Adjournment temporarily pauses a meeting or legal proceeding, allowing participants to regroup or address outside matters before resuming. This strategic break can enhance decision-making and maintain order in complex discussions. Discover how proper adjournment impacts your meetings by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
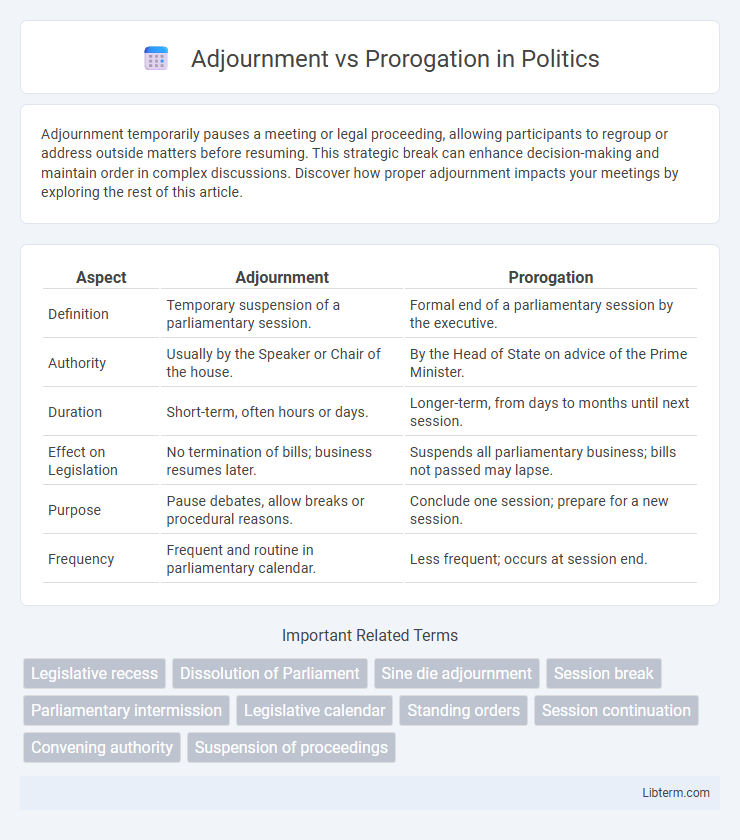
| Aspect | Adjournment | Prorogation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary suspension of a parliamentary session. | Formal end of a parliamentary session by the executive. |
| Authority | Usually by the Speaker or Chair of the house. | By the Head of State on advice of the Prime Minister. |
| Duration | Short-term, often hours or days. | Longer-term, from days to months until next session. |
| Effect on Legislation | No termination of bills; business resumes later. | Suspends all parliamentary business; bills not passed may lapse. |
| Purpose | Pause debates, allow breaks or procedural reasons. | Conclude one session; prepare for a new session. |
| Frequency | Frequent and routine in parliamentary calendar. | Less frequent; occurs at session end. |
Understanding Adjournment and Prorogation
Adjournment refers to the suspension of a parliamentary session for a short period, allowing members to take breaks without dissolving the legislative body. Prorogation involves ending a parliamentary session by the head of state, leading to a temporary halt in all parliamentary activities until the next session begins. Understanding the distinction between adjournment and prorogation is crucial for grasping parliamentary procedures and legislative timelines.
Definition of Adjournment
Adjournment refers to the temporary suspension or postponement of a meeting or session by a parliamentary body, allowing members to reconvene at a later time or date. It is typically used to pause proceedings without dissolving the legislative assembly, ensuring that unfinished business can be resumed efficiently. Unlike prorogation, adjournment does not terminate the session but merely interrupts it for a specified period.
Definition of Prorogation
Prorogation refers to the formal ending of a parliamentary session by the head of state or their representative, effectively suspending all parliamentary business until the next session begins. Unlike adjournment, which temporarily pauses proceedings within the same session, prorogation dissolves all current legislative activity and pending matters. This process resets the parliamentary agenda, requiring new bills to be introduced in the subsequent session.
Key Differences: Adjournment vs Prorogation
Adjournment refers to the temporary suspension of a parliamentary session, allowing it to resume later without ending the legislative period. Prorogation ends a session entirely, halting all parliamentary activities until the next session is formally opened. Unlike adjournment, prorogation clears all pending bills and resets the agenda, impacting legislative continuity.
Legal Basis for Adjournment
The legal basis for adjournment is typically grounded in procedural rules established by legislative bodies or courts, allowing temporary suspension or postponement of proceedings to manage time, gather information, or address unforeseen circumstances. Adjourning a session does not terminate its legislative authority but pauses activities until resumed. This authority is often codified in parliamentary laws, court rules, or specific statutes within each jurisdiction.
Legal Framework for Prorogation
Prorogation is a formal mechanism within the constitutional framework, executed by the head of state or their representative, to suspend a parliamentary session without dissolving the legislature. Legal frameworks governing prorogation vary by jurisdiction but typically stem from constitutional provisions or statutory laws delineating the powers and limits of executive authorities. Courts sometimes review prorogation's legality, balancing executive prerogative against parliamentary sovereignty in democratic governance.
Effects on Parliamentary Proceedings
Adjournment temporarily halts parliamentary proceedings, allowing sessions to resume at a later time without dissolving the current agenda or affecting ongoing legislation. Prorogation ends a parliamentary session, effectively suspending all pending bills and orders, requiring them to be reintroduced in the next session if needed. While adjournment maintains legislative continuity, prorogation resets the parliamentary agenda and can delay policy-making and debates.
Powers Responsible for Adjournment and Prorogation
The power responsible for adjournment lies with the presiding officer of a legislative body, such as the Speaker in the House of Representatives or the Chairman in the Rajya Sabha, allowing short breaks within sessions. Prorogation, however, is a prerogative exercised by the Head of State or Governor, on the advice of the Council of Ministers, to end a parliamentary session entirely. These distinct powers reflect the procedural mechanisms that regulate the continuity and suspension of legislative business.
Historical Examples of Adjournment and Prorogation
Historical examples of adjournment include the 1852 U.S. Senate adjournment during the debate over the Compromise of 1850, which temporarily halted legislative proceedings amid intense sectional conflict. Prorogation is exemplified by the 2019 UK Parliament prorogation, where Prime Minister Boris Johnson suspended Parliament for five weeks during Brexit negotiations, sparking legal challenges. These instances showcase the strategic use of adjournment to pause debate and prorogation to end a parliamentary session, influencing legislative timelines and political outcomes.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Adjournment and Prorogation
Choosing between adjournment and prorogation depends on the legislative agenda's scope and duration. Adjournment temporarily suspends parliamentary sessions without dissolving the assembly, allowing quick resumption, whereas prorogation ends a session and clears pending business, requiring fresh commencement afterward. Legislative authorities prioritize adjournment for short breaks and prorogation for concluding sessions before significant transitions or policy reviews.
Adjournment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com