Deliberative democracy emphasizes informed and respectful discussion among citizens to shape public decisions. It encourages diverse viewpoints and critical thinking, fostering collective reasoning that strengthens democratic legitimacy. Discover how this participatory approach can transform your understanding of governance in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
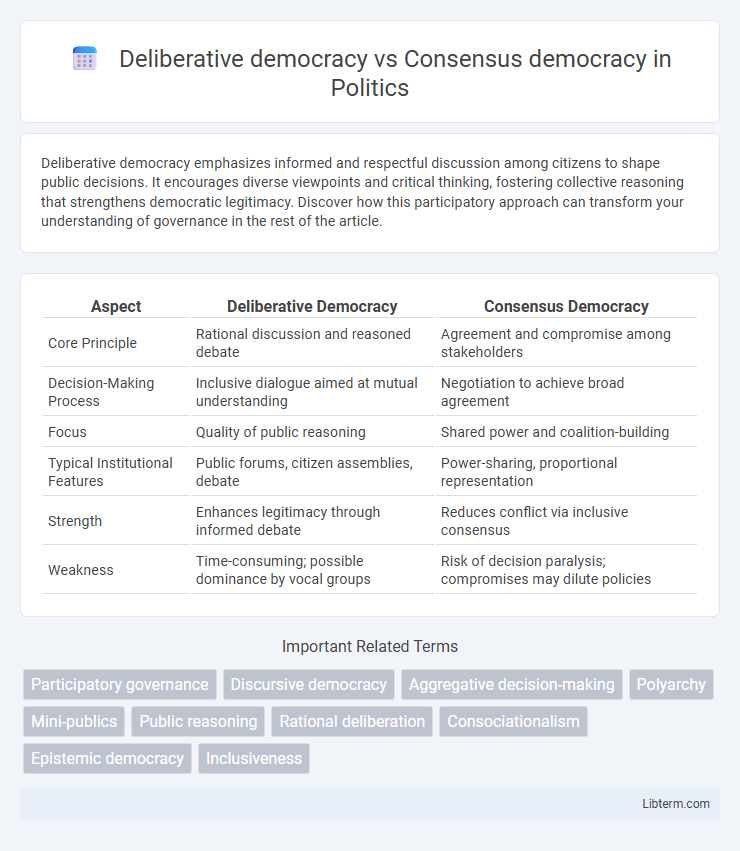
| Aspect | Deliberative Democracy | Consensus Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Rational discussion and reasoned debate | Agreement and compromise among stakeholders |
| Decision-Making Process | Inclusive dialogue aimed at mutual understanding | Negotiation to achieve broad agreement |
| Focus | Quality of public reasoning | Shared power and coalition-building |
| Typical Institutional Features | Public forums, citizen assemblies, debate | Power-sharing, proportional representation |
| Strength | Enhances legitimacy through informed debate | Reduces conflict via inclusive consensus |
| Weakness | Time-consuming; possible dominance by vocal groups | Risk of decision paralysis; compromises may dilute policies |
Understanding Deliberative Democracy
Deliberative democracy emphasizes reasoned discussion and inclusive debate where citizens actively engage in exchanging diverse viewpoints to reach well-informed decisions. It prioritizes transparency, critical thinking, and equal participation, aiming to enhance legitimacy by fostering collective reasoning beyond mere voting. Unlike consensus democracy, which seeks unanimous agreement, deliberative democracy values informed dialogue that shapes public opinion and policy outcomes through constructive argumentation.
Defining Consensus Democracy
Consensus democracy emphasizes broad agreement among diverse political actors, aiming to incorporate multiple viewpoints and ensure inclusivity in decision-making processes. It features power-sharing mechanisms such as coalition governments, proportional representation, and minority rights protection to foster cooperation and prevent domination by a single group. This democratic model prioritizes dialogue, compromise, and mutual respect to achieve decisions that reflect the collective will of society.
Key Principles of Deliberative Democracy
Deliberative democracy centers on reasoned discussion and the active participation of citizens in decision-making, emphasizing transparency, inclusiveness, and equal voice to ensure legitimacy and informed consensus. It requires public deliberation where diverse perspectives are exchanged, promoting rational debate rather than mere voting outcomes. Key principles include deliberation guided by reason, equal participation rights, and a commitment to common good through collective reasoning.
Core Values of Consensus Democracy
Consensus democracy emphasizes inclusivity, power-sharing, and accommodation of diverse interests to achieve broad agreement among stakeholders. Core values include cooperation, mutual respect, and compromise, aiming to prevent domination by any single group and ensuring minority voices are heard. This model fosters stability and legitimacy by promoting collective decision-making based on extensive negotiation and consensus-building.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Deliberative democracy emphasizes open discussion and reasoned debate among citizens or representatives to reach decisions, prioritizing legitimacy through informed consensus. Consensus democracy focuses on power-sharing and broad agreement among multiple political actors or parties, often employing institutional mechanisms like coalition-building to ensure inclusive decision-making. The decision-making process in deliberative democracy is rooted in dialogical exchange, whereas consensus democracy relies on negotiation and compromise to maintain stability and representation.
Strengths of Deliberative Democracy
Deliberative democracy excels in fostering inclusive, reasoned dialogue among diverse participants, ensuring that decisions reflect well-considered public reasoning rather than mere majority rule. Its emphasis on transparency and equality in discourse enhances legitimacy and public trust in policy outcomes. This model reduces polarization by encouraging empathy and mutual understanding, which often leads to more sustainable and accepted decisions.
Benefits of Consensus Democracy
Consensus democracy promotes broad agreement among diverse political groups, ensuring more inclusive decision-making and reducing polarization. It fosters stability by encouraging cooperation and compromise, which often leads to policies with wider acceptance and longer-lasting impact. This model enhances legitimacy and citizen trust as it represents a greater variety of interests and voices within the political system.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Model
Deliberative democracy faces challenges such as the risk of unequal participation, where power imbalances hinder genuine dialogue, and the difficulty of ensuring informed and inclusive deliberations in diverse societies. Consensus democracy struggles with decision-making gridlock due to the necessity of broad agreement, often leading to diluted policies and slow governmental action. Both models encounter criticisms regarding scalability and practical implementation in large, complex political systems.
Practical Examples from Around the World
Deliberative democracy emphasizes informed, reflective discussion among diverse citizens, as seen in Iceland's constitutional reform process where citizen assemblies shaped policy proposals. Consensus democracy prioritizes broad agreement and power-sharing, exemplified by Switzerland's multiparty government and frequent referenda enabling inclusive decision-making. Countries like Germany blend these models by incorporating deliberative forums within a consensus-driven parliamentary system to enhance legitimacy and public trust.
Future Prospects and Hybrid Approaches
Deliberative democracy emphasizes informed public discussion to enhance decision legitimacy, while consensus democracy prioritizes broad agreement among diverse groups to ensure stability and inclusion. Future prospects indicate growing interest in hybrid approaches that combine the reflective quality of deliberation with the integrative mechanisms of consensus to address complex policy challenges. These models leverage digital platforms and participatory technologies to foster more inclusive, transparent, and adaptive democratic processes.
Deliberative democracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com