Neoliberalism promotes free-market capitalism, advocating minimal state intervention to encourage economic growth and individual entrepreneurship. Its policies often emphasize deregulation, privatization, and reduction of government spending on social programs. Discover how neoliberalism shapes your economy and society by exploring key impacts and critiques in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
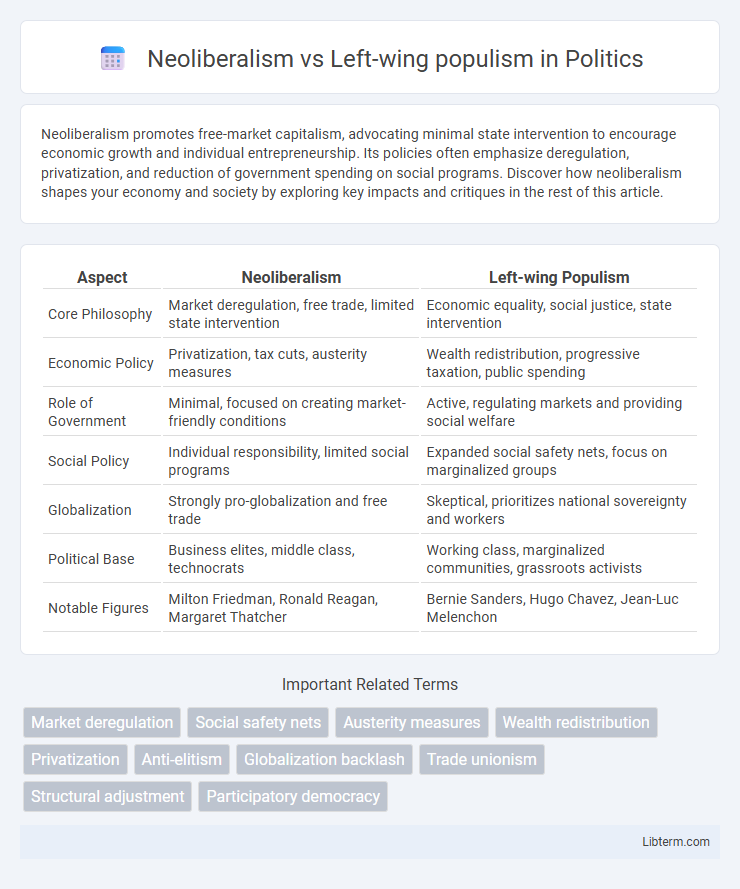
| Aspect | Neoliberalism | Left-wing Populism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Philosophy | Market deregulation, free trade, limited state intervention | Economic equality, social justice, state intervention |
| Economic Policy | Privatization, tax cuts, austerity measures | Wealth redistribution, progressive taxation, public spending |
| Role of Government | Minimal, focused on creating market-friendly conditions | Active, regulating markets and providing social welfare |
| Social Policy | Individual responsibility, limited social programs | Expanded social safety nets, focus on marginalized groups |
| Globalization | Strongly pro-globalization and free trade | Skeptical, prioritizes national sovereignty and workers |
| Political Base | Business elites, middle class, technocrats | Working class, marginalized communities, grassroots activists |
| Notable Figures | Milton Friedman, Ronald Reagan, Margaret Thatcher | Bernie Sanders, Hugo Chavez, Jean-Luc Melenchon |
Understanding Neoliberalism: Core Principles and Beliefs
Neoliberalism centers on free-market capitalism, emphasizing deregulation, privatization, and reduced government intervention to drive economic growth. It advocates for individual responsibility, competition, and globalization as key mechanisms to increase efficiency and innovation. Core beliefs include limiting the welfare state and promoting open markets to foster entrepreneurial opportunities and attract investment.
Defining Left-wing Populism: Origins and Ideological Foundations
Left-wing populism originates from critiques of neoliberalism's emphasis on free markets, privatization, and reduced government intervention, advocating for social justice, economic equality, and expanded welfare. Ideologically, it combines progressive policies, anti-elitism, and grassroots mobilization, aiming to empower marginalized groups and challenge corporate power. This political movement draws from socialist, progressive, and labor traditions, emphasizing state intervention to redistribute wealth and protect public services.
Historical Context: The Rise of Neoliberalism and Left-wing Populism
Neoliberalism emerged in the late 20th century as a response to the economic stagnation of the 1970s, emphasizing free markets, deregulation, and reduced government intervention to promote economic growth. Left-wing populism gained momentum as a reaction against the social inequalities exacerbated by neoliberal policies, advocating for wealth redistribution, expanded social services, and increased governmental control over the economy. The historical context of these movements reflects a global ideological shift marked by contrasting approaches to economic management and social justice since the 1980s.
Economic Policies: Market Deregulation vs. Economic Redistribution
Neoliberalism advocates for market deregulation, emphasizing reduced government intervention, free trade, and privatization to promote economic growth and efficiency. Left-wing populism, in contrast, supports economic redistribution through increased social spending, progressive taxation, and stronger labor protections to reduce inequality and empower marginalized groups. These opposing economic policies reflect fundamental differences in addressing wealth distribution and market dynamics.
Social Impact: Inequality, Welfare, and Social Justice
Neoliberalism often exacerbates inequality by prioritizing market-driven policies that reduce welfare support and limit social justice initiatives, favoring economic growth over redistribution. Left-wing populism emphasizes social justice through expanded welfare programs and progressive taxation to address systemic inequality and empower marginalized communities. The clash between these ideologies centers on balancing economic efficiency with equitable access to resources and social protections.
Role of the State: Minimal Intervention vs. Expansive Social Programs
Neoliberalism emphasizes minimal state intervention, advocating for free markets, deregulation, and privatization as key drivers of economic growth and personal freedom. Left-wing populism calls for expansive social programs and robust state involvement to address economic inequality, provide public services, and protect vulnerable populations. The ideological divide centers on whether the state should primarily facilitate market mechanisms or actively redistribute wealth and regulate economic activity to promote social justice.
Globalization and Its Discontents: Contrasting Responses
Neoliberalism champions globalization through free trade, deregulation, and market liberalization, promoting economic growth and integration in global markets. Left-wing populism critiques neoliberal globalization for exacerbating inequality, undermining sovereignty, and marginalizing workers, advocating for protectionist policies and social justice reforms. This ideological clash highlights divergent views on globalization's effects: neoliberalism emphasizes efficiency and competitiveness, while left-wing populism stresses equity and community-based economic resilience.
Political Rhetoric: Elites, The People, and Mobilization Strategies
Neoliberalism frames elites as technocratic experts driving market efficiency, while portraying the people as consumers benefiting from economic liberalization. Left-wing populism depicts elites as corrupt and disconnected, emphasizing the people's collective power to challenge inequality and reclaim democracy. Mobilization strategies differ, with neoliberalism relying on policy reforms and institutional mechanisms, whereas left-wing populism uses grassroots activism and emotionally charged rhetoric to galvanize mass support.
Case Studies: Neoliberal and Left-wing Populist Movements Worldwide
Neoliberalism, exemplified by the Thatcher and Reagan administrations, emphasizes free markets, deregulation, and privatization, promoting economic growth and global integration. Left-wing populist movements, such as the Bolivarian Revolution in Venezuela under Hugo Chavez and Podemos in Spain, focus on wealth redistribution, social justice, and anti-austerity policies, addressing inequality and corporate influence. Case studies reveal neoliberalism's success in fostering market efficiency, while left-wing populism highlights socio-economic disparities and community empowerment as a basis for political legitimacy.
Future Trajectories: Challenges and Prospects for Both Ideologies
Neoliberalism faces growing criticism over rising inequality and environmental degradation, pushing it toward potential reforms that emphasize sustainable growth and inclusive market policies. Left-wing populism confronts challenges in maintaining broad coalitions while addressing economic justice and anti-elitism, often struggling with governance and policy consistency. Both ideologies must adapt to shifting socio-political dynamics and global economic uncertainties, with prospects hinging on their ability to respond to demands for equitable development and democratic accountability.
Neoliberalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com