Political engagement shapes the way citizens influence policies and governance in their communities. Active participation in voting, advocacy, and public discourse strengthens democracy and promotes social change. Explore the rest of this article to discover how your involvement can make a meaningful impact.
Table of Comparison
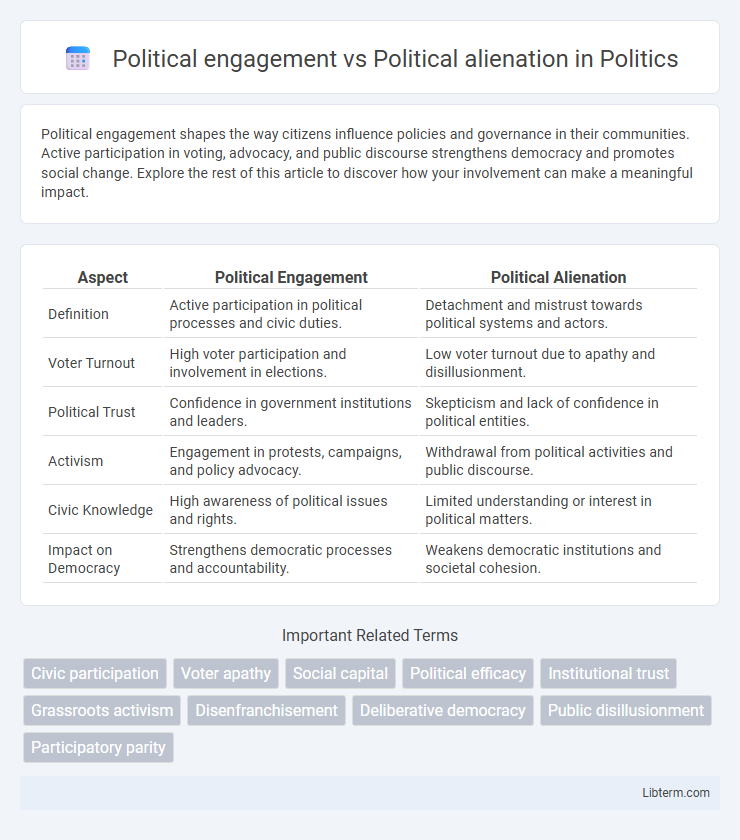
| Aspect | Political Engagement | Political Alienation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation in political processes and civic duties. | Detachment and mistrust towards political systems and actors. |
| Voter Turnout | High voter participation and involvement in elections. | Low voter turnout due to apathy and disillusionment. |
| Political Trust | Confidence in government institutions and leaders. | Skepticism and lack of confidence in political entities. |
| Activism | Engagement in protests, campaigns, and policy advocacy. | Withdrawal from political activities and public discourse. |
| Civic Knowledge | High awareness of political issues and rights. | Limited understanding or interest in political matters. |
| Impact on Democracy | Strengthens democratic processes and accountability. | Weakens democratic institutions and societal cohesion. |
Defining Political Engagement and Political Alienation
Political engagement refers to the active participation of individuals in political processes, including voting, activism, and community involvement, reflecting a sense of efficacy and connection to the political system. Political alienation signifies feelings of powerlessness, disenchantment, and detachment from political institutions, often resulting in apathy or withdrawal from civic activities. Understanding these concepts is essential for analyzing citizen behavior and democratic health in various sociopolitical contexts.
Historical Perspectives on Civic Participation
Historical perspectives on civic participation reveal that political engagement often thrives during periods of social movements, democratic reforms, and expanded suffrage, as seen in the Progressive Era and Civil Rights Movement. Conversely, political alienation has increased during times of disenfranchisement, governmental corruption, and social unrest, exemplified by the post-Reconstruction South and the tumultuous 1960s. Studies indicate that access to education, media influence, and institutional trust significantly shape the balance between political engagement and alienation across different historical contexts.
Factors Influencing Political Engagement
Socioeconomic status, education level, and access to information significantly influence political engagement, as individuals with higher education and income are more likely to participate in voting and activism. Social networks and community involvement also foster political engagement by providing support and motivation to engage in political processes. Conversely, experiences of discrimination, distrust in political institutions, and perceived inefficacy contribute to political alienation, reducing individuals' willingness to participate in democratic activities.
Causes and Symptoms of Political Alienation
Political alienation stems from causes such as lack of trust in government institutions, feelings of powerlessness, and perceived inefficacy of political participation, leading individuals to disengage. Symptoms include voter apathy, cynicism toward political leaders, and withdrawal from civic activities, which can undermine democratic processes. Understanding these factors is crucial for addressing disengagement and fostering inclusive political engagement.
The Role of Media in Shaping Political Attitudes
Media plays a crucial role in shaping political attitudes by providing information, framing issues, and influencing public discourse, which can either enhance political engagement or contribute to political alienation. Exposure to diverse media sources often increases political knowledge and participation, while sensationalism, misinformation, and biased coverage may foster distrust and disengagement among citizens. Social media platforms amplify these effects by facilitating both active political discussion and the spread of polarizing content, impacting the overall levels of political involvement in society.
Impact of Education on Civic Involvement
Higher education levels significantly increase political engagement by enhancing critical thinking, political knowledge, and a sense of civic duty, leading to greater voter turnout and participation in community activities. Conversely, lack of education often correlates with political alienation, where individuals feel disconnected from political processes and distrust institutions. Educational programs that emphasize civic literacy and active citizenship effectively reduce alienation and foster sustained involvement in democratic governance.
Demographic Trends in Political Participation
Demographic trends reveal significant disparities in political engagement and alienation, with younger adults and minority groups often exhibiting lower voter turnout and political participation rates compared to older, white populations. Socioeconomic status, educational attainment, and geographic location also strongly influence levels of political involvement, impacting community representation and policy responsiveness. Understanding these demographic patterns is crucial for developing strategies to reduce political alienation and enhance inclusive civic engagement across diverse populations.
Consequences of Political Alienation for Democracy
Political alienation often results in lower voter turnout, reduced civic participation, and diminished trust in governmental institutions, thereby weakening democratic processes. When citizens feel disconnected from political systems, it fosters apathy and disengagement, which hinders accountability and representative governance. This erosion of public involvement can lead to increased political polarization and instability within democratic societies.
Strategies to Foster Political Engagement
Strategies to foster political engagement include enhancing civic education, promoting inclusive dialogue, and increasing accessibility to voting. Implementing community-based programs and leveraging digital platforms can empower marginalized groups to participate actively in political processes. Encouraging transparency and accountability in governance builds trust, reducing political alienation and fostering sustained citizen involvement.
Future Prospects: Bridging the Engagement-Alienation Divide
Future prospects for bridging the divide between political engagement and political alienation center on empowering marginalized communities through inclusive policymaking and transparent governance. Technological advancements, such as digital platforms for civic participation, foster greater accessibility and real-time dialogue, reducing feelings of disenfranchisement. Emphasizing education on political literacy and reinforcing trust in institutions are crucial strategies to transform alienation into constructive engagement.
Political engagement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com