A stable democracy thrives on active citizen participation, transparent governance, and the protection of fundamental rights. These elements foster trust between the government and its people, ensuring political stability and social cohesion. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your engagement can strengthen democratic systems worldwide.
Table of Comparison
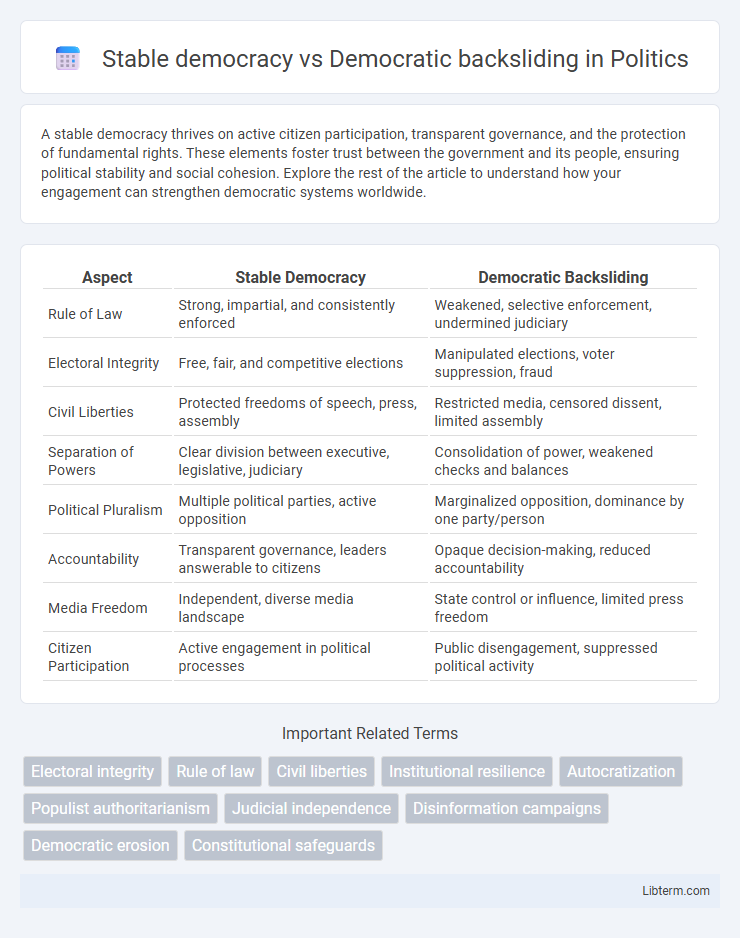
| Aspect | Stable Democracy | Democratic Backsliding |
|---|---|---|
| Rule of Law | Strong, impartial, and consistently enforced | Weakened, selective enforcement, undermined judiciary |
| Electoral Integrity | Free, fair, and competitive elections | Manipulated elections, voter suppression, fraud |
| Civil Liberties | Protected freedoms of speech, press, assembly | Restricted media, censored dissent, limited assembly |
| Separation of Powers | Clear division between executive, legislative, judiciary | Consolidation of power, weakened checks and balances |
| Political Pluralism | Multiple political parties, active opposition | Marginalized opposition, dominance by one party/person |
| Accountability | Transparent governance, leaders answerable to citizens | Opaque decision-making, reduced accountability |
| Media Freedom | Independent, diverse media landscape | State control or influence, limited press freedom |
| Citizen Participation | Active engagement in political processes | Public disengagement, suppressed political activity |
Defining Stable Democracy and Democratic Backsliding
Stable democracy is characterized by consistent adherence to democratic norms, peaceful transfers of power, and strong institutional frameworks that protect civil liberties and political rights. Democratic backsliding refers to the gradual erosion of these democratic principles, often marked by weakened rule of law, restricted press freedom, and undermined electoral integrity. Key indicators distinguishing stable democracy from backsliding include institutional resilience, protection of minority rights, and sustained public trust in democratic processes.
Key Features of Stable Democracies
Stable democracies exhibit key features such as consistent adherence to constitutional rule, protection of civil liberties, and transparent electoral processes ensuring free and fair elections. Independent judiciary systems and effective checks and balances prevent abuses of power and maintain political accountability. High levels of political participation, media freedom, and respect for minority rights further reinforce democratic stability.
Warning Signs of Democratic Backsliding
Warning signs of democratic backsliding include undermining judicial independence, restricting press freedom, and eroding electoral integrity through voter suppression or manipulation. Persistent attacks on civil liberties and political opposition signal weakening democratic norms. Monitoring these indicators is crucial for assessing the stability and resilience of democratic institutions.
Historical Examples of Each Trajectory
The Weimar Republic exemplifies democratic backsliding, collapsing into Nazi dictatorship due to economic instability and weak institutions. In contrast, post-war West Germany demonstrates a stable democracy through robust constitutional frameworks and economic recovery. Similarly, Chile's democratic regression during Pinochet's regime contrasts with Costa Rica's longstanding stable democracy, marked by continuous peaceful transitions of power.
Causes Behind Democratic Stability
Robust institutions, an independent judiciary, and free press play critical roles in maintaining stable democracy by ensuring accountability and protecting civil liberties. High levels of political participation and inclusive governance foster citizen trust and prevent the erosion of democratic norms. Economic stability and education also contribute significantly to democratic resilience by reducing social unrest and encouraging informed electoral choices.
Factors Contributing to Democratic Erosion
Factors contributing to democratic erosion include weakening institutions, declining public trust, and the rise of populist leaders who undermine checks and balances. Economic instability and political polarization exacerbate vulnerabilities in democratic systems, leading to erosion of civil liberties and judicial independence. Media manipulation and erosion of electoral integrity further accelerate democratic backsliding in previously stable democracies.
Comparative Analysis: Economic and Social Outcomes
Stable democracies tend to exhibit higher levels of economic growth and social welfare due to effective governance, transparency, and robust institutions. Democratic backsliding often correlates with increased corruption, economic volatility, and weakened social safety nets, undermining public trust and development. Comparative analysis shows that countries with stable democratic frameworks consistently outperform those experiencing democratic erosion in both GDP growth rates and social equality indices.
Role of Institutions in Safeguarding Democracy
Strong institutions like independent judiciaries, free press, and transparent electoral systems act as critical safeguards preventing democratic backsliding by enforcing the rule of law and protecting civil liberties. In stable democracies, these institutions maintain accountability and prevent the concentration of power, ensuring government actions align with constitutional principles. Weak or compromised institutions often lead to erosion of democratic norms, enabling authoritarian tendencies and undermining public trust in governance.
Case Studies: Countries at Risk
Countries at risk of democratic backsliding, such as Hungary and Turkey, exhibit erosion in judicial independence, media freedom, and electoral integrity, signaling a shift away from stable democracy. Stable democracies like Canada and Germany maintain robust institutional checks, transparent governance, and active civil societies that safeguard democratic processes. Comparative case studies reveal that the weakening of democratic norms often correlates with increased authoritarian tendencies and diminished public trust in democratic institutions.
Strategies to Prevent Democratic Backsliding
Implementing robust checks and balances, strengthening independent institutions, and ensuring judicial independence are critical strategies to prevent democratic backsliding. Promoting civic education and sustaining a vibrant civil society help maintain public support for democratic norms. Transparent electoral processes and protections for free media further safeguard against authoritarian tendencies.
Stable democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com