The red-yellow alliance represents a strategic partnership between left-wing and liberal political groups, aiming to promote progressive social policies and economic reforms. This collaboration often emphasizes sustainability, social justice, and inclusive governance, seeking to balance diverse political interests for effective policymaking. Explore the full article to understand how the red-yellow alliance impacts current political landscapes and what it means for your community.
Table of Comparison
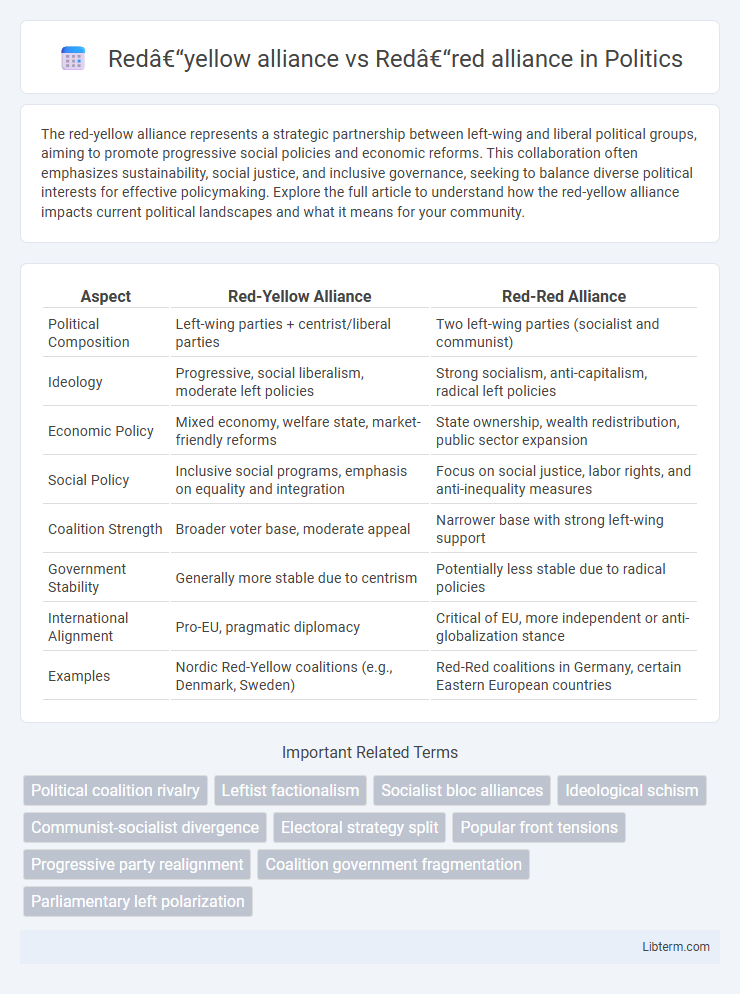
| Aspect | Red-Yellow Alliance | Red-Red Alliance |
|---|---|---|
| Political Composition | Left-wing parties + centrist/liberal parties | Two left-wing parties (socialist and communist) |
| Ideology | Progressive, social liberalism, moderate left policies | Strong socialism, anti-capitalism, radical left policies |
| Economic Policy | Mixed economy, welfare state, market-friendly reforms | State ownership, wealth redistribution, public sector expansion |
| Social Policy | Inclusive social programs, emphasis on equality and integration | Focus on social justice, labor rights, and anti-inequality measures |
| Coalition Strength | Broader voter base, moderate appeal | Narrower base with strong left-wing support |
| Government Stability | Generally more stable due to centrism | Potentially less stable due to radical policies |
| International Alignment | Pro-EU, pragmatic diplomacy | Critical of EU, more independent or anti-globalization stance |
| Examples | Nordic Red-Yellow coalitions (e.g., Denmark, Sweden) | Red-Red coalitions in Germany, certain Eastern European countries |
Introduction to Political Alliances
The Red-yellow alliance typically consists of leftist parties collaborating with centrist or liberal groups to promote social democracy and economic reform, emphasizing progressive policies and inclusivity. In contrast, the Red-red alliance unites various left-wing factions, often including socialist and communist parties, focusing on more radical socialist agendas and systemic change. Political alliances like these shape electoral strategies and policy priorities by merging distinct ideological perspectives within the broader left spectrum.
Defining the Red–Yellow Alliance
The Red-Yellow Alliance refers to a political coalition between left-wing parties (Red) and centrist or liberal parties (Yellow) aiming to combine progressive social policies with moderate economic reforms. This alliance typically emphasizes consensus-building and pragmatic governance, contrasting with the Red-Red Alliance, which involves exclusively left-wing parties advocating for more radical socialist policies. The Red-Yellow Alliance balances social justice goals with market-friendly approaches, appealing to a broader electorate than the more ideologically homogeneous Red-Red coalition.
Characteristics of the Red–Red Alliance
The Red-Red Alliance is characterized by a coalition between socialist and communist parties, emphasizing strong social welfare policies, workers' rights, and anti-capitalist stances. This alliance typically seeks to unify left-wing factions to promote comprehensive economic redistribution and public ownership of key industries. Unlike the Red-Yellow Alliance, which includes social democrats and moderates favoring market-friendly reforms, the Red-Red Alliance maintains a more radical approach to systemic change and rejects neoliberal economic models.
Historical Background of Both Alliances
The Red-yellow alliance traces its roots to the early 20th century, emerging from labor movements that combined socialist and liberal ideologies to promote workers' rights alongside progressive social policies. In contrast, the Red-red alliance originated from left-wing coalitions primarily between communist and socialist parties, often emphasizing radical economic reforms and anti-capitalist agendas during the post-World War II era. Historical contexts show the Red-yellow alliance often participating in broader parliamentary democracies, while the Red-red alliance typically aligned with more revolutionary or radical leftist movements in response to socio-political upheavals.
Key Political Parties Involved
The Red-yellow alliance primarily involves the Social Democrats and the Liberal Party, emphasizing centrist and social-liberal policies, while the Red-red alliance consists of the Social Democrats and the Socialist People's Party, focusing on left-wing and social-democratic ideals. Key political parties in the Red-yellow bloc support market-friendly reforms and social welfare balance, whereas the Red-red coalition advocates for broader social equity and environmental sustainability. These alliances shape parliamentary dynamics by aligning distinct policy priorities and voter bases within Denmark's multiparty system.
Ideological Differences and Similarities
The Red-Yellow alliance, typically encompassing social democrats and liberal centrists, prioritizes market-friendly economic policies combined with progressive social reforms, whereas the Red-Red alliance unites socialist and communist factions advocating for more radical wealth redistribution and stronger state intervention. Both alliances share a commitment to social justice, workers' rights, and combating economic inequality, but differ significantly in their approach to capitalism and the role of the state in the economy. While the Red-Yellow alliance often supports mixed economies and incremental change, the Red-Red alliance emphasizes systemic change and greater public ownership of resources.
Electoral Impact and Voter Base
The Red-yellow alliance, typically a coalition between social democratic and liberal parties, often appeals to centrist and progressive voters seeking moderate reform and economic stability, broadening its electoral impact across urban and suburban constituencies. In contrast, the Red-red alliance, comprised mainly of social democrats and socialist or left-wing parties, mobilizes a voter base motivated by stronger redistributive policies and social justice, consolidating support among working-class and left-leaning urban populations. Electoral outcomes show that the Red-yellow alliance tends to attract swing voters and the politically moderate center, while the Red-red alliance secures a loyal, ideologically driven base, influencing policy debates and coalition dynamics differently in parliamentary systems.
Policy Agendas and Legislative Goals
The Red-yellow alliance, primarily centered on social democracy and environmental sustainability, emphasizes progressive policies such as climate change mitigation, social welfare expansion, and labor rights protection. In contrast, the Red-red alliance, which often unites socialist and left-wing democratic parties, prioritizes wealth redistribution, public ownership of key industries, and expanded social safety nets to address economic inequality. Both alliances aim to strengthen workers' rights but diverge in their approaches to market regulation and public sector involvement, reflecting differing legislative goals that shape national policy agendas.
Real-world Examples and Case Studies
The Red-yellow alliance, exemplified by Germany's coalition between the Social Democratic Party (SPD) and the Free Democratic Party (FDP), emphasizes centrist policies blending social democracy with liberal economic reforms, as seen in the 2021 federal government. In contrast, the Red-red alliance, such as the coalition governments in Berlin between the SPD and The Left party, prioritizes more progressive social policies and redistribution efforts focused on welfare and labor rights. Case studies from Germany highlight the Red-yellow alliance's success in economic stabilization and digital innovation, while Red-red coalitions often advance comprehensive social welfare reforms and affordable housing initiatives.
Future Prospects and Political Implications
The Red-yellow alliance, combining social democratic and centrist liberal policies, aims to foster progressive reforms and economic modernization, potentially appealing to urban, educated electorates. In contrast, the Red-red alliance, uniting social democrats with socialist or leftist parties, emphasizes wealth redistribution, stronger social safety nets, and increased public sector involvement, targeting working-class and economically disadvantaged voters. Future prospects hinge on their ability to address climate change, economic inequality, and social justice, with political implications including shifts in coalition dynamics, legislative priorities, and electoral strategies within parliamentary systems.
Red–yellow alliance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com