Incompetence in the workplace can lead to decreased productivity, poor decision-making, and overall organizational inefficiency. Recognizing signs of incompetence early allows leaders to provide targeted training and support, enhancing team performance. Explore the full article to understand how addressing incompetence can transform your work environment.
Table of Comparison
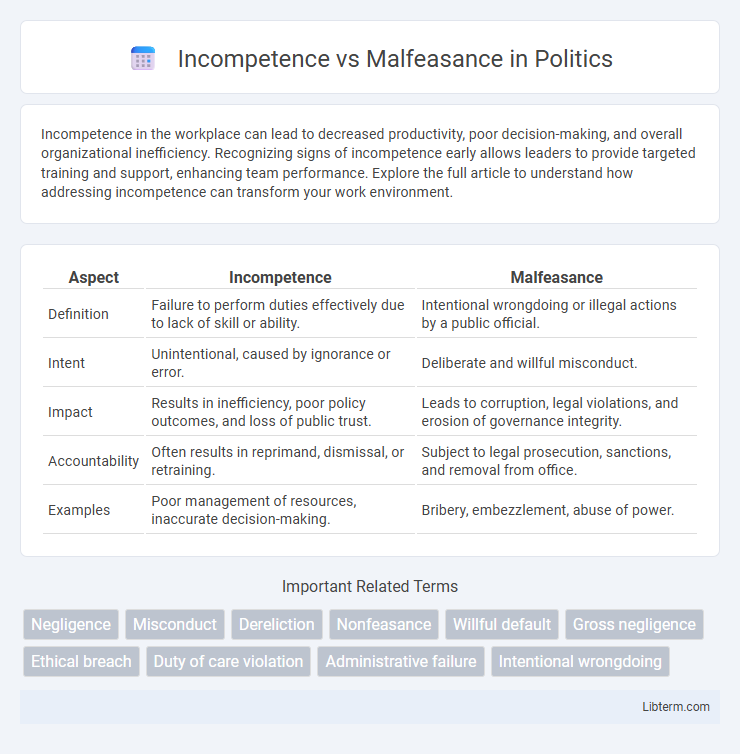
| Aspect | Incompetence | Malfeasance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Failure to perform duties effectively due to lack of skill or ability. | Intentional wrongdoing or illegal actions by a public official. |
| Intent | Unintentional, caused by ignorance or error. | Deliberate and willful misconduct. |
| Impact | Results in inefficiency, poor policy outcomes, and loss of public trust. | Leads to corruption, legal violations, and erosion of governance integrity. |
| Accountability | Often results in reprimand, dismissal, or retraining. | Subject to legal prosecution, sanctions, and removal from office. |
| Examples | Poor management of resources, inaccurate decision-making. | Bribery, embezzlement, abuse of power. |
Understanding Incompetence: Definition and Examples
Incompetence refers to the lack of ability, skill, or knowledge required to perform a job or task effectively, often resulting in errors or substandard outcomes. Examples include a manager failing to understand critical financial data or an employee consistently missing deadlines due to poor time management. Unlike malfeasance, which involves intentional wrongdoing, incompetence stems from unintentional incapacity rather than deliberate misconduct.
What is Malfeasance? Key Characteristics
Malfeasance is the intentional conduct that is wrongful or unlawful, especially by a public official or a person in authority. Key characteristics include deliberate wrongdoing, violation of legal or ethical standards, and actions taken knowingly to cause harm or injustice. Unlike incompetence, which involves unintentional errors or lack of ability, malfeasance implies purposeful misconduct with malicious intent.
Incompetence vs Malfeasance: Core Differences
Incompetence refers to the lack of skill, ability, or knowledge required to perform tasks effectively, often resulting in unintentional errors or poor outcomes. Malfeasance, on the other hand, involves intentional wrongdoing or misconduct, such as fraud or abuse of power, with the purpose of causing harm or gaining illicit benefits. The core difference lies in intent: incompetence is characterized by unintentional failure, while malfeasance is defined by deliberate unethical or illegal actions.
Recognizing Signs of Incompetence in the Workplace
Recognizing signs of incompetence in the workplace includes identifying consistent failure to meet performance standards, lack of necessary skills or knowledge, and inability to complete tasks efficiently. Employees showing repeated errors, poor decision-making, and failure to adapt or learn from feedback often indicate incompetence rather than malfeasance. Early detection through performance reviews and clear communication can help address incompetence before it significantly impacts team productivity and morale.
Identifying Malfeasance: Red Flags and Warning Signs
Identifying malfeasance involves recognizing key red flags such as unexplained financial discrepancies, consistent failure to meet ethical standards, and deliberate concealment of information. Patterns of intentional misconduct, abuse of authority, and breaches of fiduciary duty often distinguish malfeasance from simple incompetence. Early detection relies on thorough audits, whistleblower reports, and vigilant oversight mechanisms to prevent significant organizational harm.
Impact of Incompetence on Organizations
Incompetence in organizations leads to decreased productivity, increased errors, and higher operational costs, undermining overall business efficiency. It fosters a culture of low morale and diminished employee engagement, negatively affecting teamwork and innovation. The cumulative effect of incompetence often results in customer dissatisfaction and damage to the organization's reputation.
Consequences of Malfeasance: Legal and Ethical Implications
Malfeasance involves intentional wrongdoing or misconduct, leading to severe legal consequences such as civil lawsuits, criminal charges, and financial penalties. Ethical implications include loss of professional licenses, reputational damage, and breach of fiduciary duty, eroding public trust in institutions. Organizations facing malfeasance often implement rigorous compliance programs and ethics training to mitigate risks and restore accountability.
Preventing Incompetence: Best Practices for Management
Implementing rigorous training programs and clear performance metrics significantly reduces incompetence within organizations. Regular feedback sessions and continuous professional development ensure employees align with company goals and industry standards. Leadership commitment to fostering a culture of accountability and open communication prevents errors stemming from skill gaps or negligence.
Addressing Malfeasance: Policies and Accountability Measures
Addressing malfeasance requires robust policies that include clear definitions of prohibited conduct, stringent enforcement mechanisms, and transparent reporting channels. Accountability measures such as independent audits, whistleblower protections, and disciplinary actions ensure that unethical behavior is identified and penalized effectively. Implementing these frameworks fosters organizational integrity and deters future misconduct by holding individuals responsible for intentional wrongdoing.
Incompetence or Malfeasance? How to Distinguish and Respond
Incompetence involves a lack of skill or knowledge leading to unintentional errors, while malfeasance refers to intentional wrongdoing or misconduct. Distinguishing between the two requires thorough investigation of intent, patterns of behavior, and evidence such as documented mistakes versus deliberate actions. Responses to incompetence often include training, supervision, or reassignment, whereas malfeasance typically demands disciplinary action, legal consequences, and ethical accountability.
Incompetence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com