, promoting nationalist rhetoric, and addressing the concerns of marginalized groups. The distinct leadership styles highlight conservatives' preference for institutional continuity versus populists' appeal to popular sovereignty and direct political engagement.
Policy Approaches: Economy, Society, and Governance
Conservative policy approaches emphasize free-market capitalism, limited government intervention, and fiscal responsibility to foster economic stability and growth. Populist policies prioritize economic redistribution, protectionism, and social welfare programs aimed at addressing inequality and empowering marginalized communities. Governance in conservatism stresses rule of law, institutional continuity, and decentralized authority, while populism advocates for direct citizen involvement and challenges established elites to increase political responsiveness.
Electoral Impact and Public Support
Conservative parties typically maintain stable electoral support through established voter bases prioritizing traditional values and institutional continuity. Populist movements often disrupt conventional voting patterns by appealing to widespread dissatisfaction with elites and promising radical change, leading to fluctuating but intense bursts of public support. Electoral outcomes for populists are highly context-dependent, with their impact magnified during periods of economic uncertainty or political scandal.
Challenges and Criticisms Facing Both Movements
Conservative movements often face criticism for resisting social change and being perceived as out of touch with evolving cultural norms, leading to challenges in appealing to younger demographics. Populist movements encounter difficulties combating accusations of oversimplifying complex political issues and fostering division through anti-establishment rhetoric. Both movements struggle with balancing core ideological principles while addressing the demands of increasingly diverse and polarized electorates.
The Future of Conservatism and Populism
The future of conservatism hinges on adapting core principles like limited government and fiscal responsibility to address contemporary social and economic challenges without alienating emerging voter demographics. Populism's future will likely involve balancing charismatic grassroots appeal with establishing sustainable policy frameworks that resist authoritarian tendencies. Both movements must navigate the interplay between maintaining ideological purity and achieving pragmatic governance to remain influential in evolving political landscapes.
Conservative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com