Political ideology shapes the beliefs and values that guide individuals and groups in their views on governance, policy, and social organization. It influences how societies allocate power and resources, impacting decisions on freedom, equality, and justice. Explore the rest of this article to understand the key political ideologies and how they affect your world.
Table of Comparison
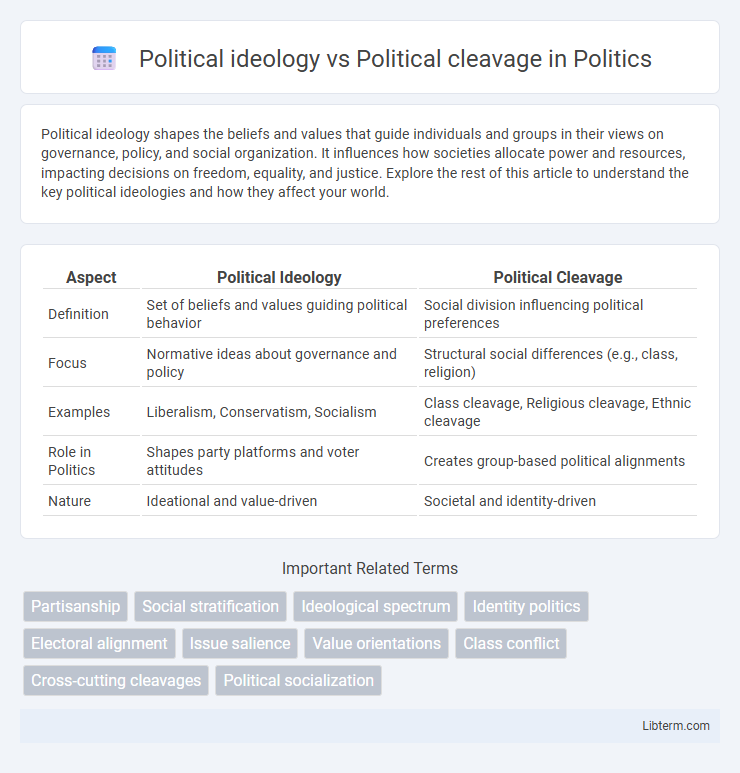
| Aspect | Political Ideology | Political Cleavage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set of beliefs and values guiding political behavior | Social division influencing political preferences |
| Focus | Normative ideas about governance and policy | Structural social differences (e.g., class, religion) |
| Examples | Liberalism, Conservatism, Socialism | Class cleavage, Religious cleavage, Ethnic cleavage |
| Role in Politics | Shapes party platforms and voter attitudes | Creates group-based political alignments |
| Nature | Ideational and value-driven | Societal and identity-driven |
Introduction to Political Ideology and Political Cleavage
Political ideology refers to a set of coherent beliefs and values that guide individuals or groups in understanding political goals and policies, shaping attitudes toward government and society. Political cleavage represents social divisions that manifest in political conflicts, typically along lines such as class, religion, ethnicity, or region, influencing voting behavior and party alignment. Understanding the relationship between political ideology and cleavage is essential for analyzing how structured political preferences emerge from underlying social group differences.
Defining Political Ideology
Political ideology refers to a coherent set of beliefs and values about the desired goals and functioning of a political system, shaping opinions on governance, social order, and public policy. It provides a framework for interpreting political information and guiding political behavior, often categorized into liberalism, conservatism, socialism, and other major traditions. Political cleavage, in contrast, represents the deep societal divisions based on factors such as class, religion, ethnicity, or geography that influence political allegiance and party competition.
Understanding Political Cleavage
Political cleavage refers to the deep and lasting divisions within society, such as class, religion, or ethnicity, that shape political preferences and voting behavior. Understanding political cleavage is crucial for analyzing how these societal divisions influence party systems, policy debates, and election outcomes. Political ideology, by contrast, represents a coherent set of beliefs about government and society, often aligning with specific cleavages but focusing more on value-based political perspectives.
Historical Evolution of Ideologies and Cleavages
Political ideology has evolved through distinct historical phases, reflecting shifts in economic structures, social classes, and cultural values, while political cleavages have historically emerged from persistent societal divisions such as religion, ethnicity, and class. The Industrial Revolution catalyzed modern ideologies like liberalism and socialism, simultaneously intensifying cleavages between urban and rural populations, as well as capitalists and workers. Understanding the interplay between evolving ideologies and entrenched cleavages is crucial for analyzing contemporary political systems and electoral behavior worldwide.
Core Differences Between Political Ideology and Cleavage
Political ideology represents a set of beliefs and values that guide political behavior and policy preferences, while political cleavage refers to deep societal divisions, such as those based on class, ethnicity, or religion, that shape group identities and political alignments. Ideologies provide a coherent framework for interpreting political issues, whereas cleavages reflect structural fault lines within society that influence voting patterns and party systems. Understanding these differences is crucial for analyzing how political identities form and how conflicts manifest in democratic processes.
Factors Influencing Political Ideologies
Factors influencing political ideologies include socioeconomic status, education, cultural background, and media exposure, shaping individuals' beliefs and values. Political ideologies often reflect core principles about government roles and social policies, while political cleavages represent divisions based on identity or interest groups such as class, religion, and ethnicity. Understanding these factors reveals how political ideologies form and contribute to the emergence of cleavages within societies.
Factors Shaping Political Cleavages
Political cleavages are deeply influenced by social factors such as class, religion, ethnicity, and geography that divide societies into distinct political groups. Economic disparities, cultural identities, and historical conflicts also shape cleavages by creating persistent divisions in political preferences and party alignment. Political ideology interacts with these cleavages by providing a framework for interpreting social divisions and mobilizing collective action around shared values and policy goals.
The Role of Ideology in Political Alignments
Political ideology serves as a foundational framework that shapes individuals' beliefs and values, guiding their political alignments and party preferences. Political cleavages represent deep societal divisions, such as class, religion, or ethnicity, that influence group loyalties and voting behavior. The interplay between ideology and cleavage determines the structure of political competition and the stability of democratic systems.
Impact of Political Cleavages on Party Systems
Political cleavages, such as class, religion, and ethnicity, shape the structure and dynamics of party systems by creating distinct voter alignments and interests. These cleavages influence party formation, electoral competition, and policy agendas by embedding long-term social divisions within political parties. The strength and number of political cleavages determine whether party systems evolve into two-party, multi-party, or fragmented arrangements, directly impacting political stability and governance.
Interrelationship and Contemporary Significance
Political ideology and political cleavage are interrelated as ideologies often shape the foundations of social and political divisions, leading to distinct group alignments based on values, beliefs, and policy preferences. Contemporary significance lies in how these cleavages influence electoral behavior, party systems, and policy-making, reflecting ongoing debates over identity, economic inequality, and cultural issues. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for analyzing political polarization, voter mobilization, and the stability of democratic institutions in modern societies.
Political ideology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com