E-administration streamlines public sector operations through digital platforms, enhancing efficiency and accessibility for citizens. Government services become more transparent, reducing paperwork and wait times while improving data security. Discover how e-administration can transform your interaction with public services in the full article.
Table of Comparison
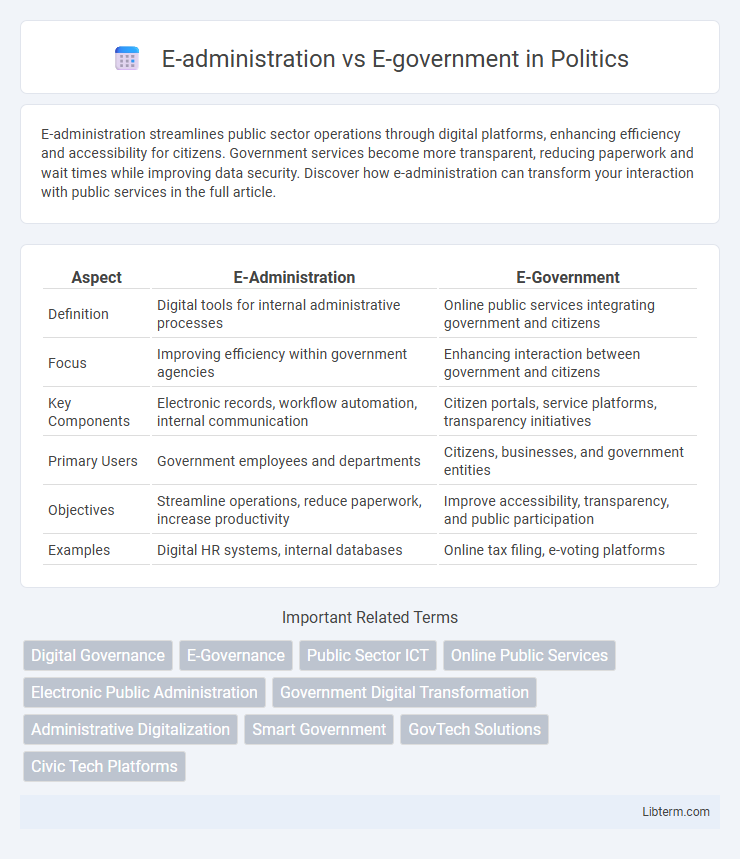
| Aspect | E-Administration | E-Government |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital tools for internal administrative processes | Online public services integrating government and citizens |
| Focus | Improving efficiency within government agencies | Enhancing interaction between government and citizens |
| Key Components | Electronic records, workflow automation, internal communication | Citizen portals, service platforms, transparency initiatives |
| Primary Users | Government employees and departments | Citizens, businesses, and government entities |
| Objectives | Streamline operations, reduce paperwork, increase productivity | Improve accessibility, transparency, and public participation |
| Examples | Digital HR systems, internal databases | Online tax filing, e-voting platforms |
Introduction to E-Administration and E-Government
E-administration refers to the digital management and automation of internal government processes aimed at improving efficiency, transparency, and service delivery within public institutions. E-government encompasses a broader scope by integrating e-administration with online platforms to facilitate interaction and communication between government bodies and citizens or businesses. Both concepts leverage information and communication technologies to enhance governance, streamline operations, and promote participatory democracy.
Defining E-Administration: Key Concepts
E-administration refers to the digital transformation of internal government processes to enhance efficiency, transparency, and service delivery by utilizing advanced information and communication technologies (ICT). It primarily focuses on optimizing administrative workflows, document management, and internal communication within public sector organizations to improve resource allocation and reduce bureaucratic delays. Key concepts include automation of routine tasks, electronic record-keeping, and use of integrated IT systems to support decision-making and policy implementation.
Defining E-Government: Core Elements
E-Government encompasses the use of digital technologies by public sector organizations to improve the delivery of government services, enhance transparency, and foster citizen engagement. Core elements of E-Government include online service provision, digital communication channels, and integrated information management systems that enable seamless interaction between government entities and citizens. These components collectively promote efficiency, accessibility, and accountability in public administration.
Main Differences Between E-Administration and E-Government
E-administration focuses on improving internal government processes through digital tools to enhance efficiency and document management, while e-government encompasses broader citizen-centric services such as online portals for public access, service delivery, and citizen engagement. E-administration primarily targets back-office functions including digital record keeping and workflow automation, whereas e-government integrates these functionalities with front-office services like e-voting, tax filing, and public information dissemination. The key difference lies in e-administration's internal process optimization versus e-government's comprehensive approach to governance and public interaction through digital platforms.
Objectives and Goals of E-Administration
E-administration focuses on optimizing internal government processes through digital tools to enhance efficiency, transparency, and service delivery for citizens and businesses. Its primary objectives include streamlining administrative workflows, reducing paperwork, and facilitating faster decision-making within public institutions. These goals support the broader E-government vision by ensuring that government operations are more responsive, accessible, and accountable through technology integration.
Objectives and Goals of E-Government
E-Government aims to enhance public service delivery, increase transparency, and foster citizen engagement through digital platforms. Its objectives include improving governmental efficiency, reducing costs, and facilitating easy access to information and services for all stakeholders. E-Administration primarily supports these goals by streamlining internal processes and automating routine administrative tasks within government agencies.
Technological Requirements for E-Administration vs E-Government
E-administration requires robust internal IT infrastructure, secure data management systems, and user-friendly digital tools to streamline back-office operations and enhance bureaucratic efficiency. E-government demands advanced interoperability frameworks, comprehensive cybersecurity measures, and multi-channel service delivery platforms to facilitate seamless citizen engagement and cross-agency collaboration. Both rely on cloud computing, big data analytics, and mobile technology, but e-government emphasizes scalability and public accessibility more heavily than e-administration.
Benefits and Challenges of E-Administration
E-administration enhances public sector efficiency by digitizing internal processes, improving document management, and streamlining communication among government departments, resulting in faster service delivery and reduced operational costs. Key benefits include increased transparency, better accountability, and enhanced citizen engagement through accessible online services. Challenges involve data security concerns, the digital divide limiting access for some populations, and the need for comprehensive staff training to effectively implement and maintain e-administration systems.
Benefits and Challenges of E-Government
E-government enhances public service efficiency by enabling online access to government services, increasing transparency, and reducing administrative costs. Key benefits include improved citizen engagement, faster service delivery, and streamlined internal processes through digital platforms. Challenges involve cybersecurity risks, digital divide issues limiting access for some populations, and the need for robust legal and regulatory frameworks to ensure data privacy and trust.
Future Trends in E-Administration and E-Government
Future trends in E-Administration and E-Government emphasize artificial intelligence integration, enhancing service personalization and operational efficiency. Blockchain technology will advance transparency and security in public records, fostering greater citizen trust. Cloud computing adoption is expected to increase scalability and facilitate interagency data sharing for seamless government services.
E-administration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com