Privacy rights protect your personal information from unauthorized use and ensure control over how data about you is collected, shared, and stored. These rights are essential in a digital age where online activities and data breaches pose significant risks to your confidentiality and freedom. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to safeguard your privacy effectively.
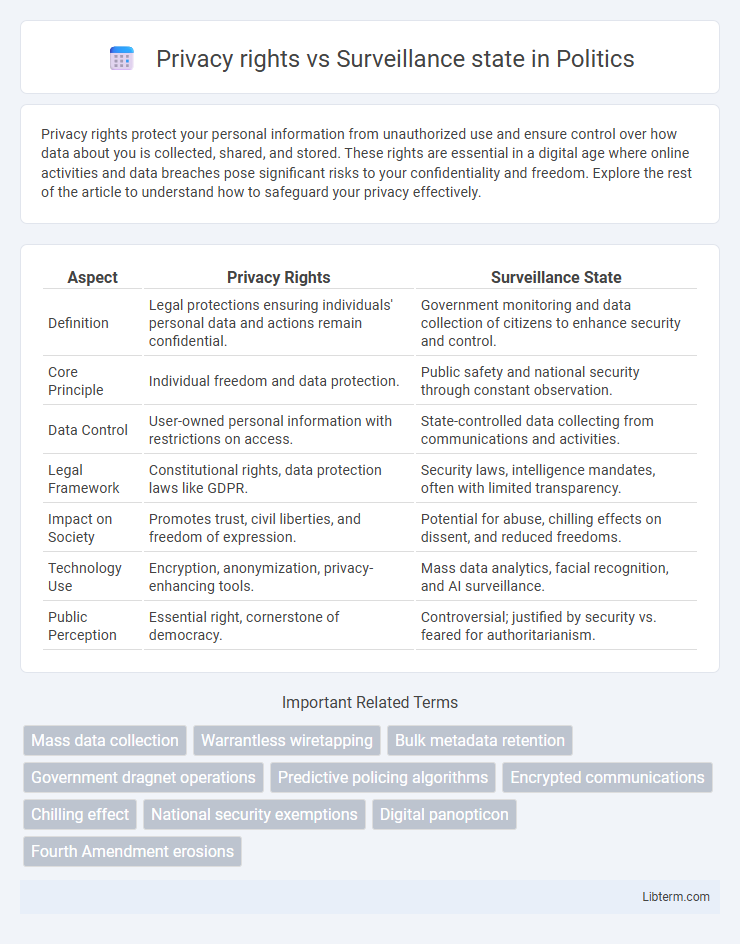
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Privacy Rights | Surveillance State |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal protections ensuring individuals' personal data and actions remain confidential. | Government monitoring and data collection of citizens to enhance security and control. |
| Core Principle | Individual freedom and data protection. | Public safety and national security through constant observation. |
| Data Control | User-owned personal information with restrictions on access. | State-controlled data collecting from communications and activities. |
| Legal Framework | Constitutional rights, data protection laws like GDPR. | Security laws, intelligence mandates, often with limited transparency. |
| Impact on Society | Promotes trust, civil liberties, and freedom of expression. | Potential for abuse, chilling effects on dissent, and reduced freedoms. |
| Technology Use | Encryption, anonymization, privacy-enhancing tools. | Mass data analytics, facial recognition, and AI surveillance. |
| Public Perception | Essential right, cornerstone of democracy. | Controversial; justified by security vs. feared for authoritarianism. |
Understanding Privacy Rights in the Digital Age
Privacy rights in the digital age encompass the protection of personal data from unauthorized collection, use, and surveillance by governments and corporations. The rise of surveillance technologies, including facial recognition and data mining, challenges traditional notions of privacy and necessitates robust legal frameworks like the GDPR and CCPA. Understanding digital privacy rights empowers individuals to control their personal information and advocate for transparency and accountability in data practices.
Defining the Surveillance State
The surveillance state refers to a government system that extensively monitors, collects, and analyzes citizens' personal data, often through electronic means such as CCTV cameras, internet tracking, and telecommunications interception. This pervasive monitoring aims to enhance national security and public safety but raises significant concerns about individual privacy rights and potential abuses of power. The balance between protecting civil liberties and ensuring effective surveillance remains a critical issue in modern democracies.
Historical Context of Privacy and Surveillance
The historical context of privacy and surveillance reveals a long-standing tension between individual rights and state power, tracing back to early legal frameworks like the Magna Carta that emphasized protection from arbitrary intrusion. The 20th century saw significant expansion in surveillance capabilities, particularly during wartime and the Cold War era, prompting legislative responses such as the U.S. Privacy Act of 1974 and the European Convention on Human Rights Article 8. Technological advancements in digital communication have intensified this conflict, raising complex issues around data collection, government transparency, and citizen privacy protections.
Legal Frameworks Governing Privacy
Legal frameworks governing privacy establish comprehensive protections to balance individual rights against state surveillance powers. Key instruments such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the Fourth Amendment in the United States limit unauthorized data collection and require transparency from government agencies. These laws mandate oversight mechanisms, judicial review, and strict data handling protocols to prevent abuse while allowing lawful surveillance for national security purposes.
Government Justifications for Surveillance
Government justifications for surveillance often emphasize national security, crime prevention, and public safety as primary reasons for monitoring activities. Intelligence agencies cite threats such as terrorism, cybercrime, and organized crime to legitimize extensive data collection and surveillance programs. The balance between safeguarding privacy rights and ensuring effective governance remains a central debate in democratic societies.
Technology’s Role in Expanding Surveillance
Advancements in artificial intelligence and big data analytics have exponentially increased the surveillance capabilities of state actors, enabling the monitoring of individuals across digital platforms and public spaces. The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and facial recognition technology further intensifies concerns over mass data collection and potential abuses of privacy rights. Encryption and anonymization tools strive to protect user information, but state-led cybersecurity measures often exploit vulnerabilities to expand surveillance reach without transparent oversight.
Impacts of Mass Surveillance on Civil Liberties
Mass surveillance programs significantly erode privacy rights by enabling the extensive collection of personal data without individual consent, thereby undermining the Fourth Amendment protections against unreasonable searches. The pervasive monitoring of communications and public spaces chills free speech and association, crucial pillars of democratic societies, leading to self-censorship and diminished public trust in government institutions. Studies reveal that surveillance disproportionately targets marginalized communities, exacerbating social inequalities and threatening the foundational principles of civil liberties and human rights.
Balancing National Security and Individual Freedom
Balancing national security and individual freedom requires carefully navigating the competing demands of surveillance state practices and privacy rights protection. Effective policies must incorporate transparent oversight mechanisms, data minimization principles, and robust legal safeguards to prevent mass surveillance from eroding civil liberties. Ensuring accountability in intelligence operations while preserving citizens' privacy fosters trust and upholds democratic values in the face of security threats.
Public Perceptions and Societal Responses
Public perceptions of privacy rights versus the surveillance state vary widely, with many individuals expressing concern over governmental data collection and potential abuses of power. Societal responses include advocacy for stronger data protection laws, increased support for encryption technologies, and widespread calls for transparency and accountability in surveillance practices. The growing tension between national security interests and individual privacy rights fuels ongoing debates in policy-making and civil society activism.
Pathways to Protect Privacy in a Surveillance Era
Implementing end-to-end encryption and robust data protection laws are critical pathways to safeguard privacy in an era dominated by surveillance states. Advocating for transparency in government surveillance programs and enforcing strict oversight mechanisms help prevent abuse of power and unauthorized data collection. Empowering individuals with digital literacy and privacy tools enhances their ability to control personal information and resist pervasive monitoring.
Privacy rights Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com